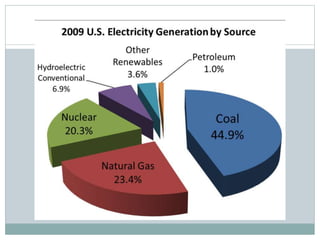
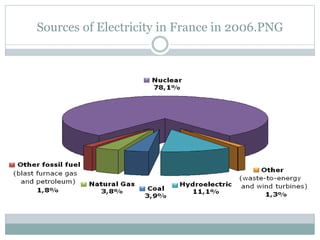
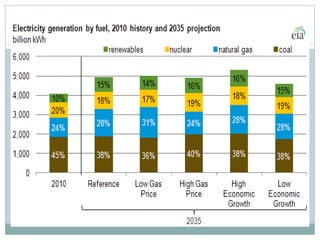
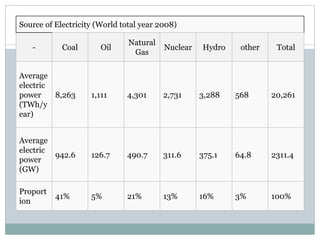
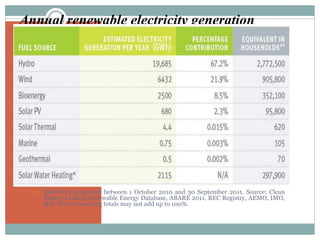
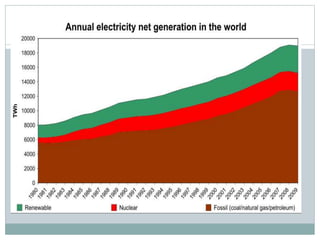
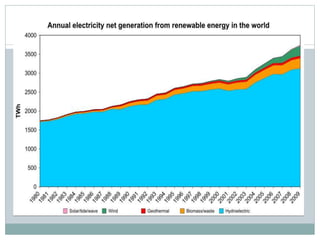
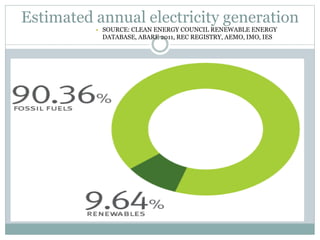
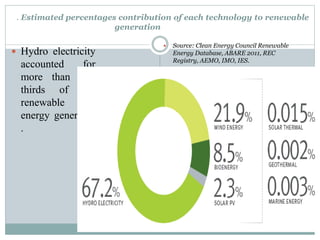
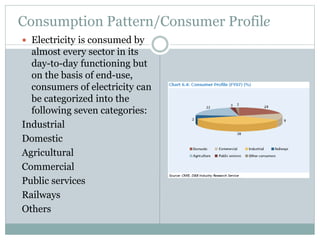
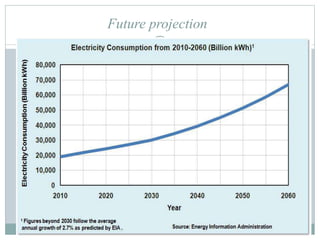
This document discusses electricity generation. It begins by introducing electricity generation and its history. It then discusses the various sources of electricity generation including fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas as well as renewable sources like wind, water, and solar. It provides statistics on global electricity generation by source. It also discusses electricity consumption trends, future projections, and the environmental impacts of electricity generation.