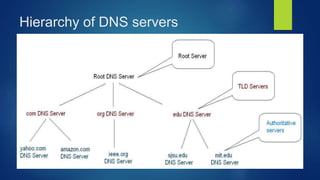
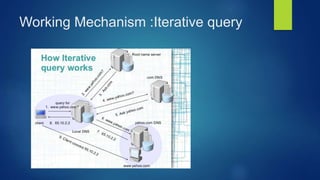
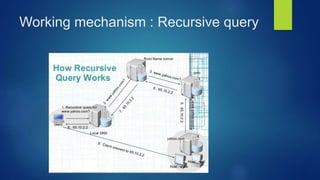
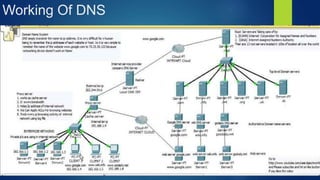
The presentation introduces DNS (Domain Name System), including its history, components, services, and working mechanism. DNS is a large distributed database that maps hostnames and domain names to IP addresses. It originated as a central HOSTS.TXT file maintained by NIC but grew too large, leading Paul Mockpetris to develop the first DNS specification in 1984. DNS has a global, hierarchical structure with name servers, resolvers, and a namespace database to provide services like address translation and load distribution through both iterative and recursive queries.