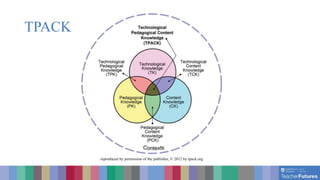
The document discusses eLearning design. It begins by defining eLearning as using technology to expand access to education and enhance teaching and learning. It then discusses the eLearning continuum from fully face-to-face instruction to fully online/distance learning. Open education principles of open sharing of knowledge are also covered. The benefits of eLearning for reaching wider audiences and offering effective instructional methods are presented. Learning domains and how they can be addressed through both eLearning and face-to-face delivery are outlined. Finally, the TPACK framework for effective technology integration is explained and factors to consider when choosing eLearning are listed.