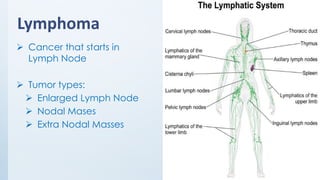
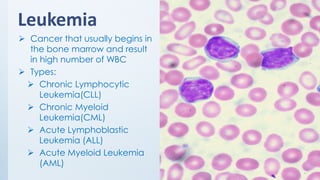
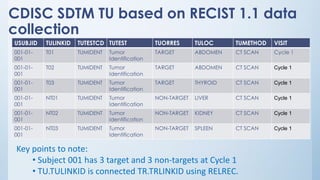
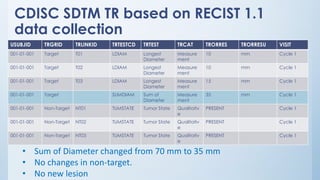
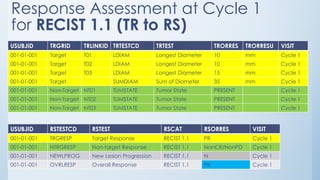
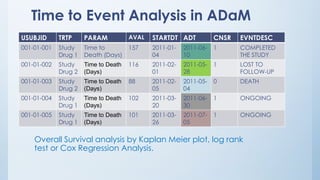
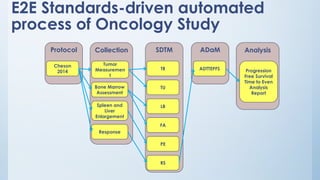
The document discusses the importance of standards in oncology studies, highlighting the economic impact and increasing prevalence of cancer. It details various oncology-specific standards, such as response criteria guidelines and CDISC standards, necessary for conducting complex oncology studies effectively. The presentation concludes with an emphasis on the benefits of a standardized approach to enhance regulatory compliance and improve efficiency in oncology research.