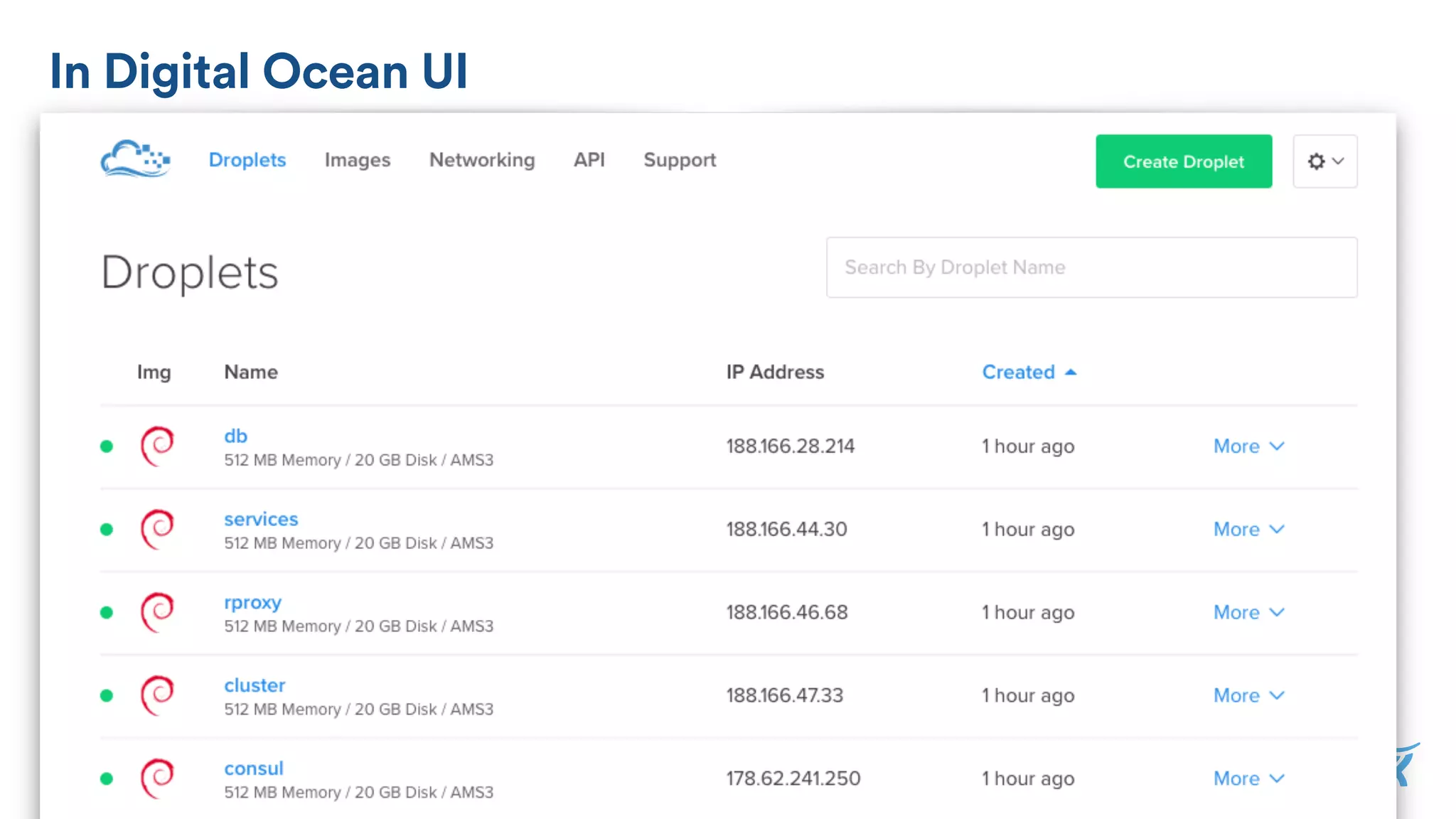
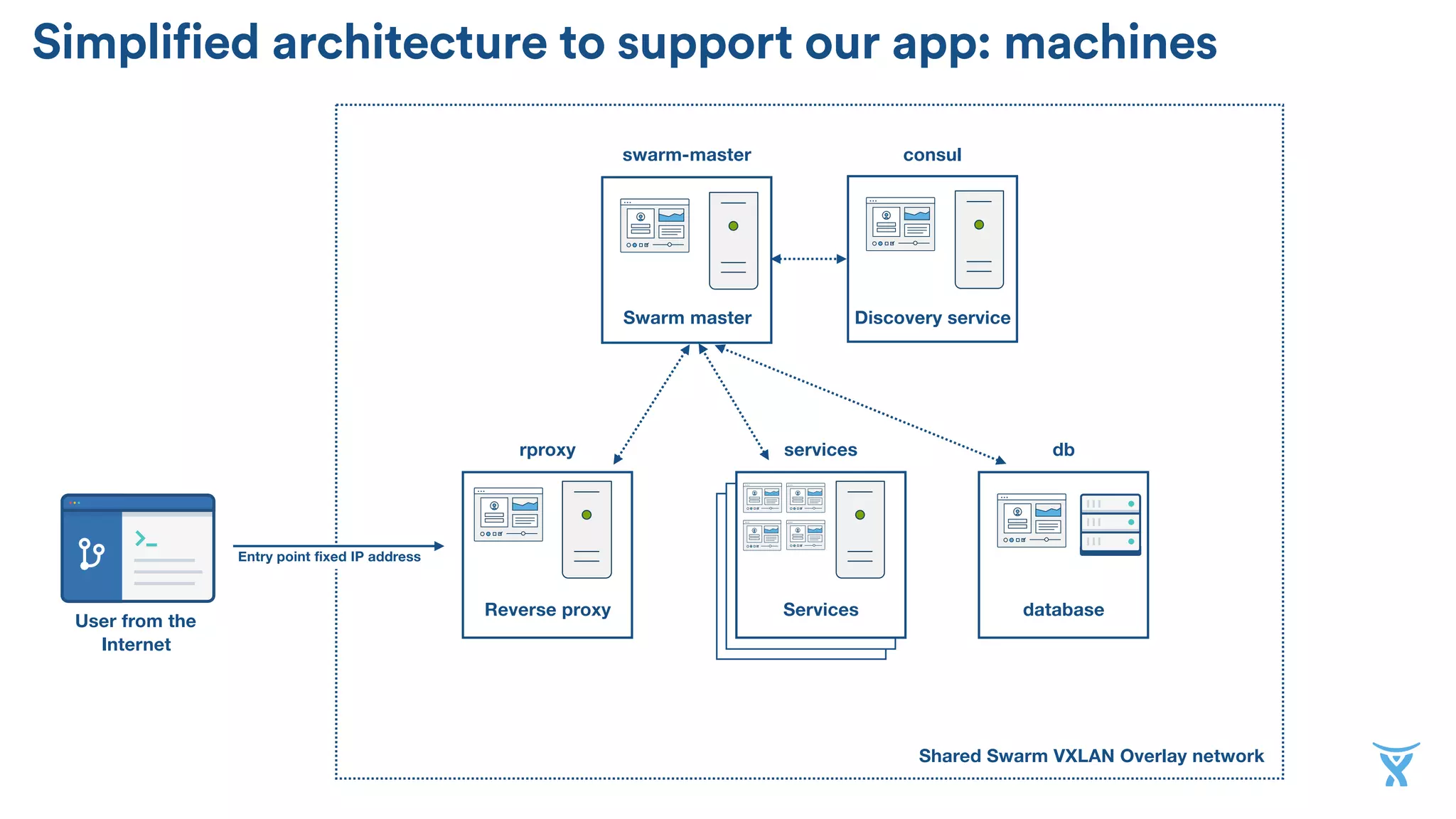
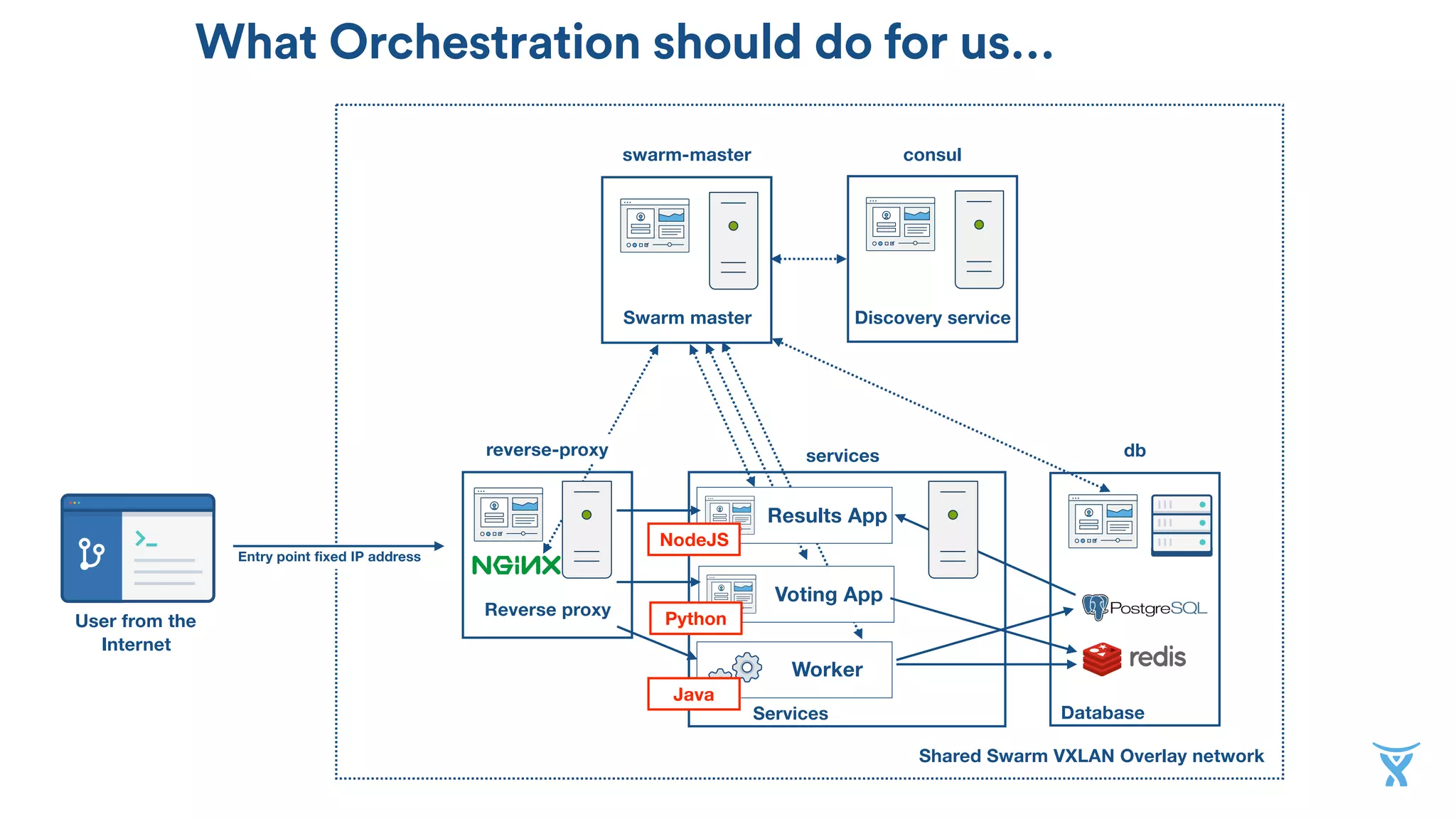
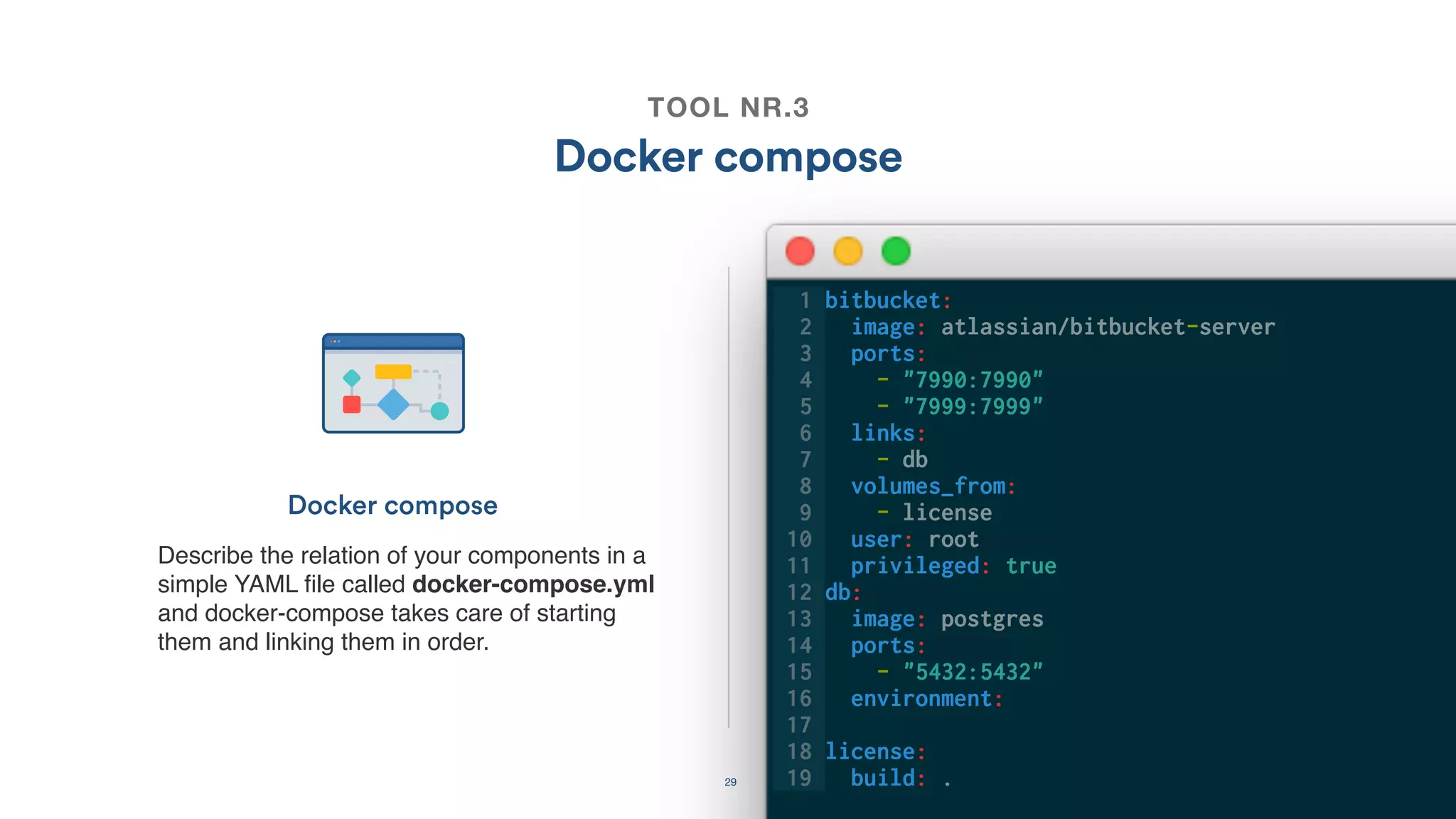
