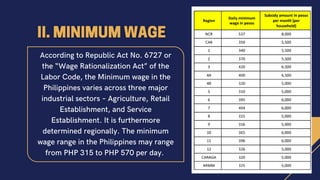
The document discusses the different types of employment in the Philippines according to the Labor Code. There are five main types: regular employment, which is for an indefinite period; casual employment, which is employment that has lasted for at least one year; probationary employment, which lasts up to six months to evaluate an employee; project-based employment, which ends once the project is completed; and seasonal employment, which is specific to certain seasons. The document also outlines the basic mandatory benefits for private sector employees according to the Labor Code, such as SSS, PhilHealth, 13th month pay, and others.