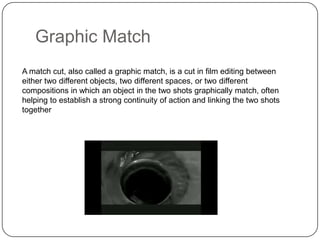
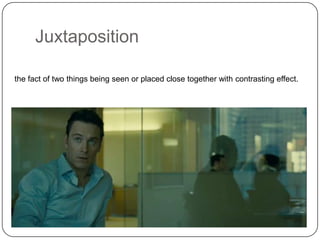
This document discusses various editing techniques used in video production. It begins by defining editing as the process of manipulating and rearranging video shots. It then outlines common goals of editing such as removing unwanted footage, choosing the best footage, creating a flow, and altering style/pace. Specific techniques are then defined, including continuity editing to maintain consistent visual elements, jump cuts as abrupt transitions, using credits to acknowledge production staff, cross cutting between simultaneous actions, cutaways to add visual interest, and match cuts between graphically similar shots.