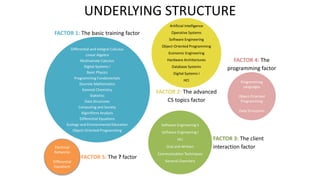
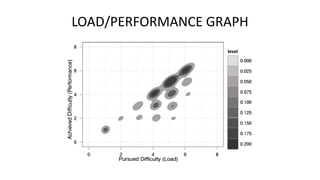
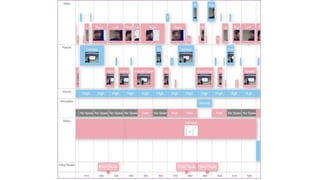
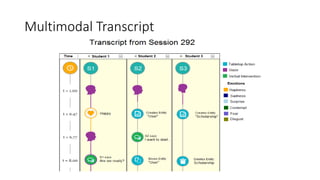
The document discusses the role of educational technologies, specifically focusing on learning analytics and artificial intelligence in optimizing learning experiences. Learning analytics involves measuring and analyzing data about learners to improve educational outcomes, while AI can enhance feedback mechanisms in academic contexts. The text highlights various examples and research efforts aimed at augmenting educational processes through data-driven insights and AI tools.