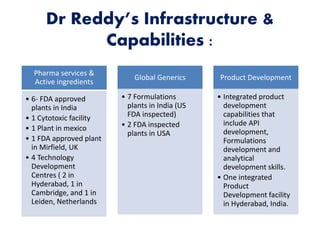
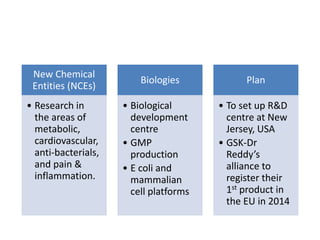
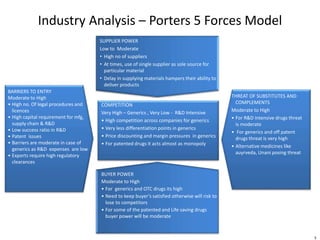
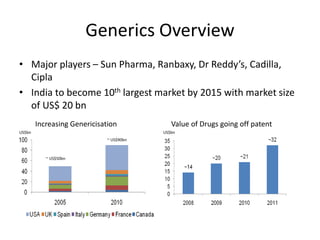
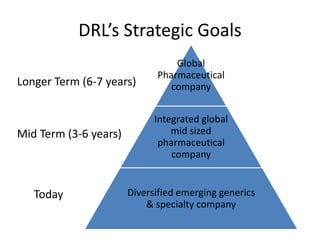
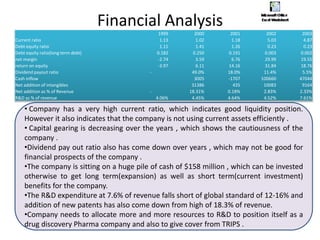
Dr. Reddy's Laboratories is a global pharmaceutical company based in Hyderabad, specializing in generic and branded drugs across various therapeutic areas. The company has experienced significant growth, with total sales of $2.1 billion in 2013 and a 14.6% year-over-year increase, while also facing challenges such as high competition and regulatory hurdles. Strategic goals include enhancing R&D capabilities and expanding its market presence, particularly in generics, to secure its position as a leading pharmaceutical entity in India.







![Dr. Reddy’s Dilemmas
• How can we be imitator [in the generics
business] and an innovator [in the discovery
business] at the same time?
• How can we be forge out licensing alliances
with large pharmaceutical companies [in the
drug discovery business] and at the same time
challenge their patents around the world [in
the specialty and generics businesses]?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drlanalysis-140816134449-phpapp02/85/Drl-analysis-14-320.jpg)