This document discusses different rules for determining if two triangles are congruent:
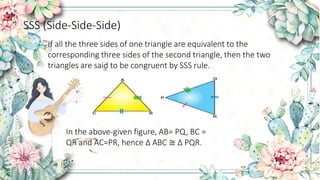
- SSS (Side-Side-Side) rule says two triangles are congruent if all three sides are equal.
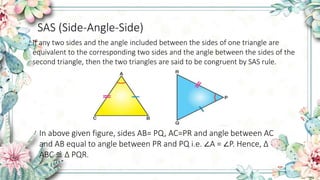
- SAS (Side-Angle-Side) rule says two triangles are congruent if two sides and the angle between them are equal.
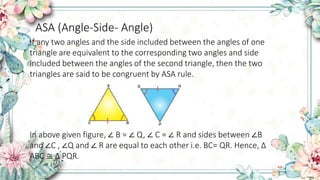
- ASA (Angle-Side-Angle) rule says two triangles are congruent if two angles and the side between them are equal.
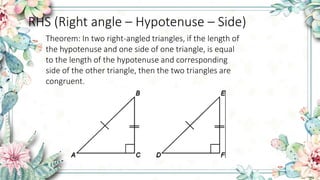
- RHS (Right angle – Hypotenuse – Side) rule says two right triangles are congruent if the hypotenuse and one side are equal.