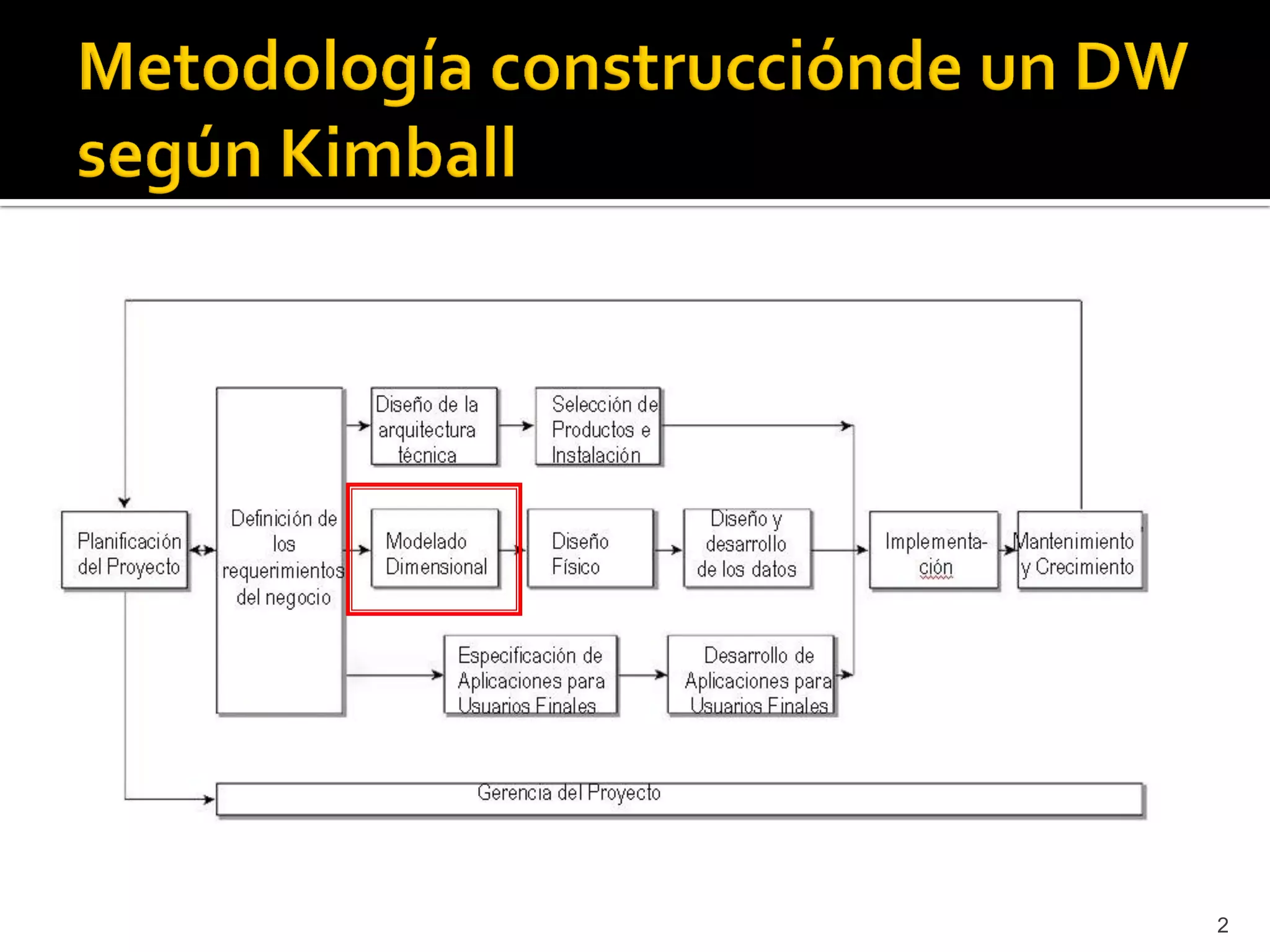
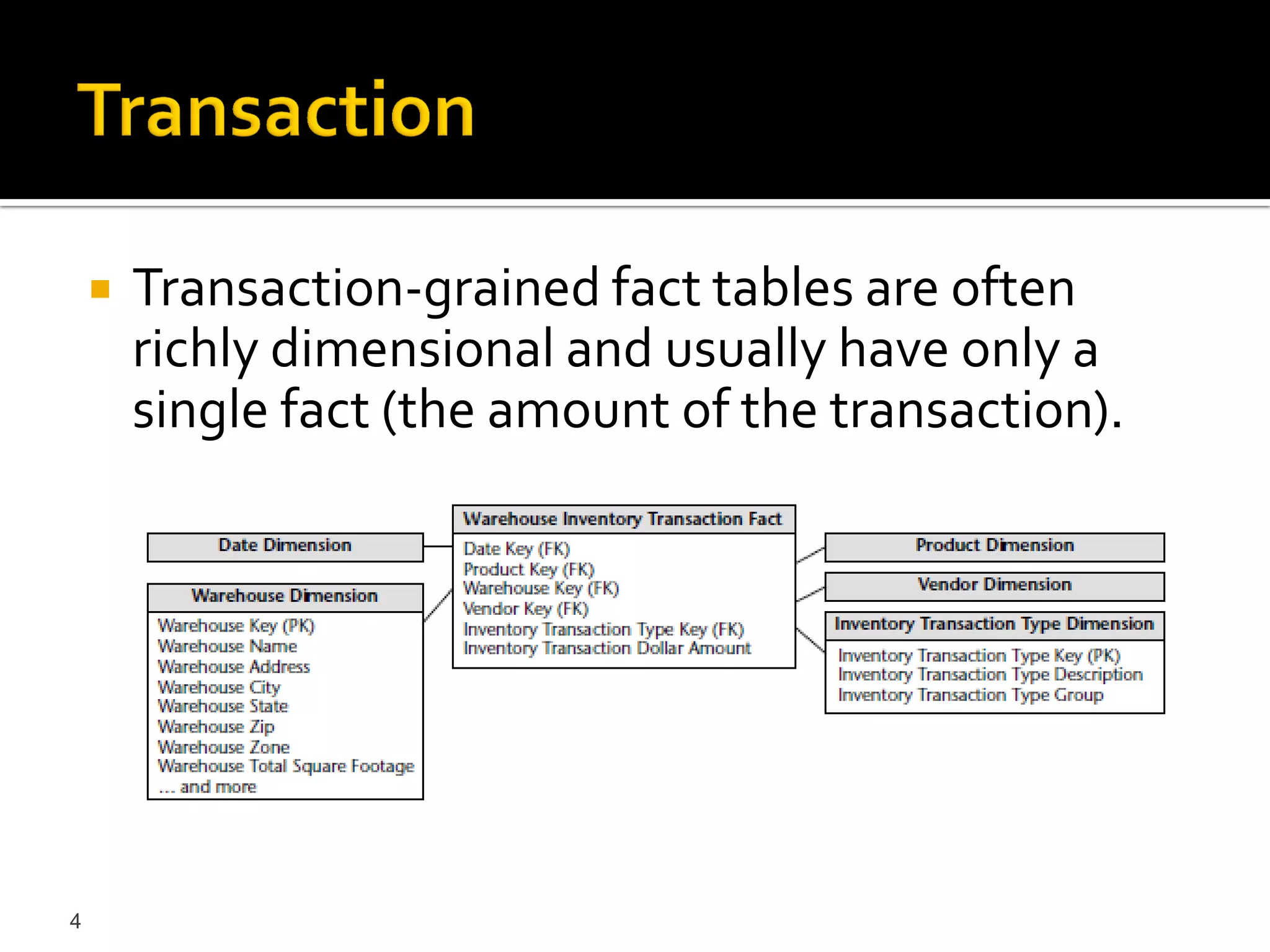
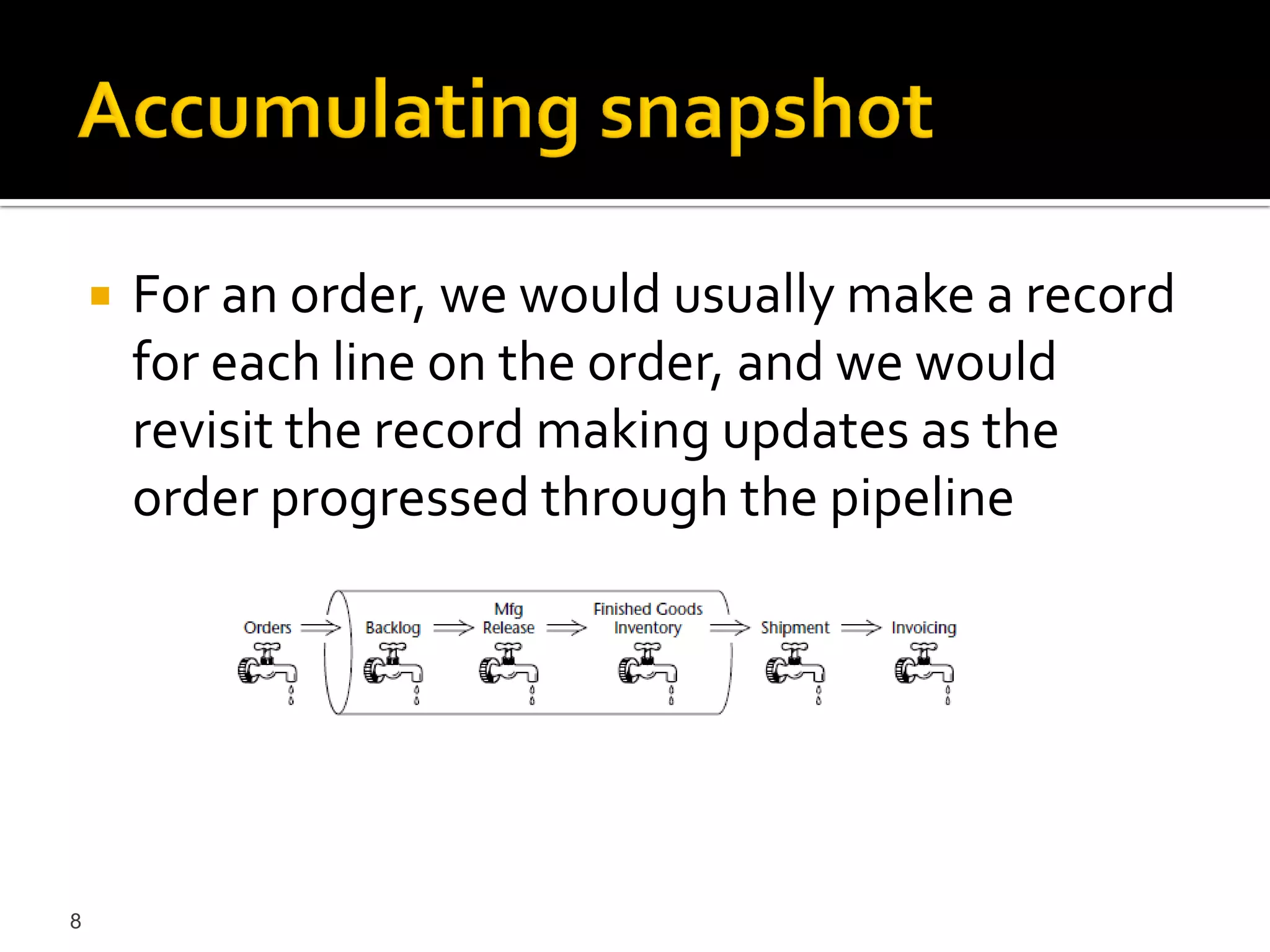
