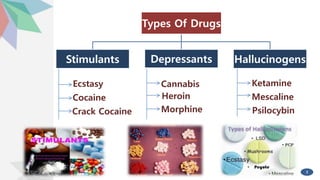
This document discusses drugs and their effects. It defines what drugs are, describes different types of drugs including stimulants, depressants and hallucinogens. It outlines the effects of drugs on the body like heart attacks and infections. Statistics are presented on drug use worldwide and in India showing increases in certain regions. Risk and protective factors for drug use are explained. India's laws against drug trafficking and amendments are summarized. Suggestions are provided for creating drug awareness among teens. The conclusion emphasizes that drug addiction can be treated and prevented through education.