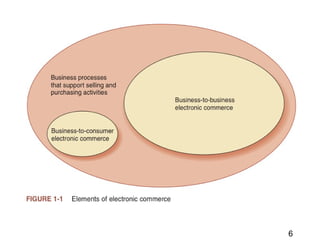
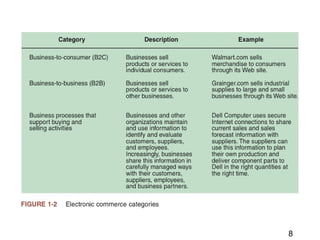
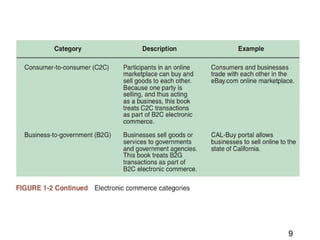
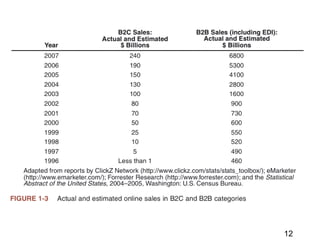
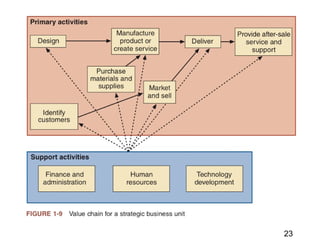
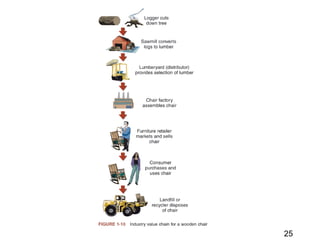
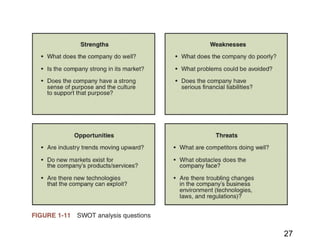
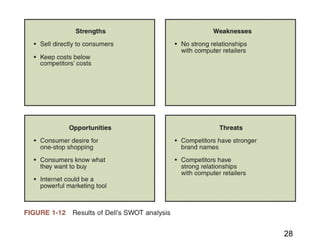
This document discusses the key concepts of electronic commerce. It describes how the second wave of e-commerce focuses on profitability through analyzing business processes and revenue models. Companies now use tools like value chain analysis and SWOT to identify opportunities in a global e-commerce environment that presents both opportunities and challenges regarding issues like trust, culture, language and infrastructure.