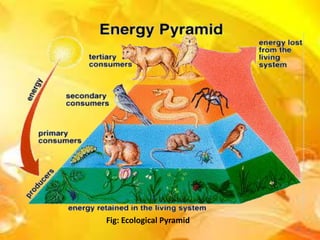
An ecosystem is a community of living and non-living organisms interacting with each other and their environment. There are various types of ecosystems defined by their structure and functional attributes. An ecosystem includes all organisms in a given area interacting with their physical environment, with a clear flow of energy and material cycles between living and non-living parts. Energy flows from producers like plants through consumers at different trophic levels in a food chain or complex food web, with roughly 10% of energy being transferred between each trophic level.