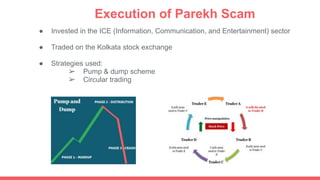
This document summarizes and compares two major financial scams in India: the Harshad Mehta scam of 1992 and the Ketan Parekh scam of 2001. Both scams involved stockbrokers artificially inflating stock prices through circular trading and using fraudulent bank documents to siphon money from banks to invest in the stock market. While Harshad Mehta used fake bank receipts, Ketan Parekh used pay orders. Both scams resulted in losses of thousands of crores for banks and investors. Both scammers were arrested and banned from stock trading, though Harshad Mehta died in 2002 without repaying his debts.