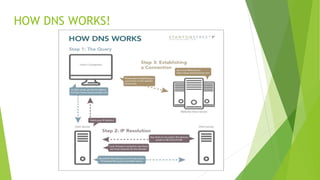
Domain Name System (DNS) is a procedure that allows users to recognize any site on the Internet through domain names instead of IP addresses. A domain name is a sequence of letters and numbers separated by periods that acts as a pointer to a unique IP address. There are different types of domain names including top-level domains like .com, .org, and country code top-level domains; as well as second-level and subdomains. DNS dates back to the early days of ARPANET when a text file mapped hostnames to numerical addresses and has evolved to be the major backbone of translating human-friendly names to computer-readable IP addresses on the internet.