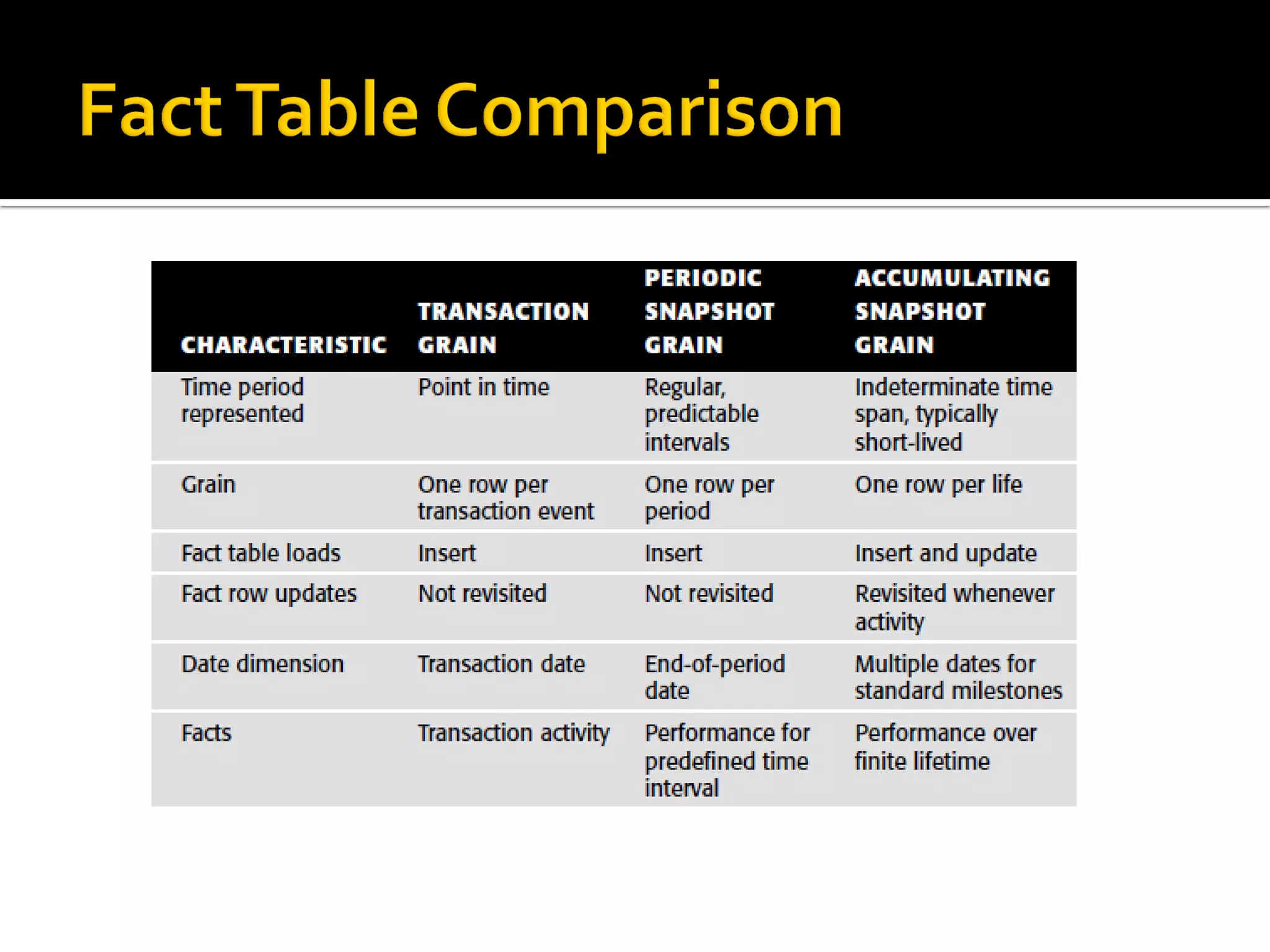
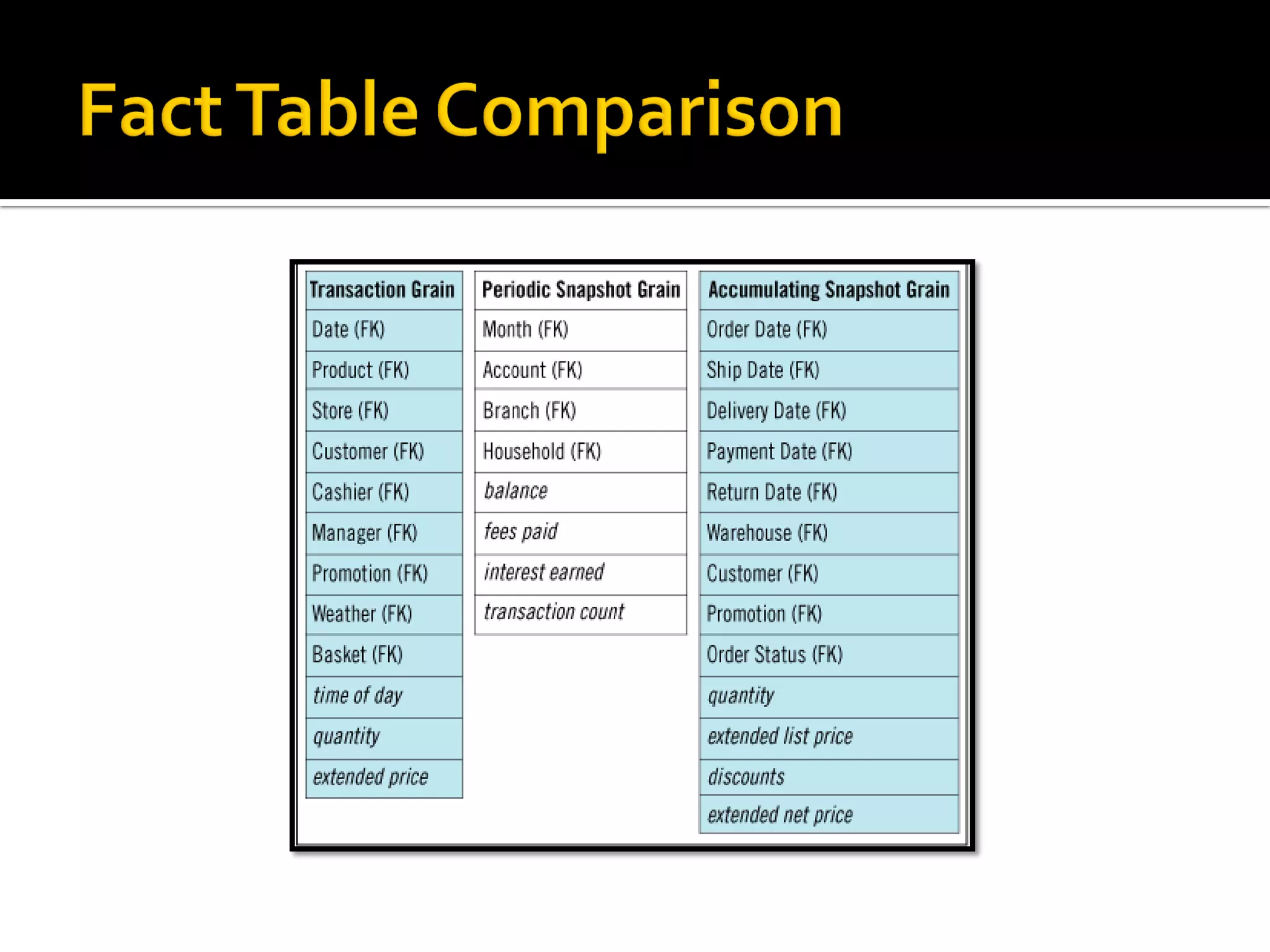
This document discusses different types of fact tables used in data warehousing: transaction fact tables track discrete processes over time; periodic snapshot fact tables record activity during repeating time periods like months; and accumulating snapshot fact tables overwrite facts as a process progresses, allowing intermediate snapshots of processes like orders. Accumulating snapshots are appropriate for short, definite processes while periodic snapshots work for long-running ones.