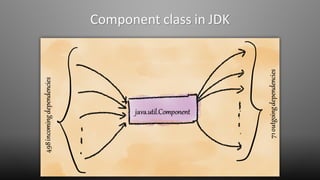
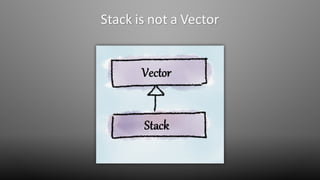
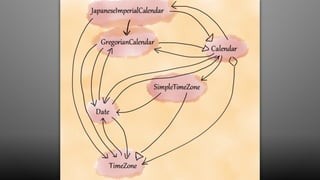
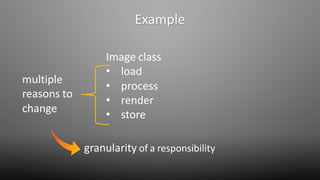
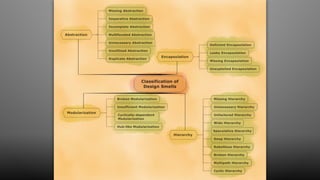
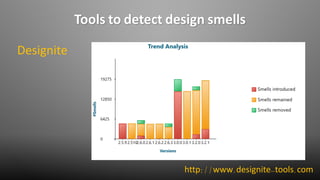
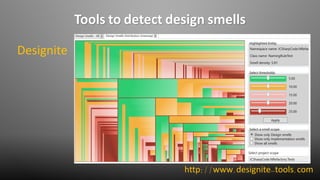
The document discusses design smells, which are structures in software design that violate principles and negatively impact quality. Some examples of design smells discussed include missing abstractions, unnecessary access, and insufficient modularization. The document advocates that software engineers should understand design smells, avoid introducing them, and refactor existing code to remove them, as all engineering disciplines must deal with non-optimal solutions. It provides references for further information on managing technical debt from design smells.
















![public class Throwable {
public void printStackTrace();
public StackTraceElement[] getStackTrace();
//other methods elided.
}
public final class StackTraceElement {
public String getFileName();
public int getLineNumber();
public String getClassName();
public String getMethodName();
public boolean isNativeMethod();
}
Refactored in Java 1.4
(Java 1.4)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doesyourdesignsmell-asas2016-161005140734/85/Does-your-design-smell-Tushar-Sharma-20-320.jpg)