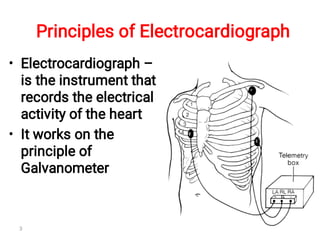
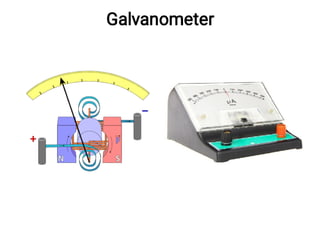
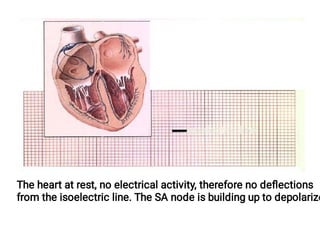
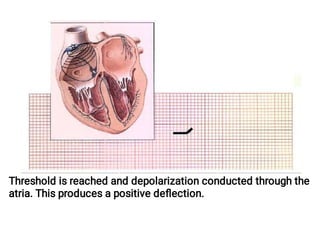
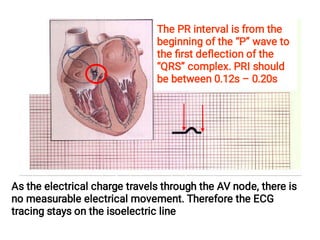
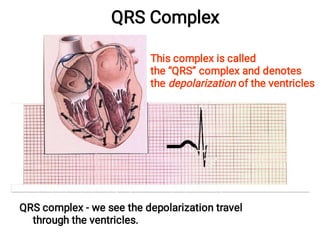
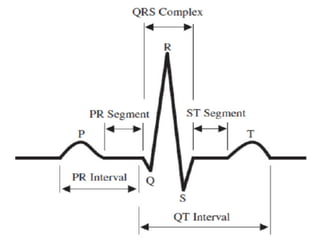
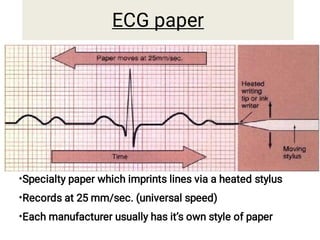
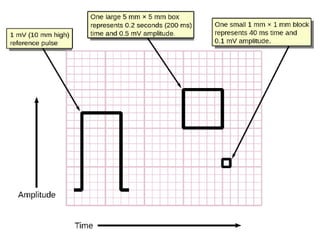
The document provides an introduction to electrocardiography (ECG) monitoring. It discusses the history and development of ECG, including Einthoven receiving the 1924 Nobel Prize for discovering the EKG. It describes the basic principles of how an ECG works to record the electrical activity of the heart. This includes using a galvanometer and different electrode configurations for 3-lead, 5-lead, and 12-lead ECG systems. The document then explains the components of an ECG tracing, including the P wave, QRS complex, T wave, and segments and intervals. It notes that an ECG can provide diagnostic evidence but the patient also needs to be examined. Finally, it briefly discusses ECG paper