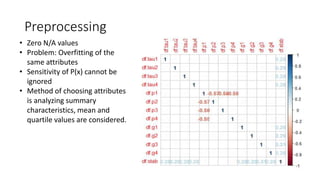
The document presents an analysis of electrical grid stability using a dataset from the UCI machine learning repository, focusing on classifying the stability into stable and unstable categories. Various machine learning methods, including Naïve Bayes, Random Forest, and Decision Tree, were employed, yielding high accuracy results, with Random Forest and Decision Tree achieving 100% accuracy. The study involves preprocessing data, attribute selection, and evaluating model performance through precision, recall, and F1 scores.



![Attributes Information
• Total - 14 predictive attributes, 1target attribute(2classes)
• tau[x] : Reaction time of participant (real from the range [0.5,10]s).
• p[x] : Nominal power consumed(negative)/produced(positive)(real).
• g[x] : Coefficient (gamma) proportional to price elasticity (real from
the range [0.05,1]s^-1).
• stab: The maximal real part of the characteristic equation root (if
positive - the system is linearly unstable)(real)
• stabf: The stability label of the system (stable/unstable)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectpa-190702042501/85/Electrical-Grid-Stability-Simulated-Data-Set-analysis-using-R-4-320.jpg)






![Splitting the dataset
• Training Data Set: 95% [9091 11] • Testing Data Set: 5% [909 11]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectpa-190702042501/85/Electrical-Grid-Stability-Simulated-Data-Set-analysis-using-R-12-320.jpg)
![Naïve Bayes Results
• Accuracy = 97.03%
• Precision [How many selected items are
relevant OR TP/(TP+FP)]= = 0.9558
• Recall [How many items are selected
relevant OR TP/TP+FN]= 0.9589
• F1 (Harmonic mean of precision and recall)=
(2 * 0.9558 * 0.9589) / (0.9558 + 0.9589) =
0.9573475](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectpa-190702042501/85/Electrical-Grid-Stability-Simulated-Data-Set-analysis-using-R-13-320.jpg)
![Random Forest Results
• Accuracy = 100%
• Precision [How many selected
items are relevant OR
TP/(TP+FP)]= 1
• Recall [How many items are
selected relevant OR TP/TP+FN]=
1
• F1 = (2 * 1* 1) / (1 + 1) = 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectpa-190702042501/85/Electrical-Grid-Stability-Simulated-Data-Set-analysis-using-R-14-320.jpg)
![Decision Tree Results
• Accuracy = 100%
• Precision [How many selected
items are relevant OR
TP/(TP+FP)]= 1
• Recall [How many items are
selected relevant OR TP/TP+FN]=
1
• F1 = (2 * 1 * 1) / (1 + 1) = 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectpa-190702042501/85/Electrical-Grid-Stability-Simulated-Data-Set-analysis-using-R-15-320.jpg)

