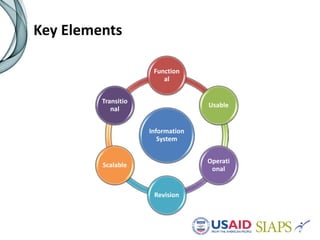
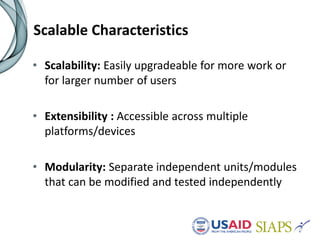
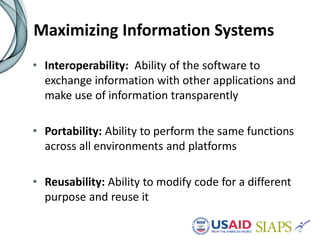
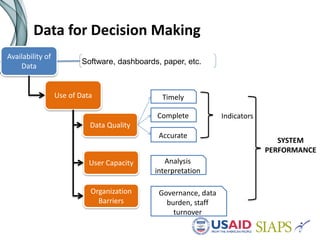
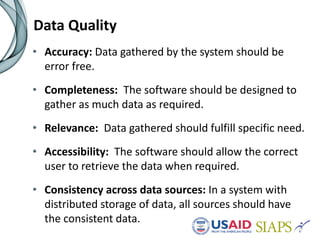
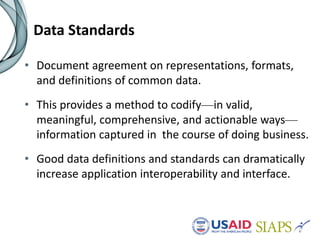
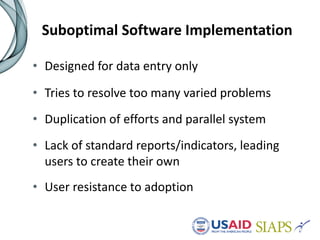
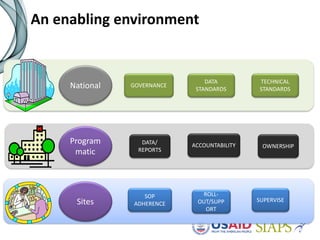
An information system should have several key elements and characteristics for success. It should be functional, usable, operational, scalable and allow for revisions. Specifically, it needs to be user-friendly, reliable, efficient, secure and easily maintained. Maximizing the system requires features like interoperability, portability, reusability and integration. High-quality data is also essential for decision making, and must be timely, complete and accurate. Common challenges to implementation include lengthy timelines and lack of post-go-live support. Critical success factors include stakeholder buy-in, local ownership and an enabling environment.