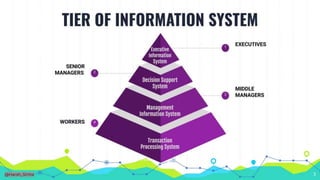
The document outlines various e-governance projects in India, including initiatives like Smart Governance, the Khajane Project, the Digital India Programme, and the e-Panchayat scheme, aimed at enhancing digital access and public service delivery. It also highlights challenges such as trust issues, the digital divide, lack of awareness, and low computer literacy that hinder the effectiveness of e-governance. Additionally, it mentions the Executive Information System as a tool designed to support decision-making for senior executives.