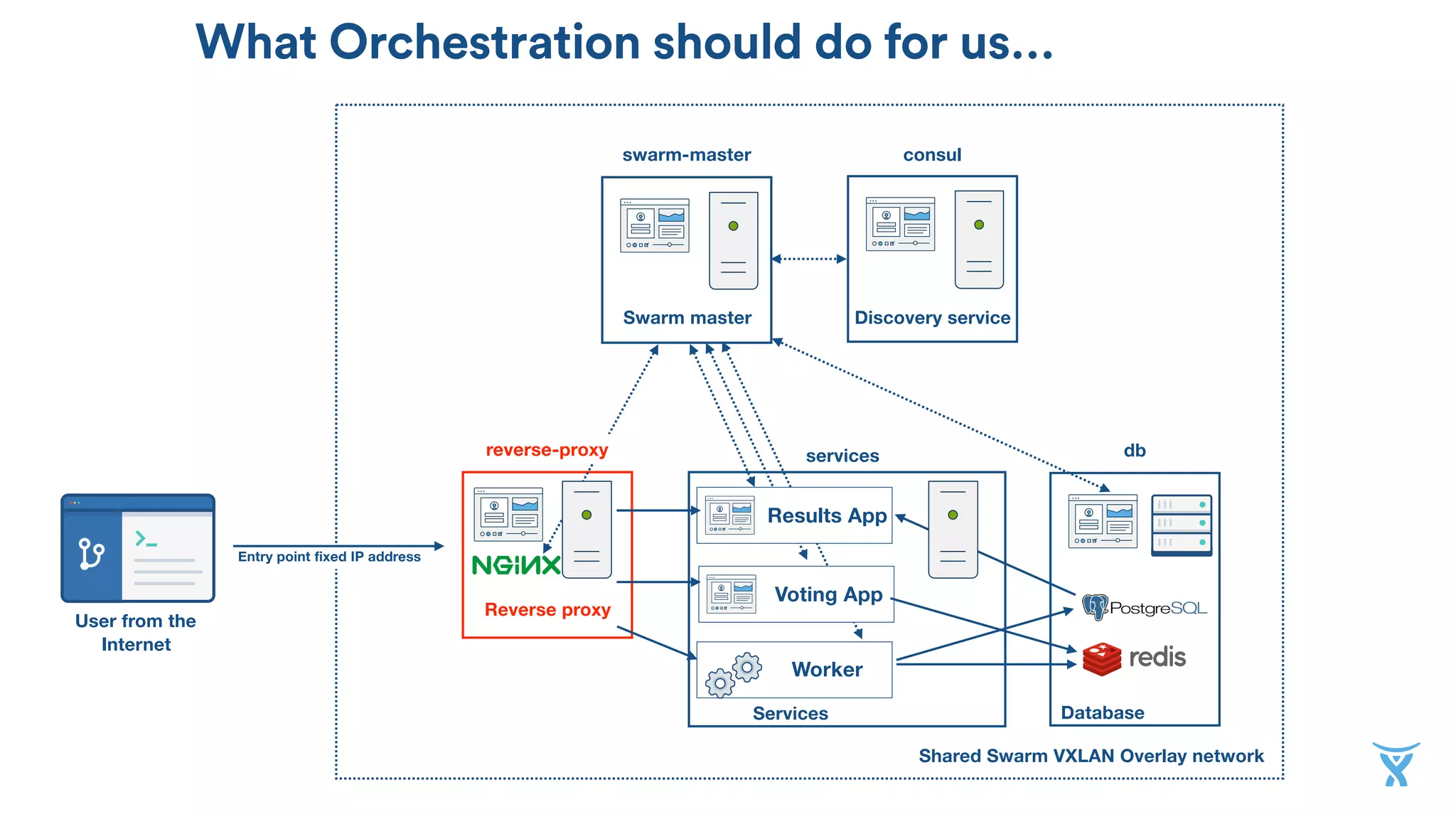
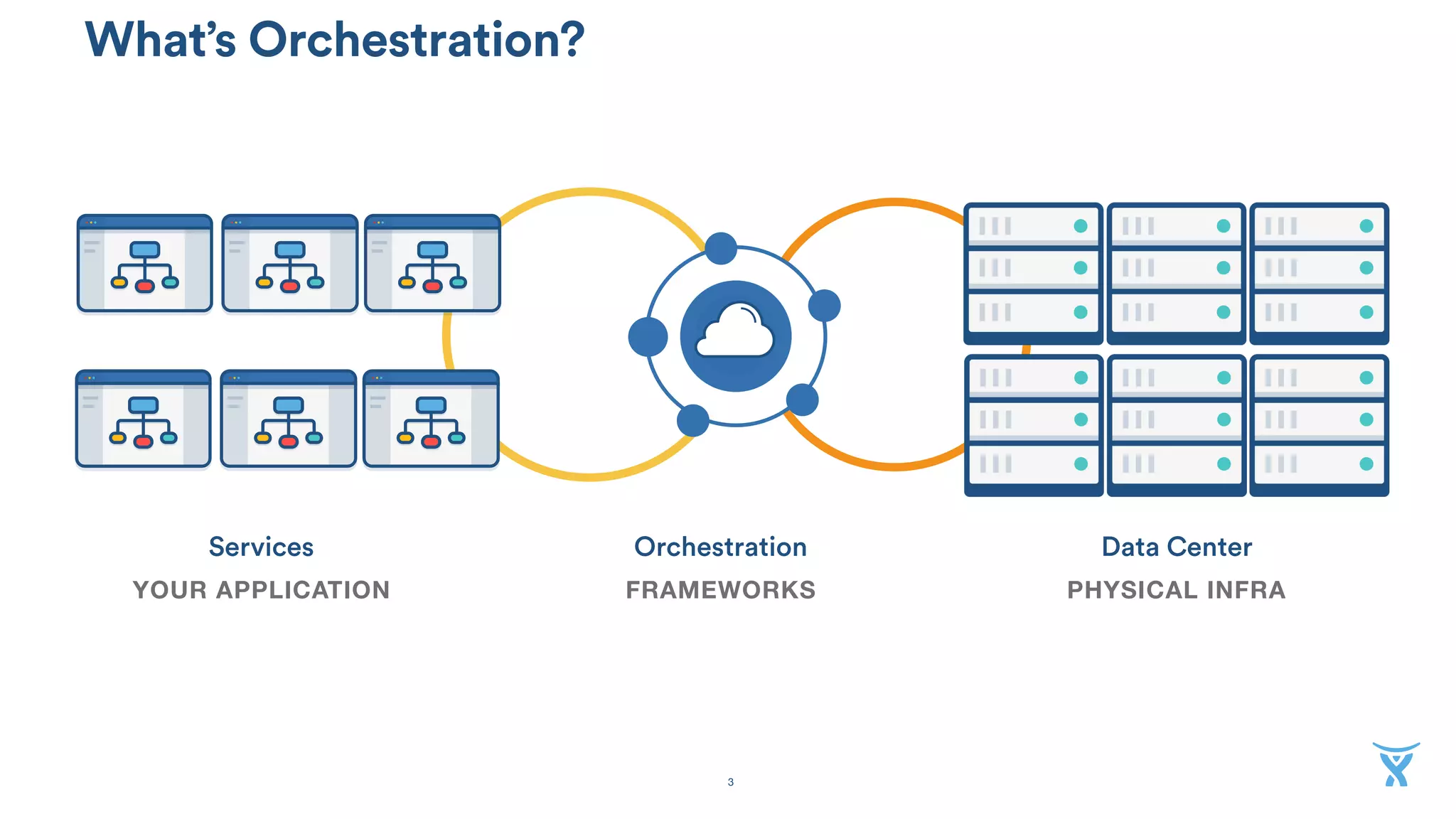
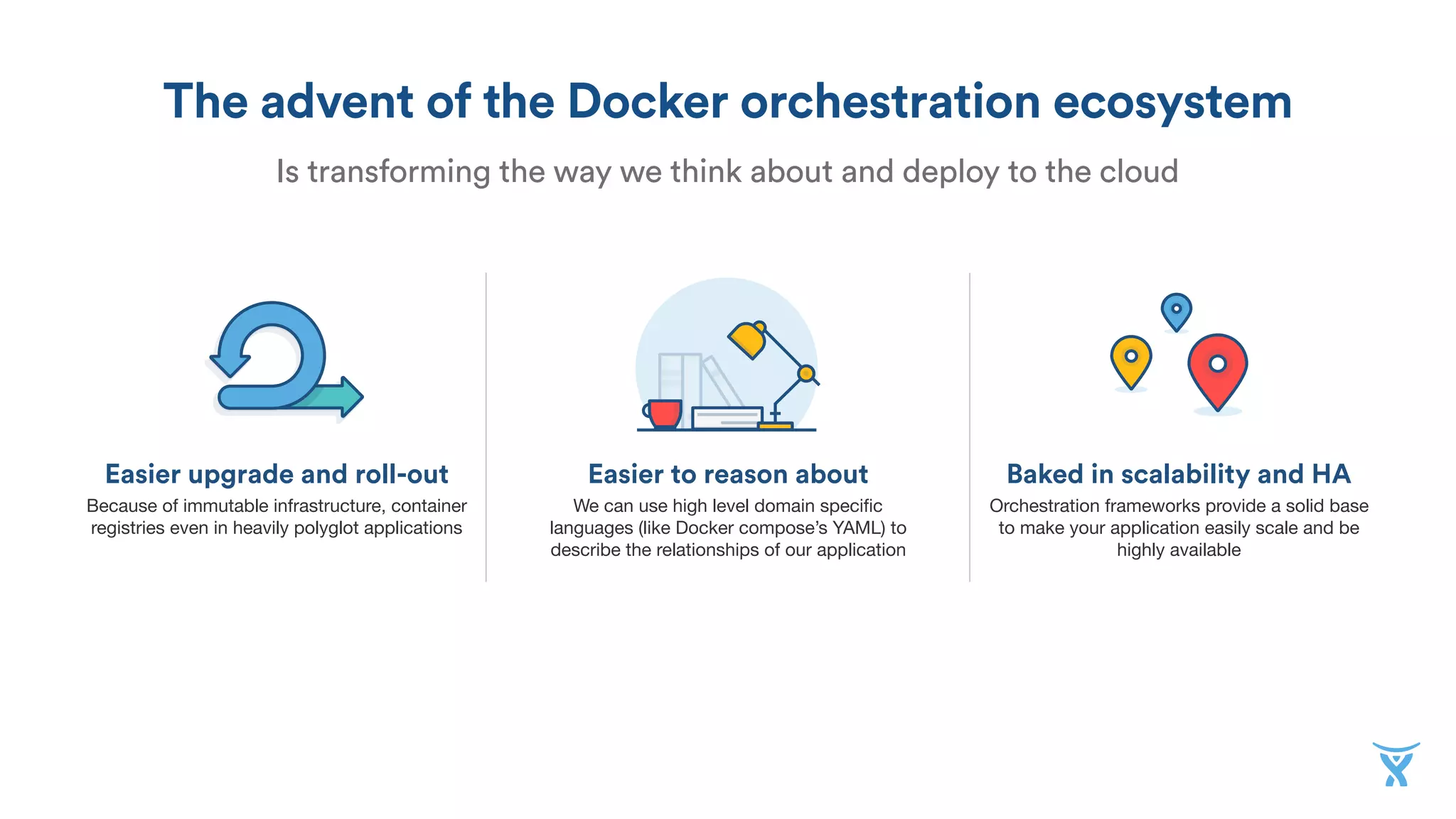
