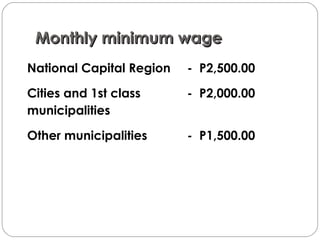
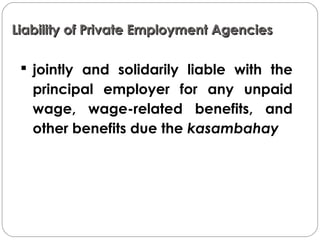
This document summarizes key aspects of Republic Act No. 10361, also known as the Batas Kasambahay or Domestic Workers Act. It provides background on the law, outlines coverage and requirements for hiring domestic workers, benefits and protections for workers, responsibilities of employers and private employment agencies, and enforcement mechanisms. Key points covered include minimum wage and leave benefits for workers, allowable reasons for termination by employers and workers, regulations on hiring of child workers, and penalties for unlawful acts.