This document provides an overview of remote procedure calls (RPC) including:
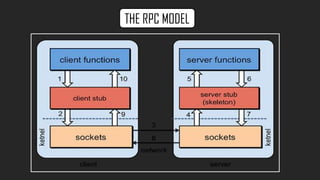
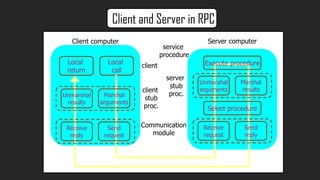
- RPC uses the client/server model where a client makes a request to a server program located on another computer. The client is suspended until the server returns results.
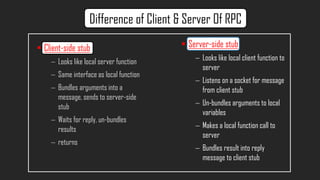
- RPC implementations generate client and server stub code that marshall/unmarshall arguments and results to handle remote communication transparently.
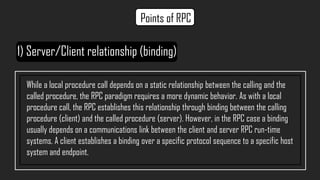
- Key aspects of RPC include the client/server binding, lack of shared memory between systems, and ability to handle independent failures on remote systems.
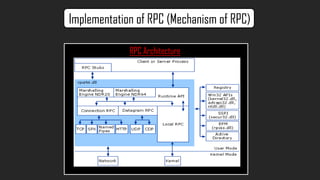
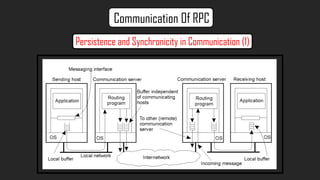
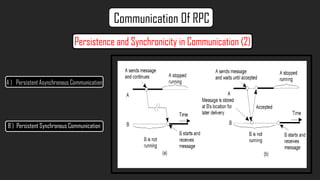
- The document discusses RPC communication models and implementations including lightweight RPC to improve performance of communication between protection domains on the same machine. It provides a case study on the Distributed Computing Environment (DCE)
![DOS[ Distributed Operating System ]
(Remote Processing Call)
RPC
Prepared By : Avishek Sarkar
Enrollment No : 130650107020
Roll No : 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dosrpcavishek130650107020-160428172041/85/Dos-rpc-avishek130650107020-1-320.jpg)