The document provides an introduction to the dplyr package in R, detailing various functions for data manipulation such as select, filter, arrange, and summarise. It includes syntax examples and operations to transform and analyze datasets effectively. Additionally, it introduces the magrittr pipe operator for chaining commands in a more readable format.


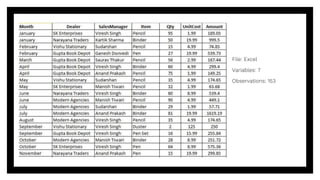
![• Keeps only those variables (columns) that you
want to retain/extract.
• Syntax: select(dataset,[column1],[column2],…)
Examples:
Select columns Month, Dealer, Item, Quantity: select(sales,Month,Dealer,Item,Qty)
Select columns from Month to Quantity: select(sales,Month:Qty)
Deselect column Month from the dataset: select(sales,-Month)
Select columns ending with the letter “r”: select(sales,ends_with("r"))
Select columns containing the letter “r”: select(sales,contains("r"))
Select columns starting the series “m”: select(sales,matches("m."))
Select columns with multiple variables: select(sales,one_of(c("Month","Dealer")))
Select columns starting with the letter “d”: select(sales,starts_with("d"))
select()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dplyrpackage-181120125534/85/dplyr-Package-in-R-5-320.jpg)


![• Orders or sorts the records (rows) based on the
variable(s).
• By default the arrangement is in ascending order.
• Syntax: arrange(dataset,column1,[column2],…)
Examples:
Sort the dataset based on Months: arrange(sales,Month)
Sort the dataset based on Months and Dealer: arrange(sales,Month,Dealer)
Arrange the data in descending order of Quantity: arrange(sales,desc(Qty))
arrange()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dplyrpackage-181120125534/85/dplyr-Package-in-R-8-320.jpg)



![• Helps create groups in a dataset based on a
varaible.
• Useful when nested with other functions.
• Syntax: group_by(dataset,column1,[column2]…)
• Ungroup Syntax: ungroup(dataset)
Example:
Create groups in the data based on Items: group_by(sales,Item)
Get the maximum units sold for each item: filter(group_by(sales,by=Item),Qty==max(Qty))
group_by()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dplyrpackage-181120125534/85/dplyr-Package-in-R-12-320.jpg)




![• Helps count the number of times a values has
appeared in a variable.
• Syntax: count(dataset, [column1],[column2],…)
Examples:
Count the number of times each Dealer has appeared: count(sales,Dealer)
Count the number of times Pen has appeared: count(sales,Item=="Pen")
count()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dplyrpackage-181120125534/85/dplyr-Package-in-R-17-320.jpg)
