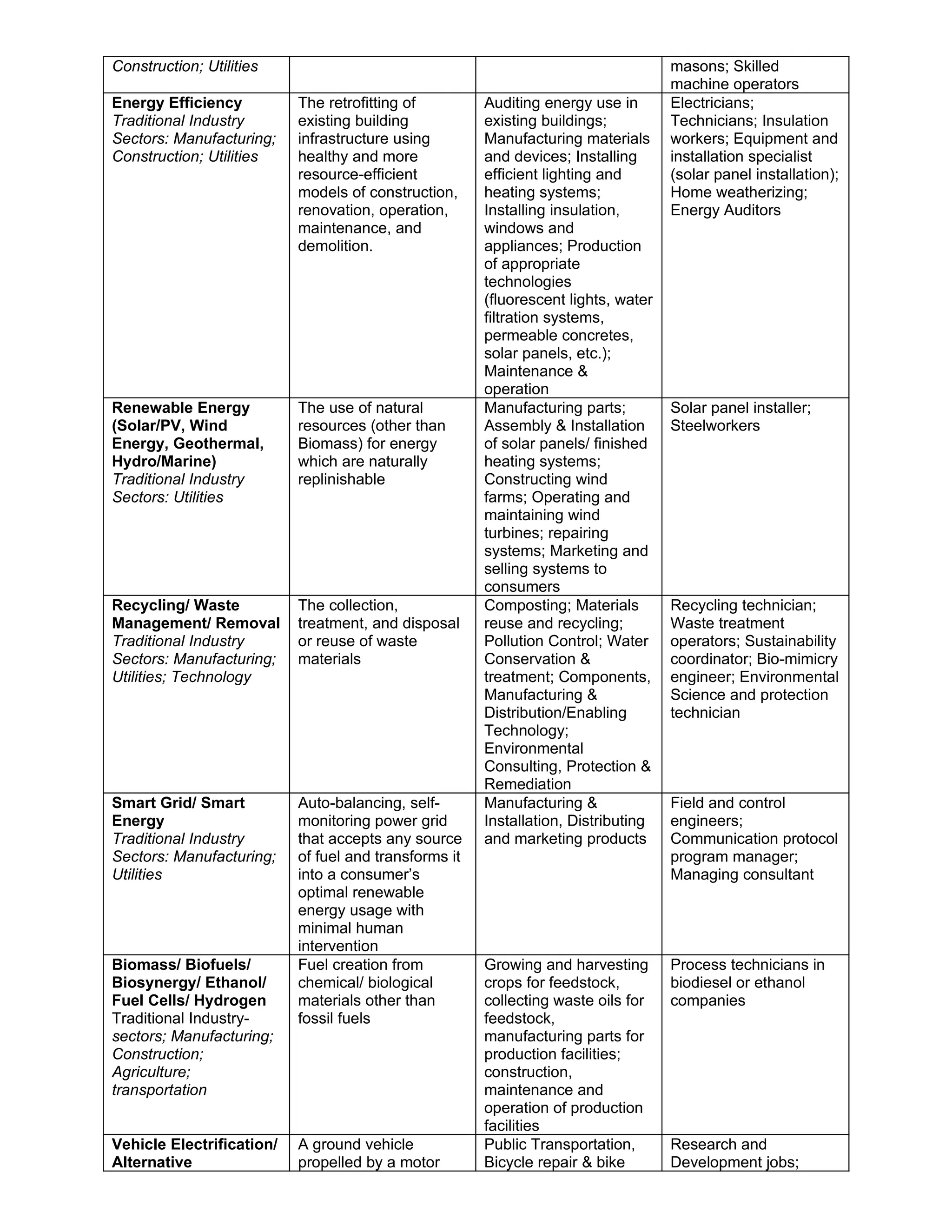
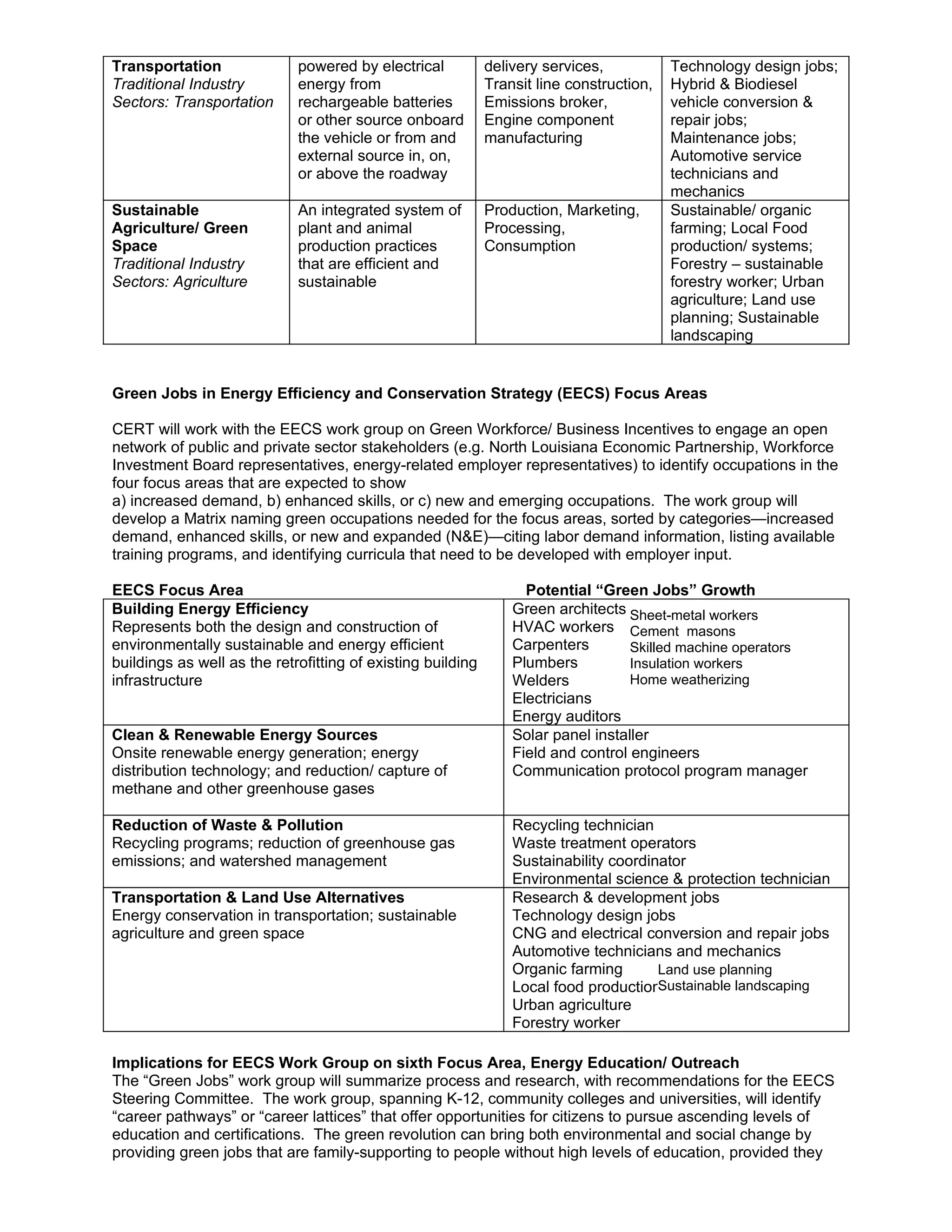
The Consortium for Education, Research & Technology (CERT) has been retained to support the Energy Efficiency and Conservation Strategy (EECS) in three key roles: identifying and aligning higher education resources, serving as a link between different organizations involved, and informing the work group. As part of this, CERT will help identify "green jobs" across various sectors that are expected to see increased demand, enhanced skills needs, or be new and emerging occupations to support the six focus areas of the EECS. CERT is also constructing a database of academic and research resources, identifying potential funding opportunities, and convening partners to support collaborative efforts around workforce development and energy education/outreach.