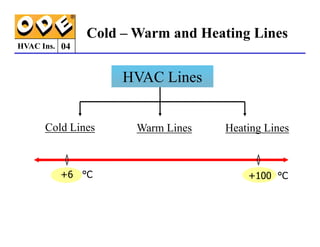
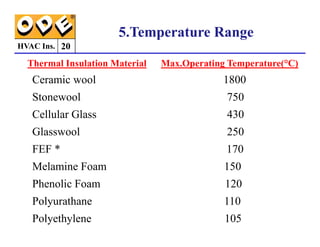
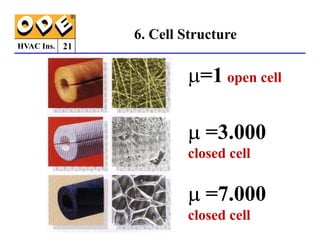
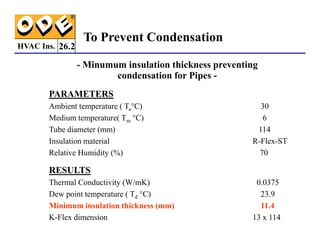
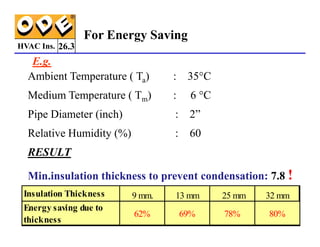
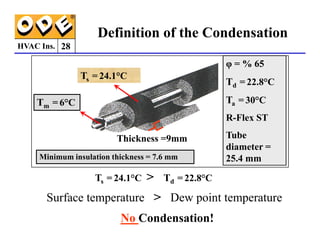
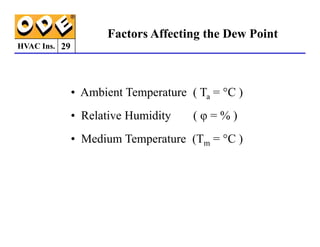
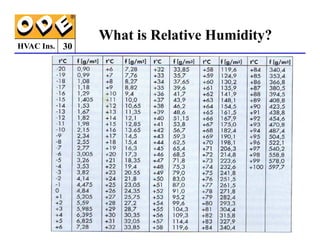
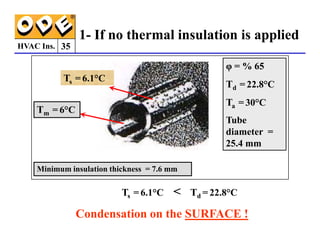
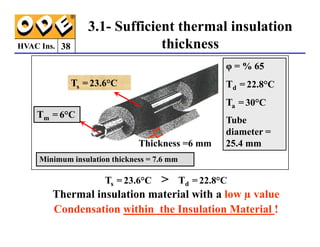
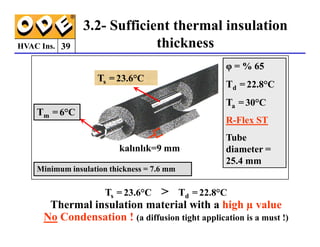
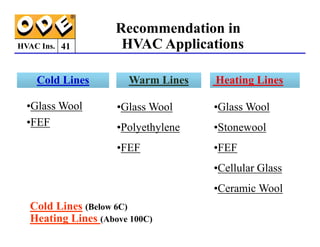
The document provides a comprehensive overview of HVAC insulation, discussing thermal insulation, its materials, and technical requirements. It explains the importance of preventing heat loss/gain in buildings through the use of various insulation materials, their classifications, and relevant standards. Additionally, it outlines how to calculate necessary insulation thickness to prevent condensation and optimize energy efficiency in HVAC applications.