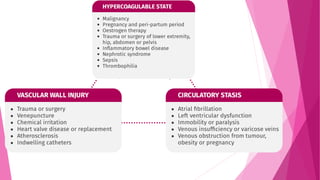
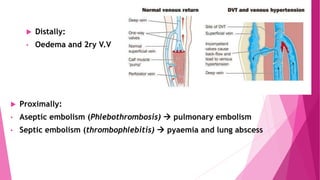
1) Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can be caused by Virchow's triad of factors that increase the likelihood of blood clots: damage to vessel walls, slowed blood flow, and increased coagulability.
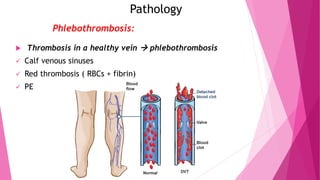
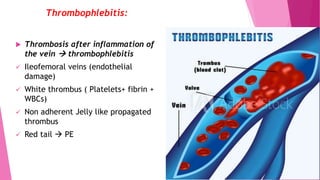
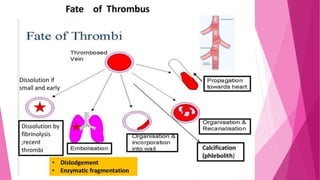
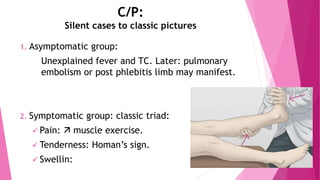
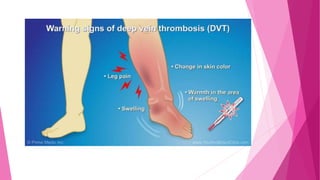
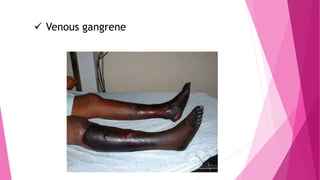
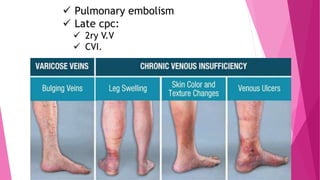
2) DVT presents as either phlebothrombosis, a clot in a healthy vein, or thrombophlebitis, a clot after vein inflammation. Complications include pulmonary embolism and infection.
3) Diagnosis involves tests like Doppler ultrasound, CT scans, and blood tests. Treatment focuses on prevention with stockings and blood thinners, or surgery to remove clots.