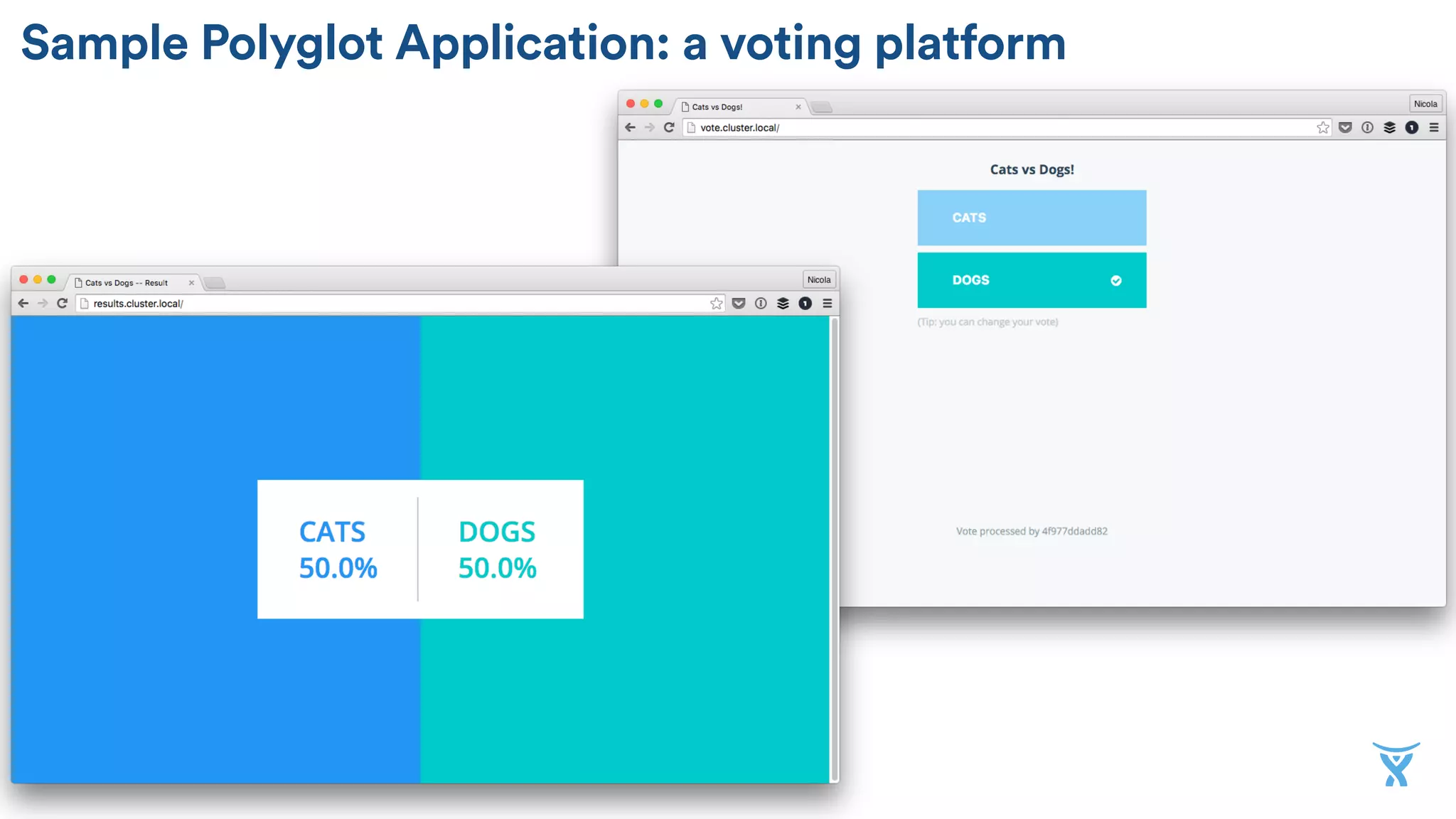
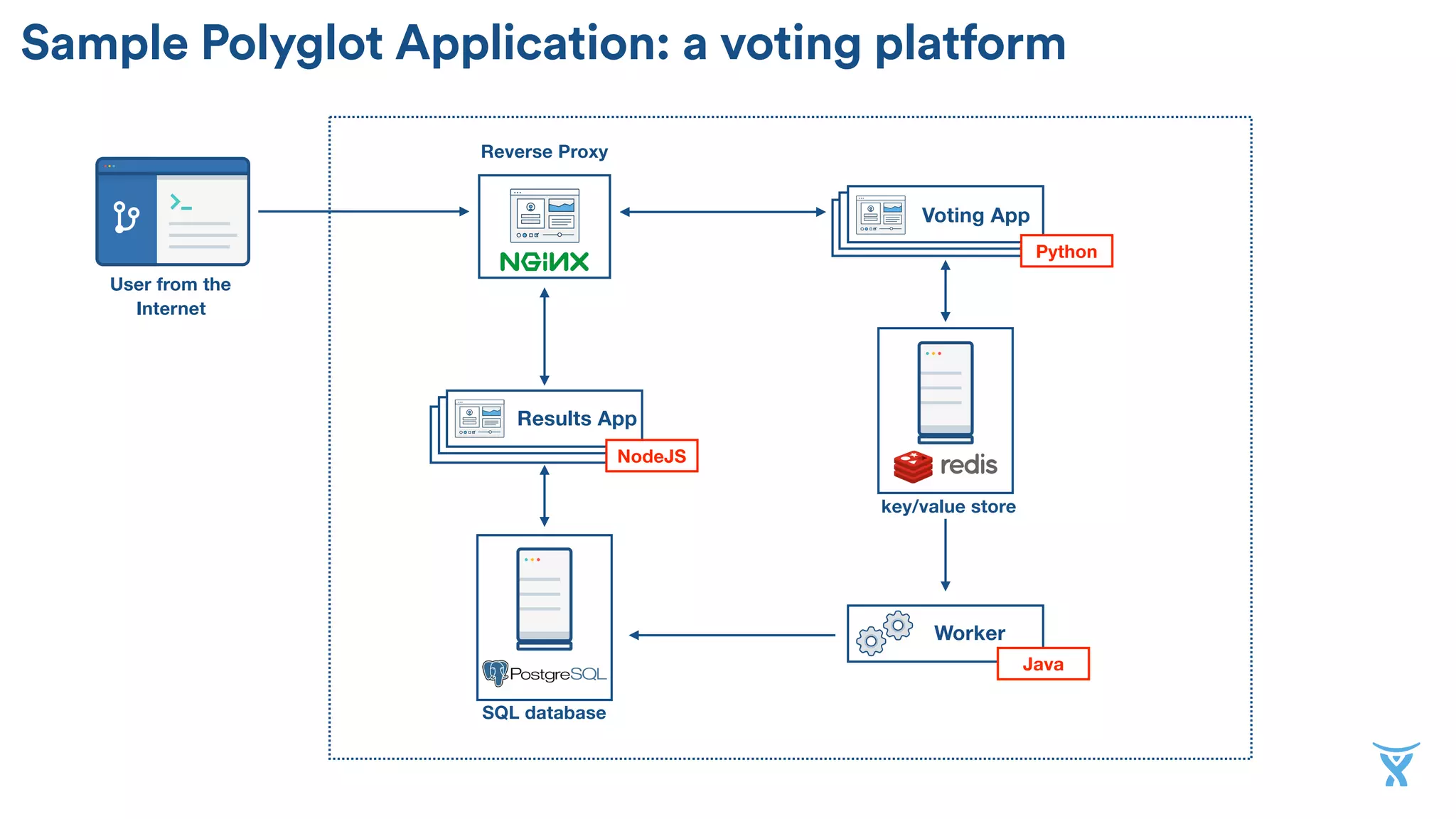
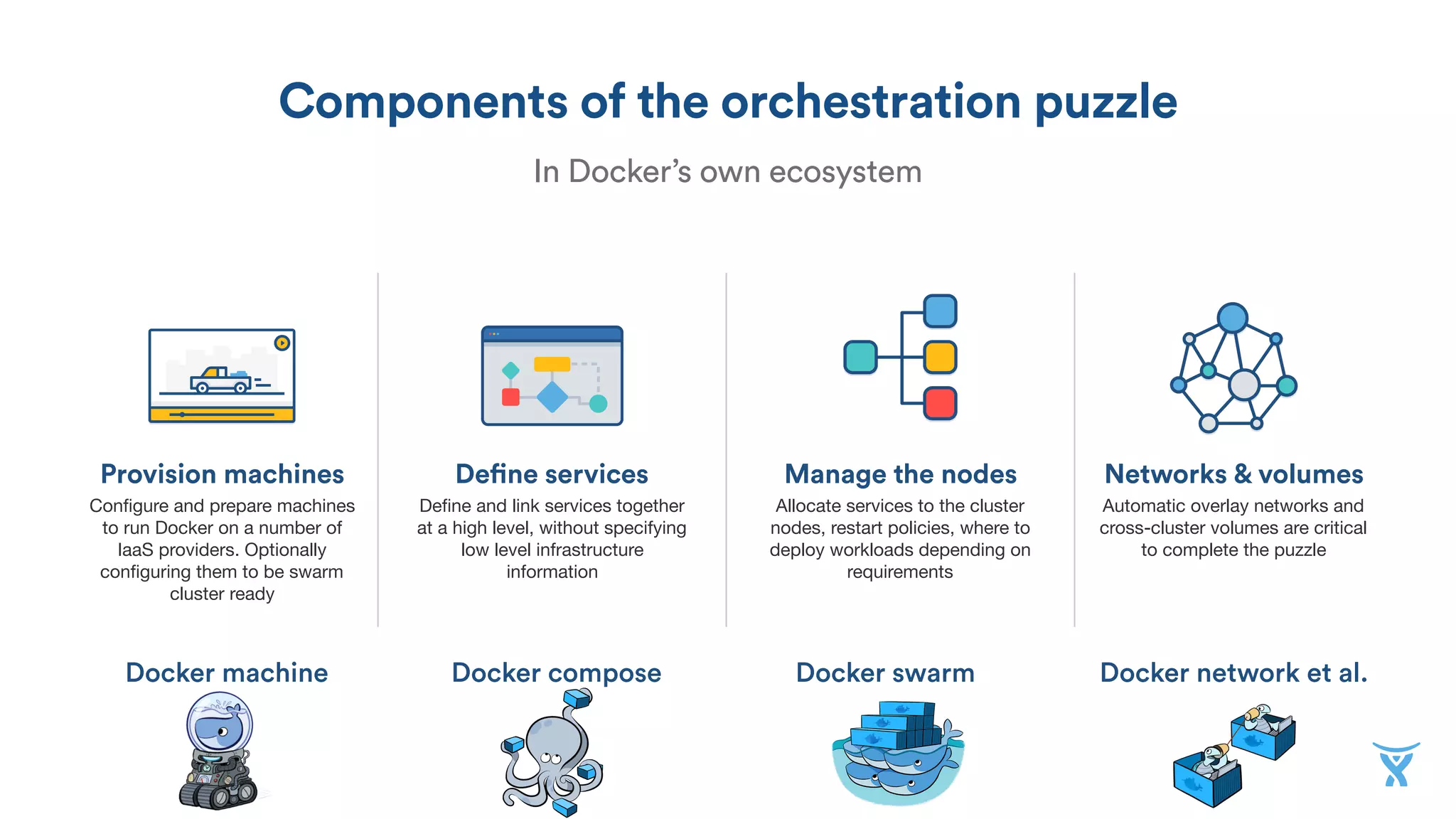
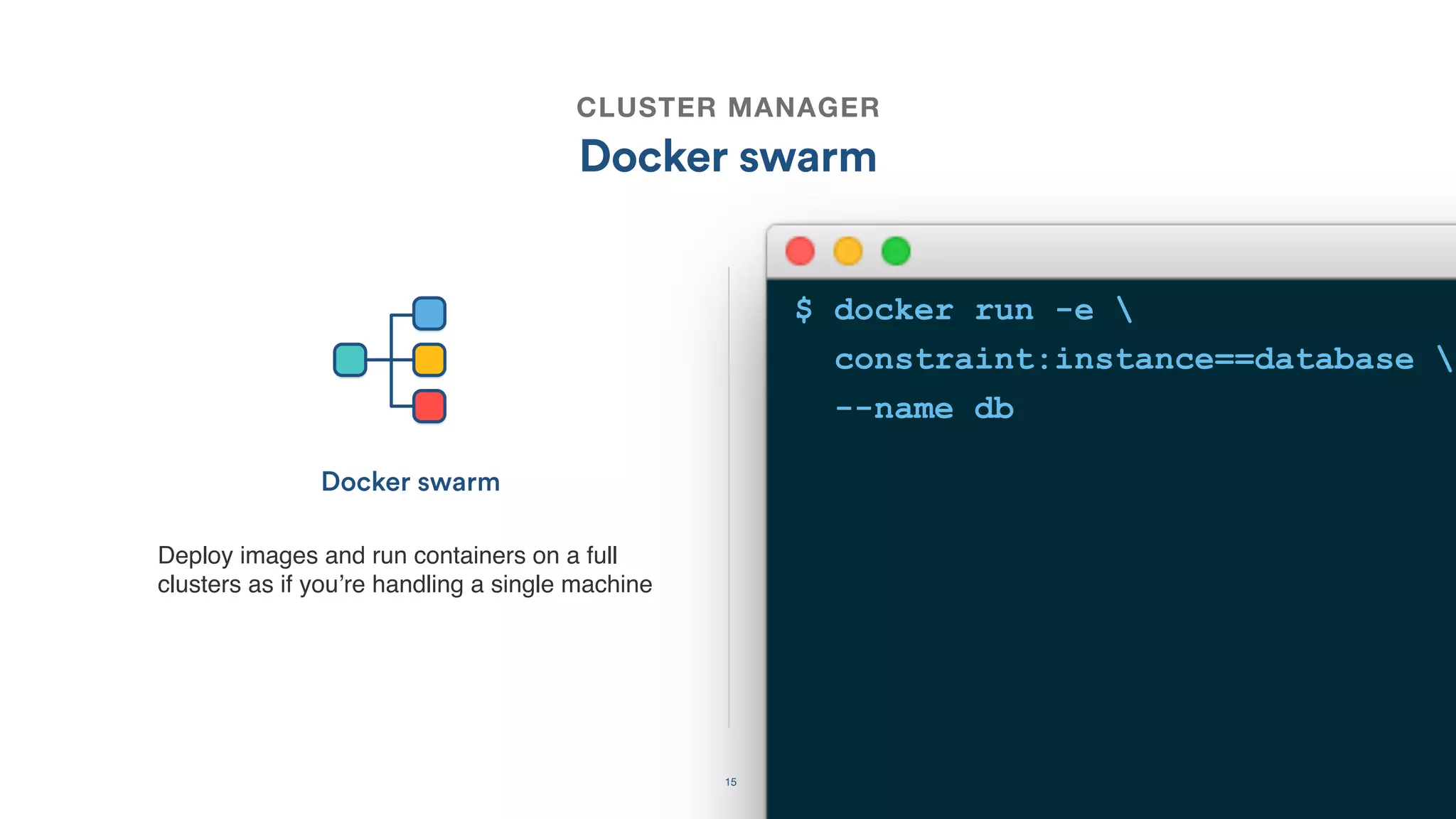
