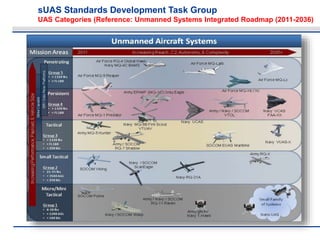
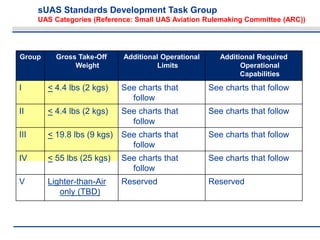
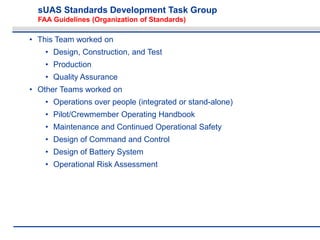
The document discusses the objectives and approach of the sUAS Standards Development Task Group, which aims to finalize draft standards related to design, construction, testing, production, and quality assurance for small unmanned aircraft systems (sUAS). The Task Group will work to ensure the standards are acceptable to the FAA and provide affordable, reliable solutions for industry and users. It outlines the Task Group's core team, constraints including FAA guidelines, and process for developing consensus standards through multiple ballots and revisions in alignment with the FAA's Notice of Proposed Rulemaking.