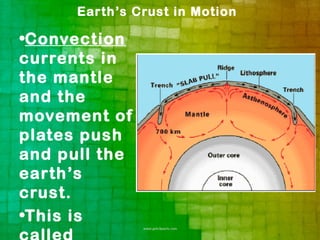
Convection currents in the Earth's mantle and the movement of tectonic plates apply stress to the crust, causing it to break along faults or fold. This movement is responsible for earthquakes and volcanic activity, often occurring at plate boundaries. When stress exceeds rock strength, it releases suddenly in earthquakes. Seismic waves from quakes travel through the Earth and can be recorded on seismographs. Magma rises from hot spots in the mantle and at plate boundaries, fueling volcanic eruptions at the surface that pose hazards through lava flows, ash falls, and pyroclastic flows.