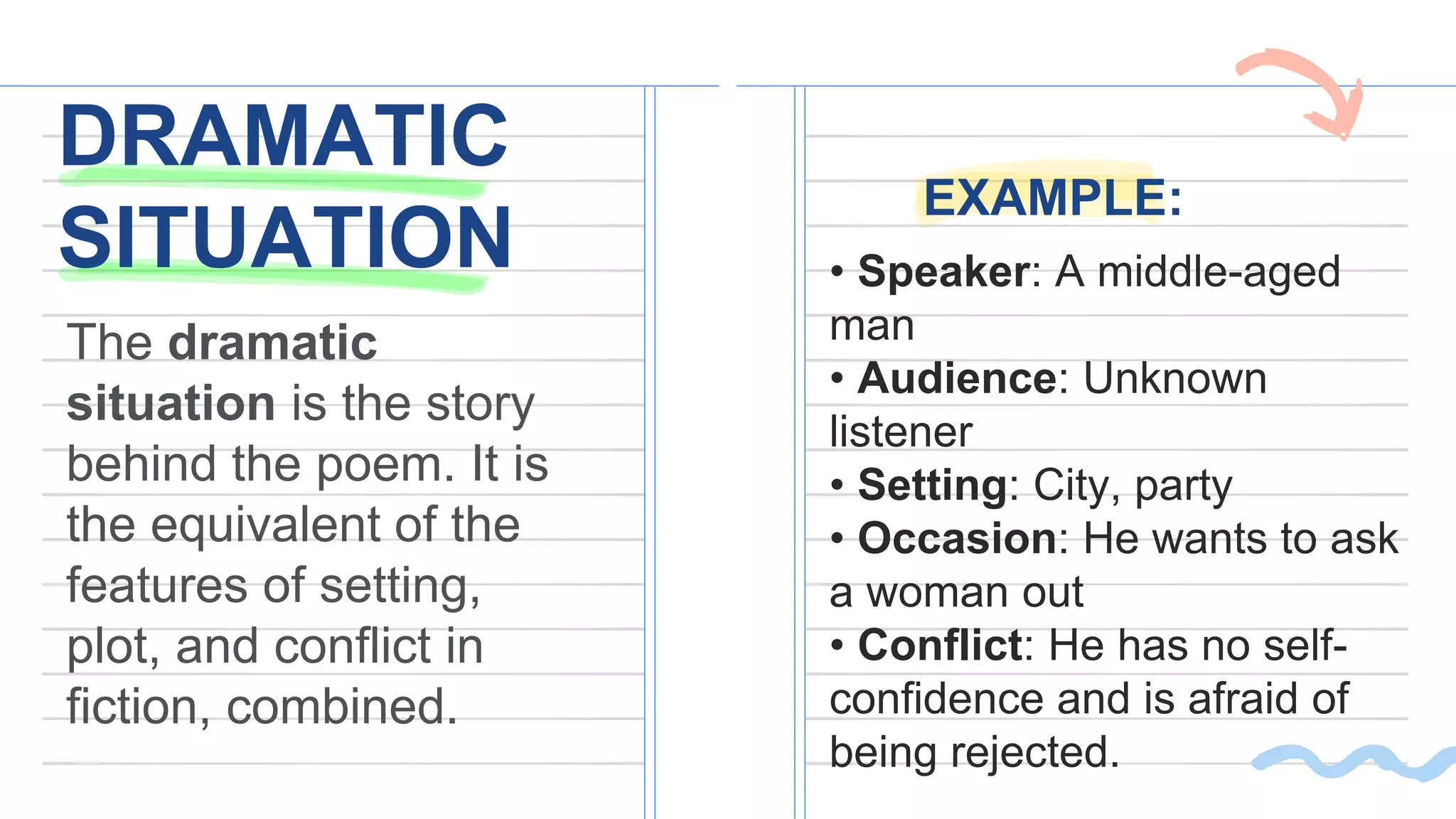
This document defines and provides examples of the key elements of poetry. It discusses persona, dramatic situation, images, symbolism, figures of speech, diction, syntax, tone, and sound and sense. Poetry is defined as a concentrated imaginative writing that formulates awareness of experience through language, meaning, sound, and rhythm. These elements are the building blocks that poets use to engage the senses and convey deeper meanings in their work.