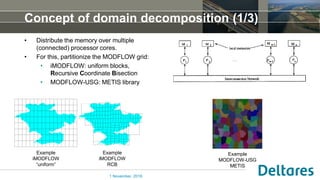
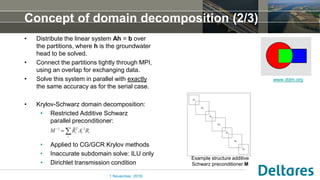
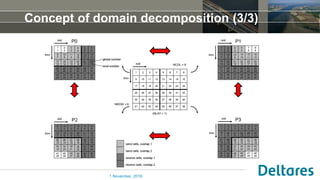
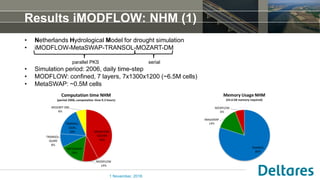
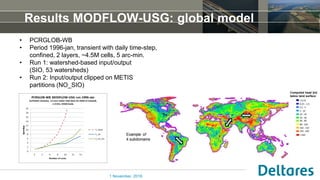
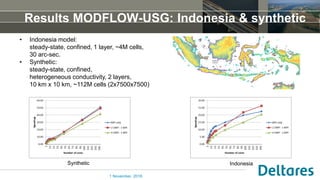
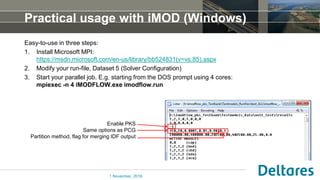
The document summarizes a new Parallel Krylov Solver (PKS) package that allows for parallel computing of large hydrological models. PKS divides the model grid and linear system over multiple processor cores using domain decomposition techniques. It has been incorporated into several Deltares hydrological models including MODFLOW, iMODFLOW, and MODFLOW-USG. Results show speedups of up to 5x for large national models of the Netherlands and good agreement with serial solutions. PKS makes it possible to efficiently solve high-resolution hydrological problems for decision support.