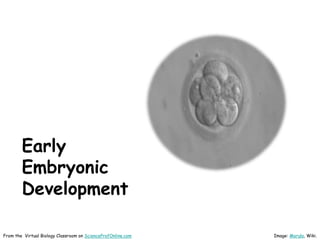
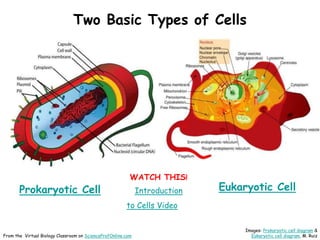
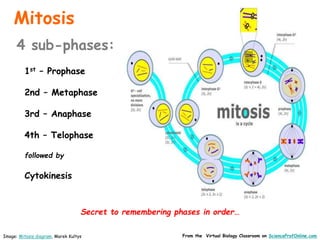
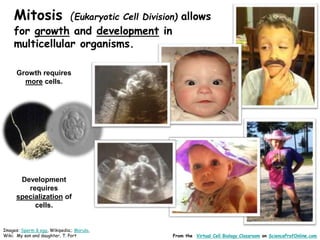
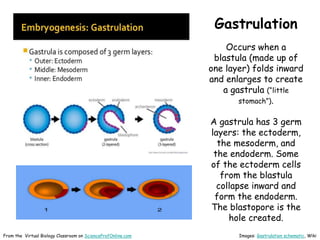
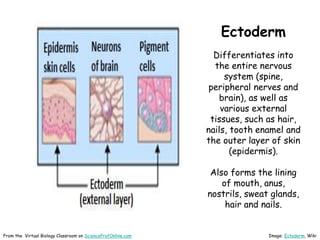
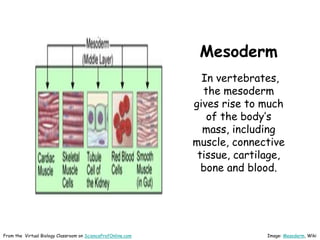
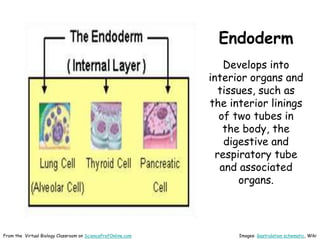
This document provides information about the website Science Prof Online (SPO) and its resources for teaching and learning about science. SPO offers fully developed virtual science classrooms with educational materials like PowerPoint presentations, articles, images, practice questions, and video tutorials. Many of the PowerPoint files are available in different formats for various uses. Images and links are properly attributed. The site is meant to be a helpful free resource for students, educators, and anyone interested in science.