Embed presentation
Downloaded 24 times


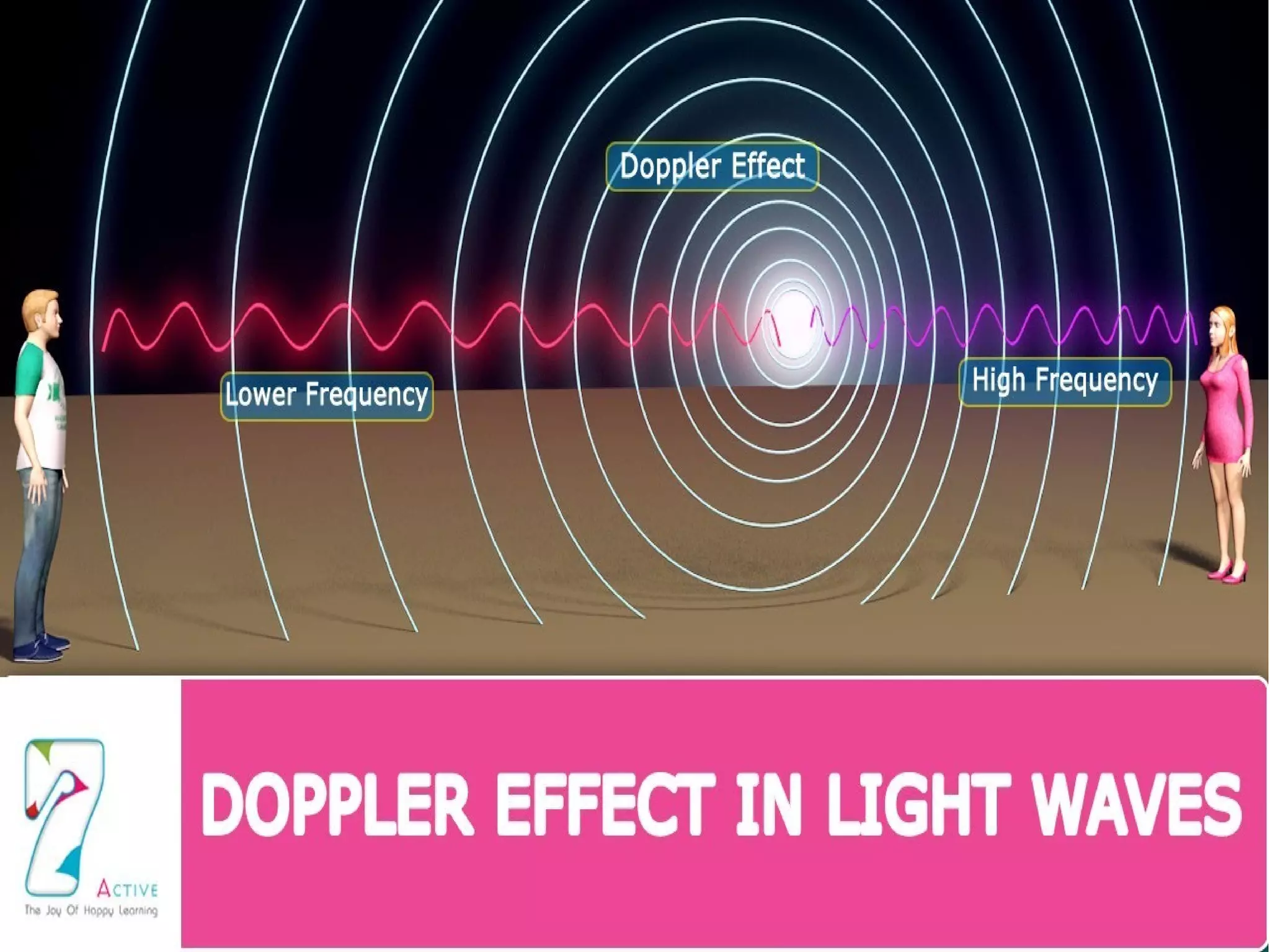

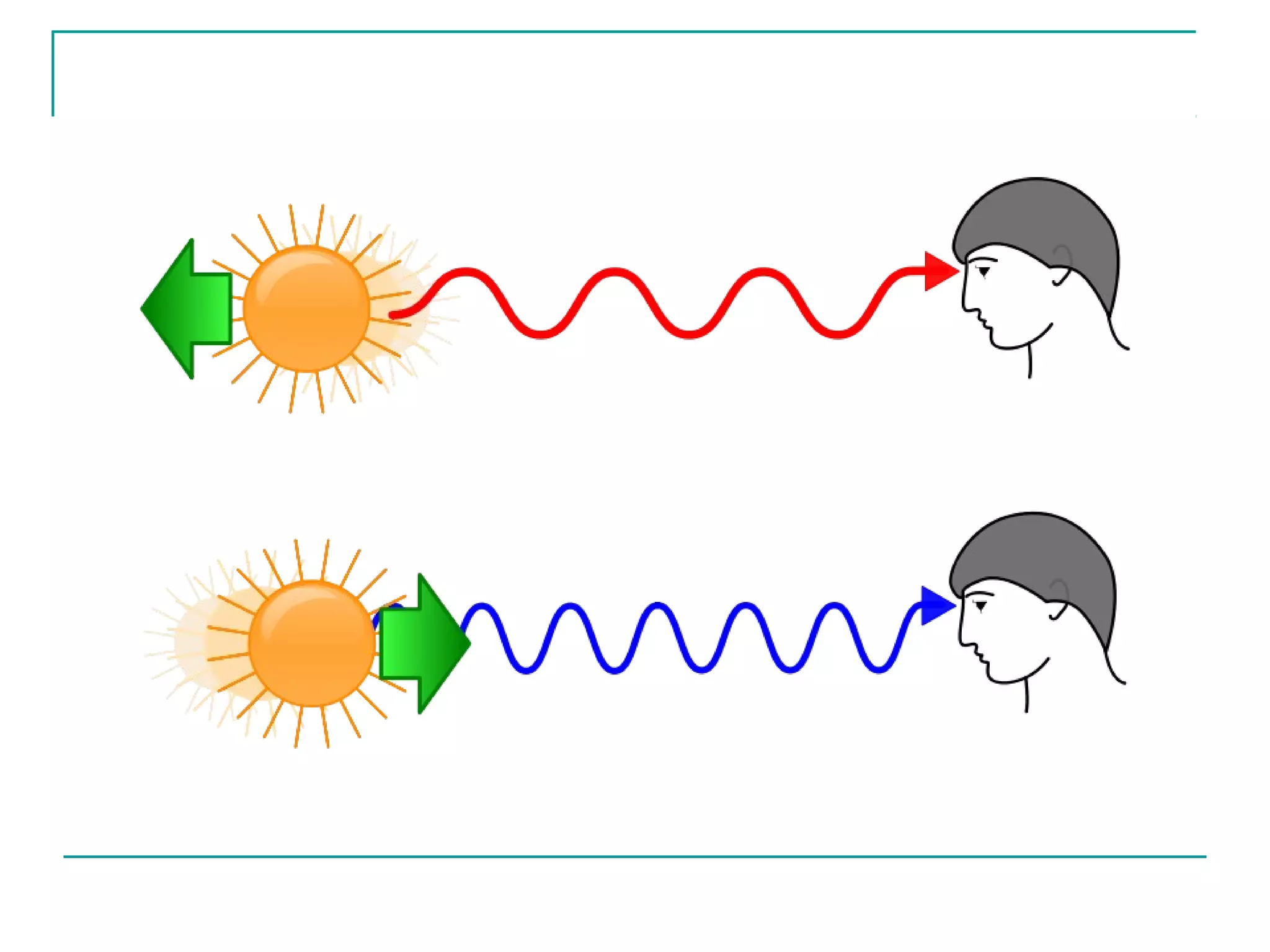










The document discusses the Doppler effect and how it allows astronomers to measure the motion of stars and galaxies relative to Earth. A shift toward the red indicates the galaxy is moving away from Earth, a shift toward the blue means it is approaching, and no shift means it is at rest. It also briefly mentions that images from different types of telescopes like ultraviolet, infrared, and X-ray look very different and describes how spectrographs use prisms and gratings to split light into its spectrum.














