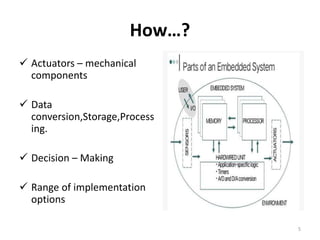
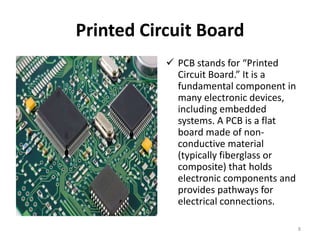
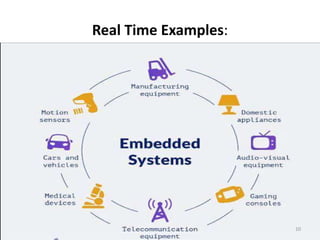
Embedded systems combine both hardware and software to provide dedicated services to a larger system or device. They contain components like a microcontroller, memory, sensors and I/O interfaces. Embedded systems are used in applications that require efficiency, reliability, and specific functionality like real-time control. They are customizable, low cost and have low power consumption. The microcontroller acts as the brain and determines the capabilities of the embedded system. Printed circuit boards are used to hold electronic components and provide electrical connections. Embedded systems perform crucial roles in industries and help drive innovation.