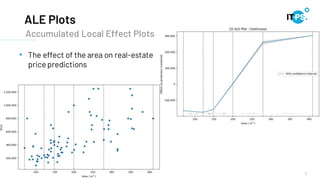
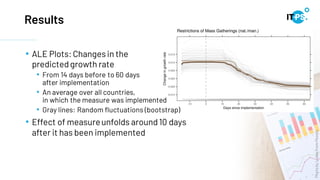
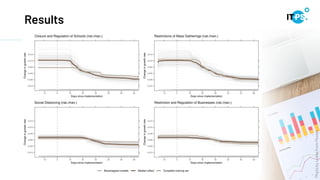
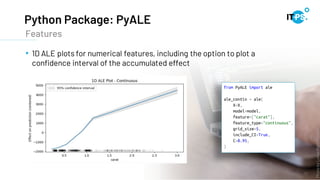
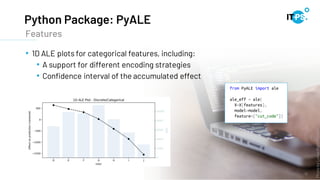
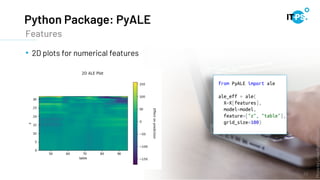
This document discusses machine learning model interpretation using accumulated local effect (ALE) plots. It describes how ALE plots can be used to visualize the effect of individual features on a model's predictions over time. As an example, the document summarizes a project that used ALE plots to analyze the effects of different COVID-19 measures in different countries. Key results included observing the average effect of measures unfolding around 10 days after implementation. The document also introduces a Python package called PyALE that can generate 1D and 2D ALE plots to aid in model interpretation.