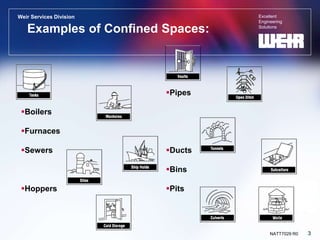
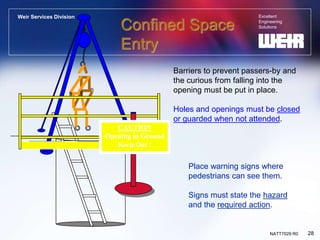
This document discusses confined space entry and safety. It defines a confined space as a space large enough for entry, with limited means of entry/exit, not meant for continuous occupancy. Examples include boilers, sewers and bins. Hazards include oxygen deficiency, toxic gases, engulfment and process hazards. Proper entry procedures require isolating, ventilating and testing the atmosphere of the space, using permits and attendants to monitor entrants. Rescue procedures and emergency planning are also vital parts of safe confined space work.