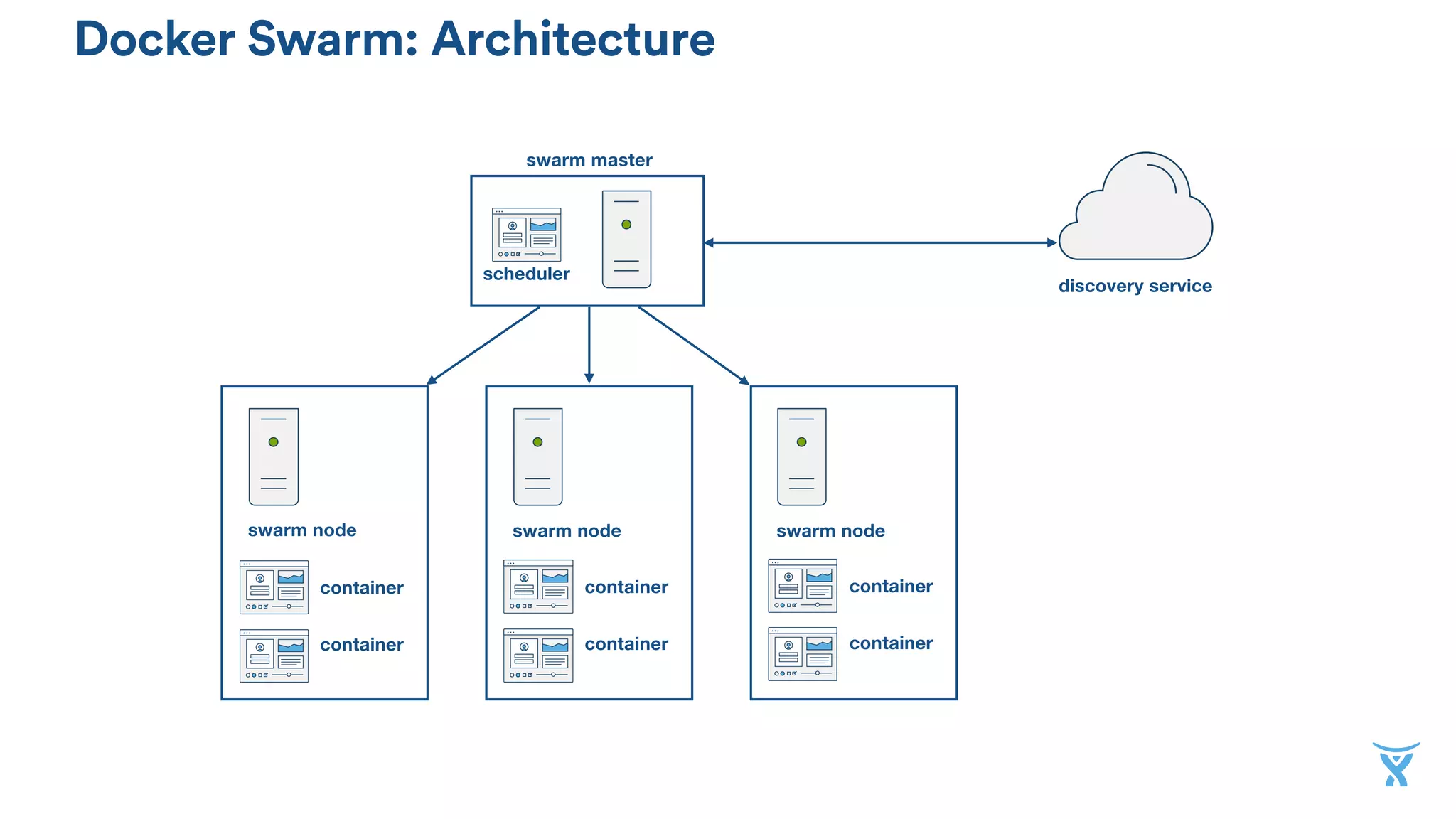
The document discusses the utilization of Docker Swarm for orchestrating micro-services, highlighting key components such as container registries, service definitions, and node management. It emphasizes the significance of high-level domain-specific languages like YAML for describing application relationships and the advantages of using orchestration frameworks for scalability and high availability. Additionally, it illustrates the setup process for running polyglot applications within a Docker ecosystem using tools like Docker Machine and Docker Compose.






