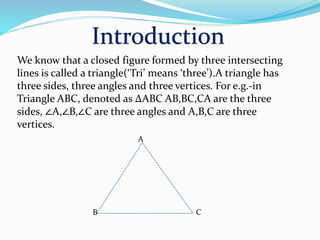
This document defines triangle congruence and the different criteria used to determine if two triangles are congruent. Two triangles are congruent if their corresponding sides and angles are equal. The criteria include: SAS (two sides and the included angle), ASA (two angles and the included side), AAS (any two angles and a non-included side), SSS (all three sides), and RHS (right angle, hypotenuse, and one other side). Examples are provided to demonstrate each congruence rule.