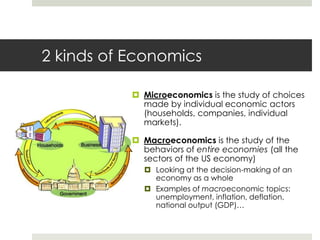
Economics is the study of how individuals and societies make choices to satisfy needs and wants using limited resources. It examines microeconomic decisions by individuals and households as well as macroeconomic issues like GDP, unemployment, and inflation for entire economies. The four factors of production that resources must be combined with are natural resources, human resources, capital resources, and entrepreneurship.