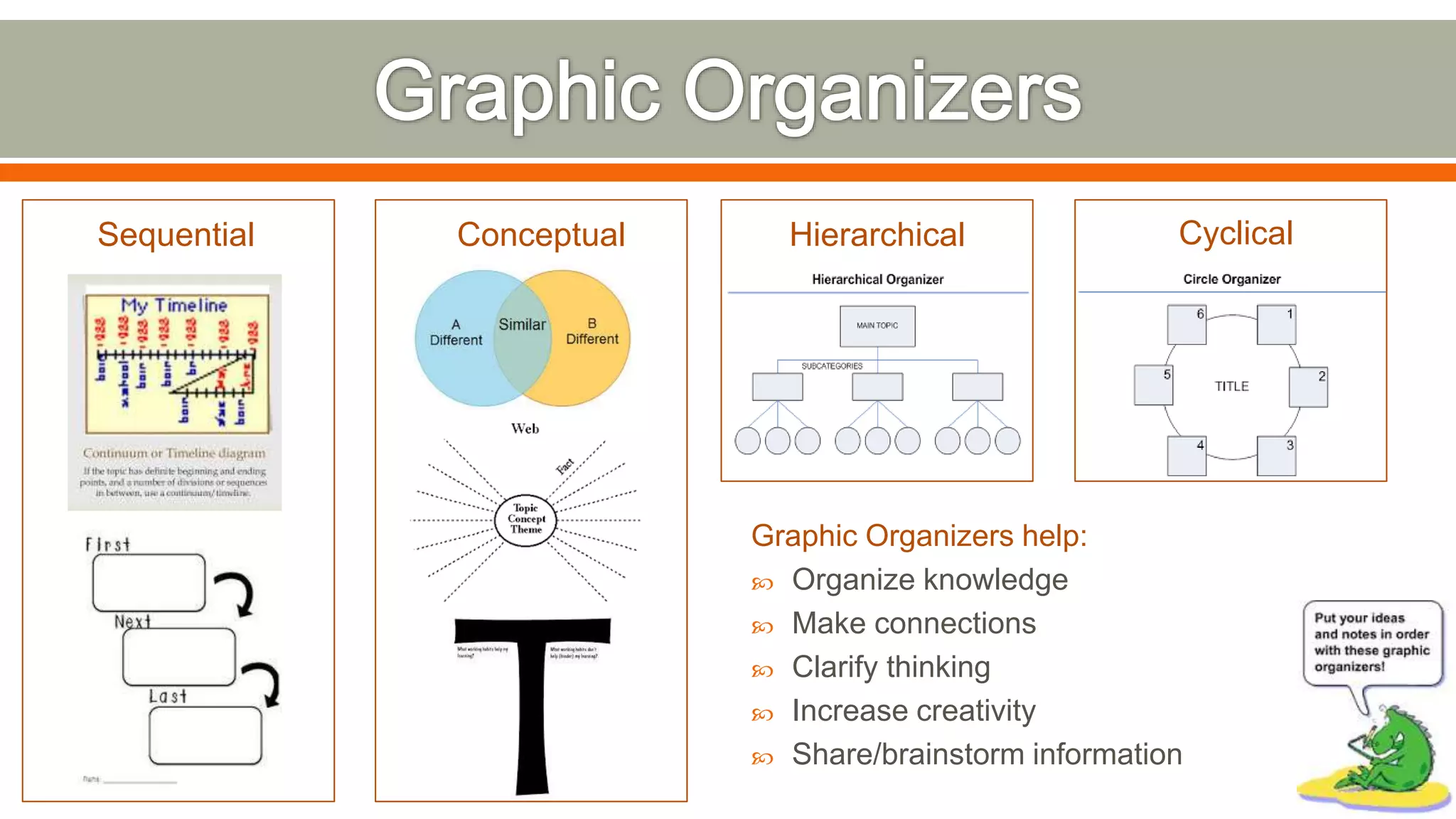
The document discusses various instructional strategies to enhance student achievement including graphic organizers, note-taking, partnering, reflection, word walls, summarizing, and rubrics. It provides details on the purpose and benefits of each strategy, as well as different types of each strategy. For example, it explains that graphic organizers help organize knowledge, make connections, and clarify thinking. It also lists common types of graphic organizers like sequential, conceptual, and hierarchical. The document recommends developing a lesson plan using two or more of the instructional strategies discussed.