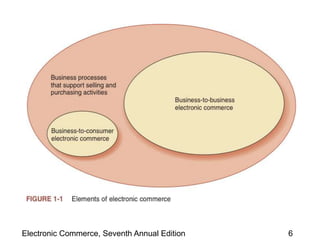
The document discusses the evolution of electronic commerce, highlighting its transition from an initial focus on advertising revenue to a more complex understanding of business models and revenue generation. It outlines the different categories of e-commerce, the advantages and disadvantages it brings, as well as the importance of strategic partnerships and understanding cultural and legal challenges in an international context. The second wave of electronic commerce emphasizes utilizing internet technologies for efficient business processes while creating new opportunities for companies globally.