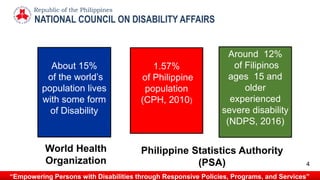
The document discusses disability perspectives and laws in the Philippines. It provides information on the National Council on Disability Affairs (NCDA), which is the policymaking body for disability rights implementation. The NCDA coordinates various government agencies and organizations. Disability is defined in both medical and social terms, and the 10 most common types are outlined. Barriers faced by persons with disabilities are explained, along with approaches to promote inclusion. Major Philippine disability laws are summarized, covering topics like accessibility, employment, health services, and political participation.