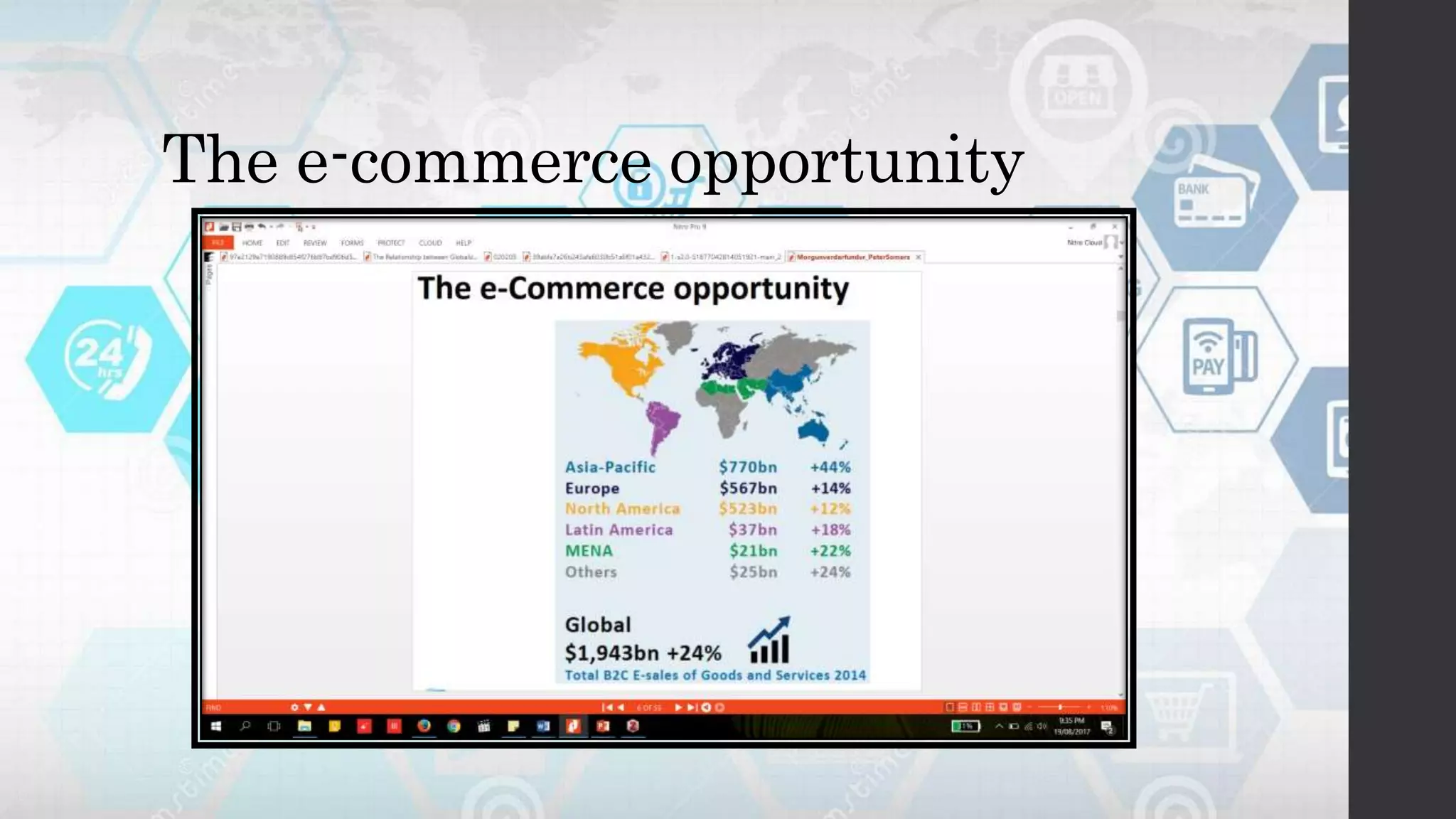
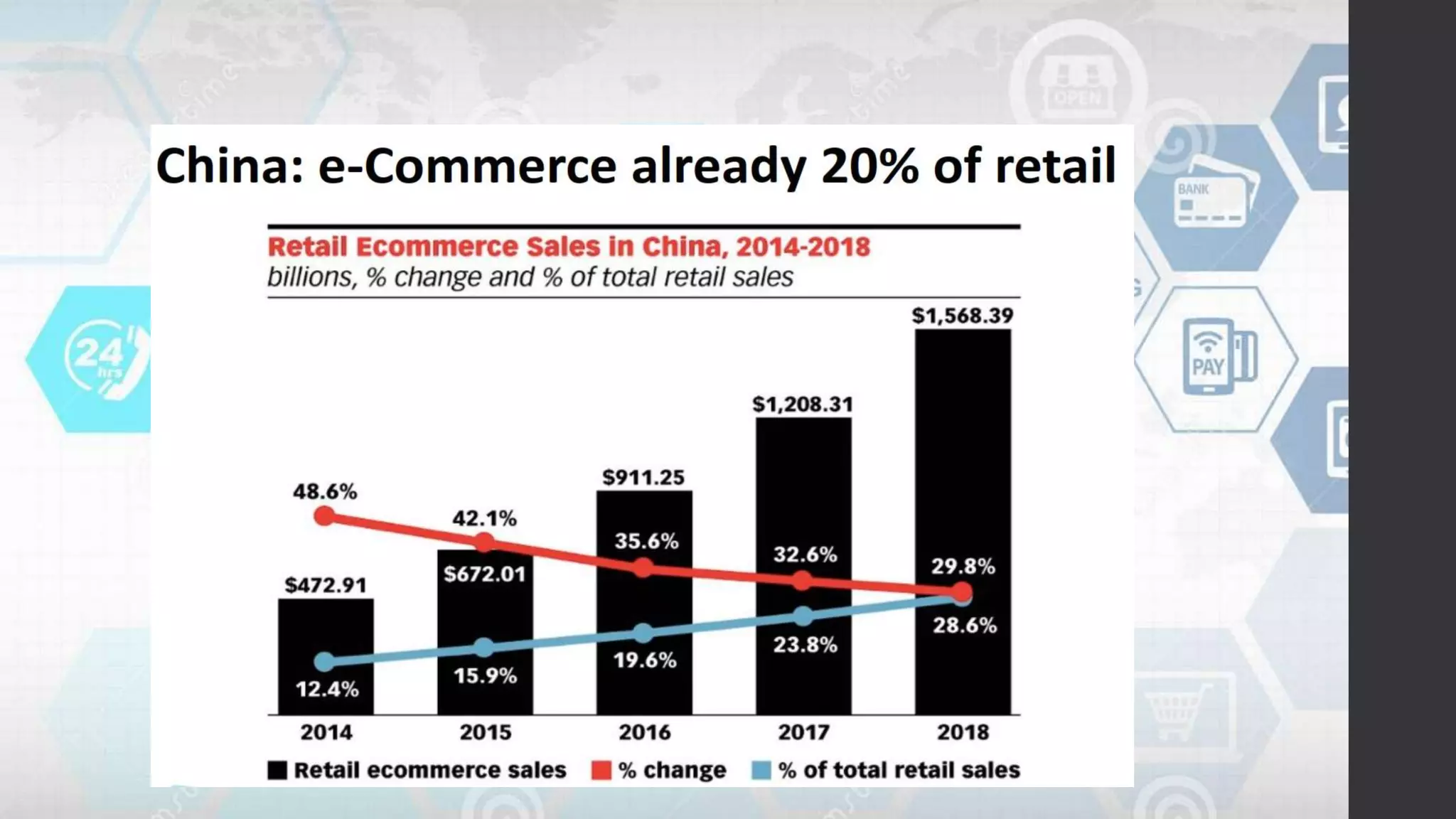
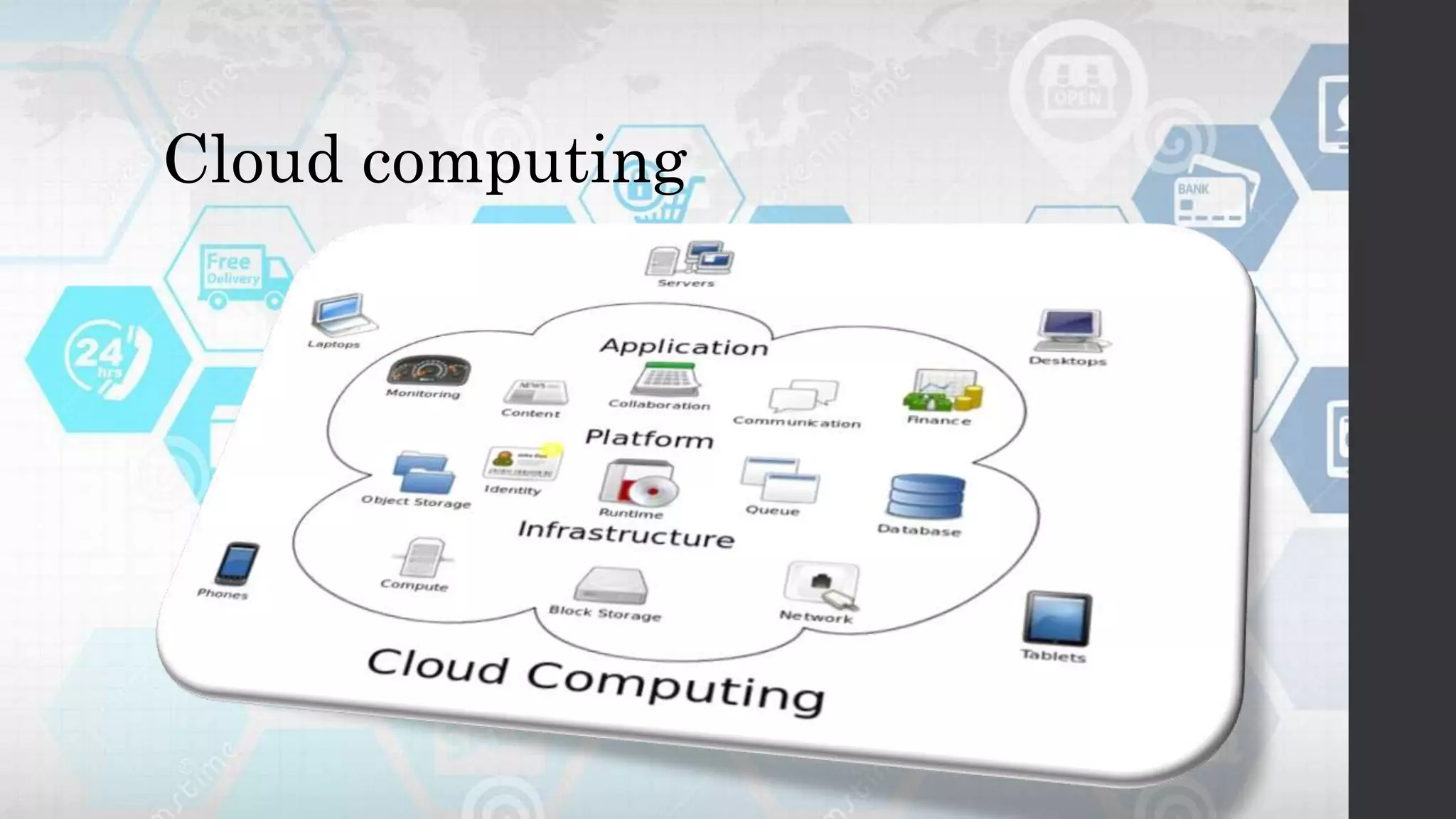
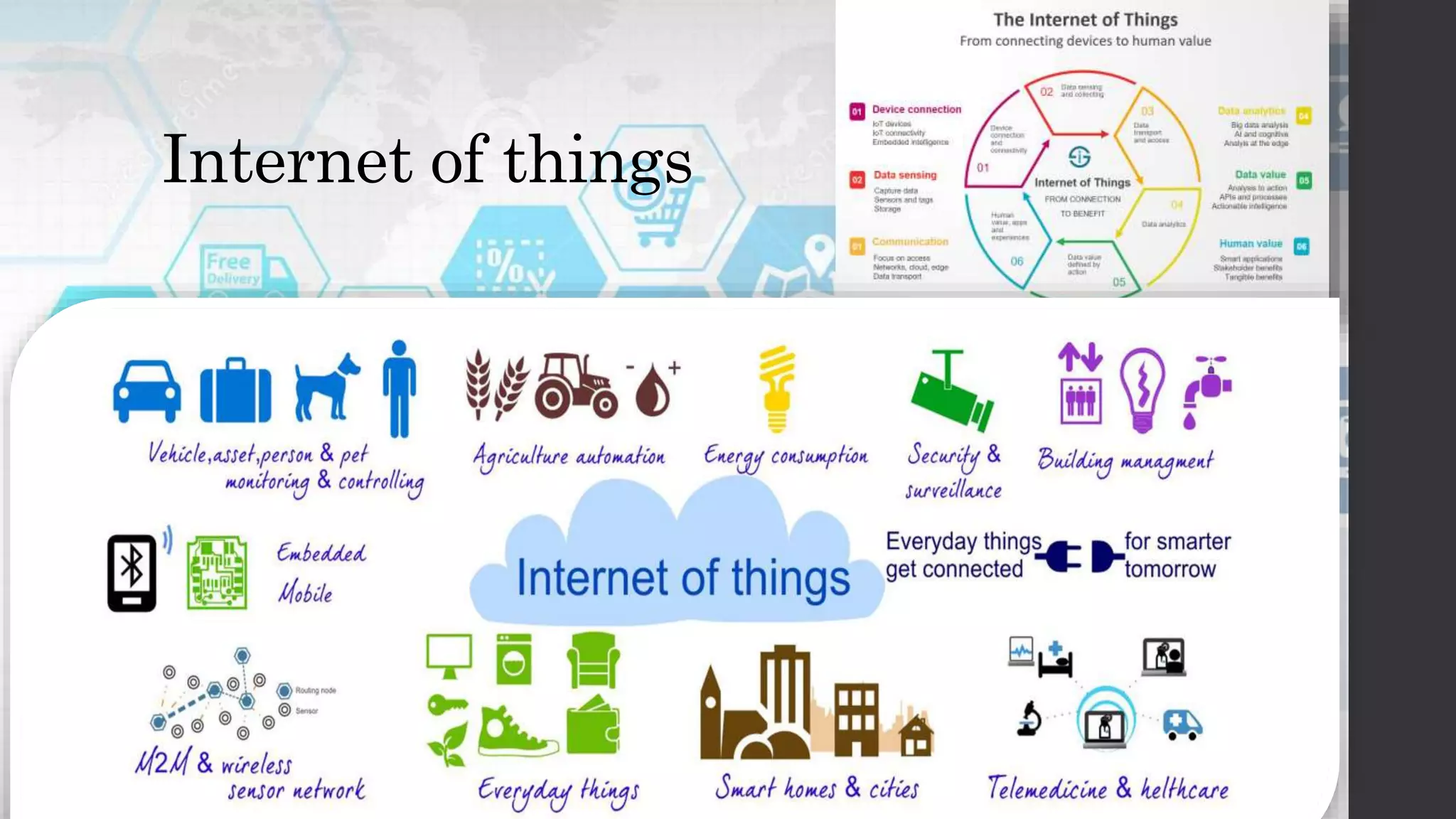
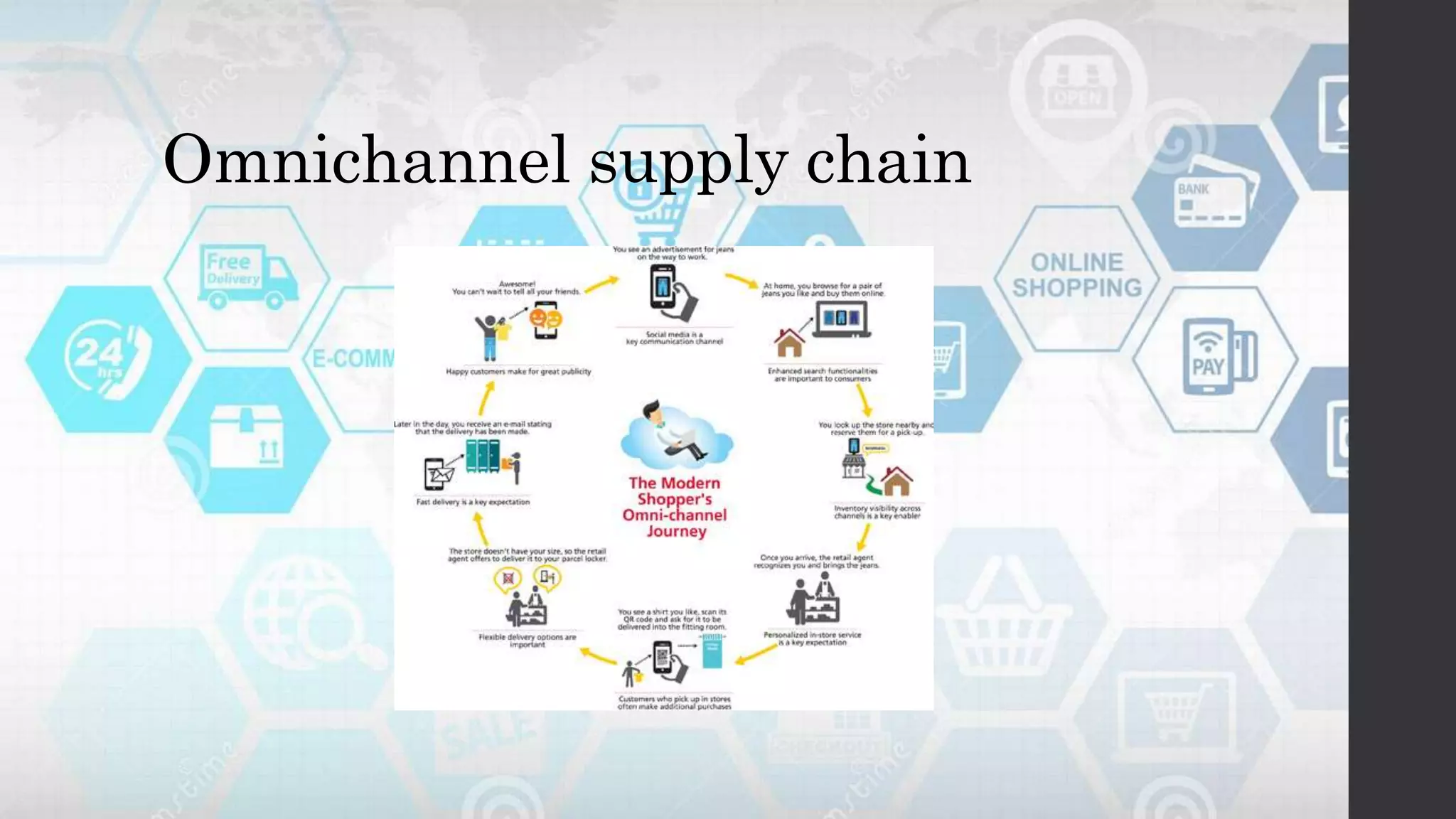
Globalization refers to the increasing interconnection of world markets through free trade and the flow of goods, services, and capital across borders. It has increased international trade and cultural exchange through the opening of markets. E-commerce, or electronic commerce, refers to buying and selling of goods and services online and has been a major contributor to globalization through technologies like the internet that facilitate cultural and economic exchange worldwide. While globalization has benefited economies through more efficient markets and competition, it has also widened the digital divide between developed and developing nations in terms of technology infrastructure needed to participate effectively in e-commerce.