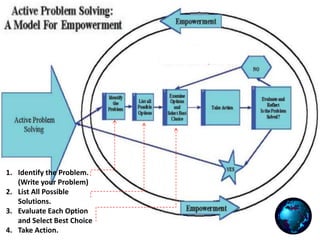
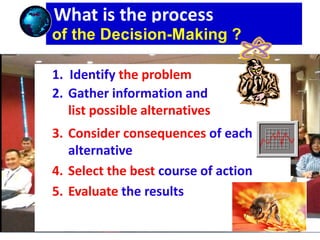
Dokumen ini membahas langkah pemberdayaan dalam pelatihan pemecahan masalah termasuk pengenalan masalah, evaluasi solusi, dan pengambilan tindakan. Manajer diharapkan untuk membantu para pelaksana dalam proses ini melalui pemberdayaan dan evaluasi keputusan. Proses pengambilan keputusan juga diuraikan dengan mempertimbangkan konsekuensi dan informasi yang relevan.