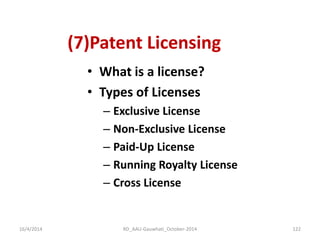
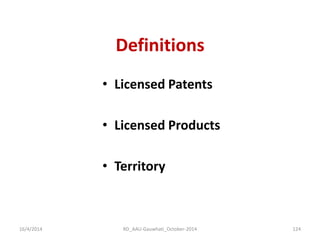
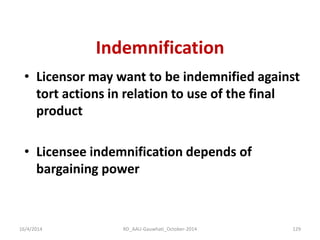
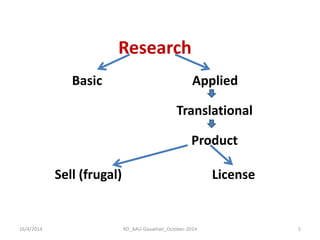
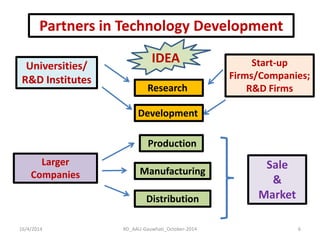
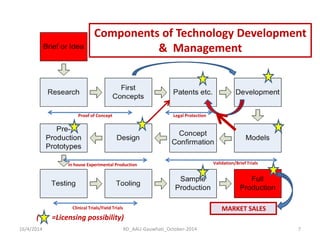
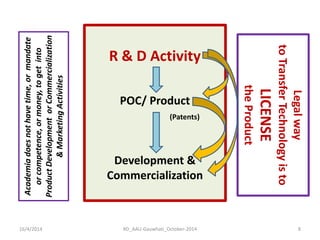
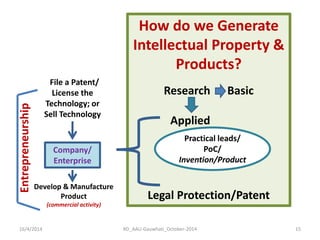
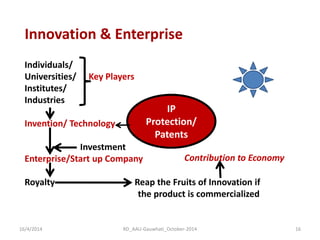
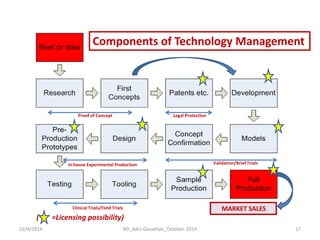
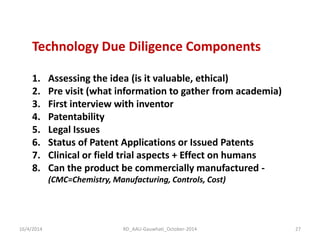
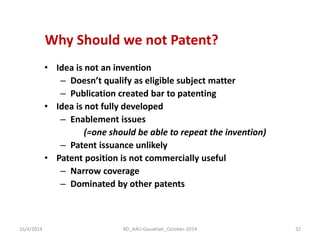
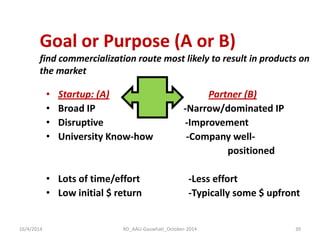
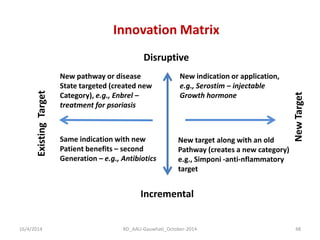
The document discusses the principles and dynamics of technology licensing, specifically in the context of biotechnology management by universities and research institutes in Assam. It outlines the importance of licensing technologies for product development and commercialization, highlighting the collaborative nature of research and the necessity for proper legal agreements. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for technology due diligence, market analysis, and strategic licensing relationships.





























































































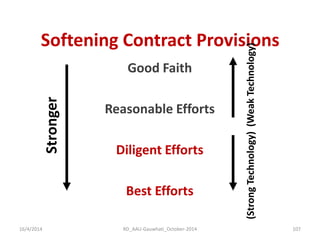
![Softening Remedies
•Materiality
“[Breach]…in any material respect.”
•Grace (cure) Periods
16/4/2014
106
RD_AAU-Gauwhati_October-2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rdlicensinginbiotech-copy-141017122902-conversion-gate02/85/Dr-Ravi-Dhar-on-Licensing-Technologies-Principals-Dynamics-106-320.jpg)

![Arbitration
•Why go to arbitration?
Example Clause:
“Any controversy or claim arising out of or relating to this Agreement, or its breach, is to be settled by arbitration administered by [organization] in accordance with its [subject matter] Rules.”
•Arbitration or Mediation? (Indian or International)
16/4/2014
109
RD_AAU-Gauwhati_October-2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rdlicensinginbiotech-copy-141017122902-conversion-gate02/85/Dr-Ravi-Dhar-on-Licensing-Technologies-Principals-Dynamics-109-320.jpg)