![19
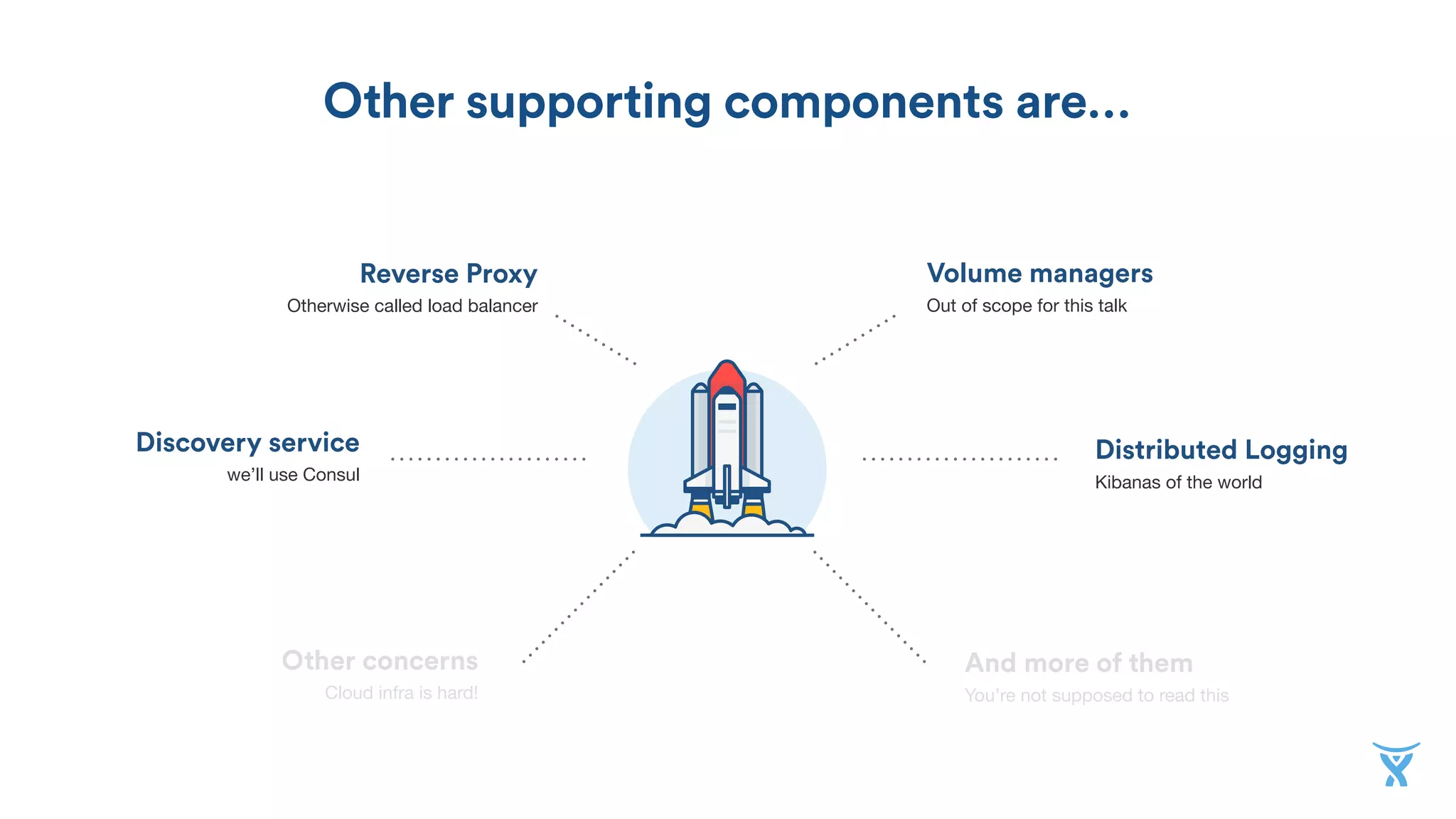
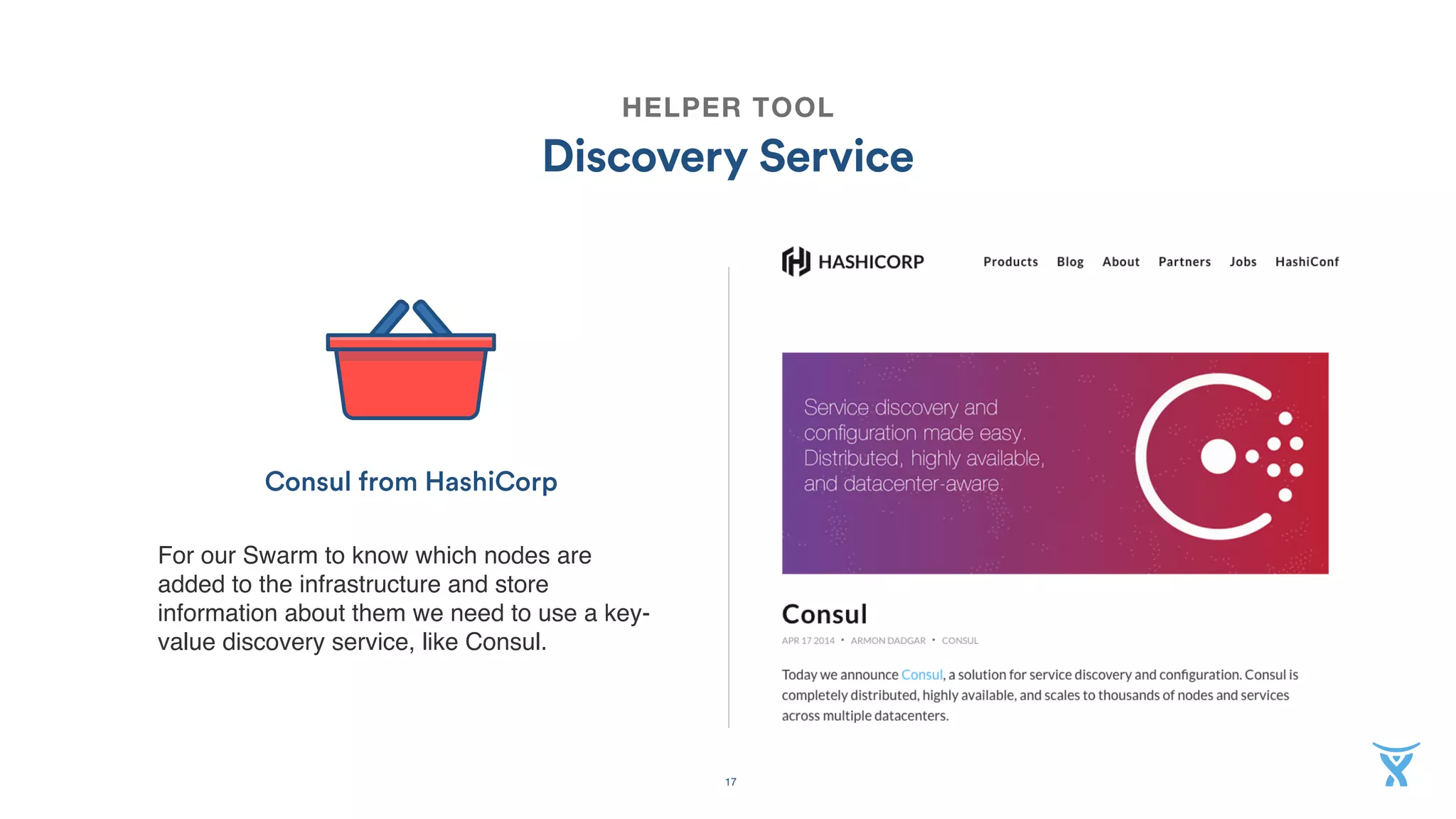
FIRST STEP
Docker machine
Simple command line tool to provision local
and remote hosts with Docker installed.
Fantastic to get up and running fast. It has
drivers for many Internet service providers
and IaaS.
Docker machine
$ docker-machine create -d v
INFO[0000] Downloading boot2
INFO[0001] Creating SSH key.
INFO[0001] Creating VirtualB
INFO[0006] Starting VirtualB
INFO[0007] Waiting for VM to
INFO[0041] "dev" has been cr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8y2jh1ytsbijerpr19gh-signature-97ac0cba55d83fa6f2a2f253a387270677bf11da9177d0b7d555fb911fc34ba2-poli-160526084215/75/Higher-order-infrastructure-from-Docker-basics-to-cluster-management-Nicola-Paolucci-Codemotion-Amsterdam-2016-19-2048.jpg)
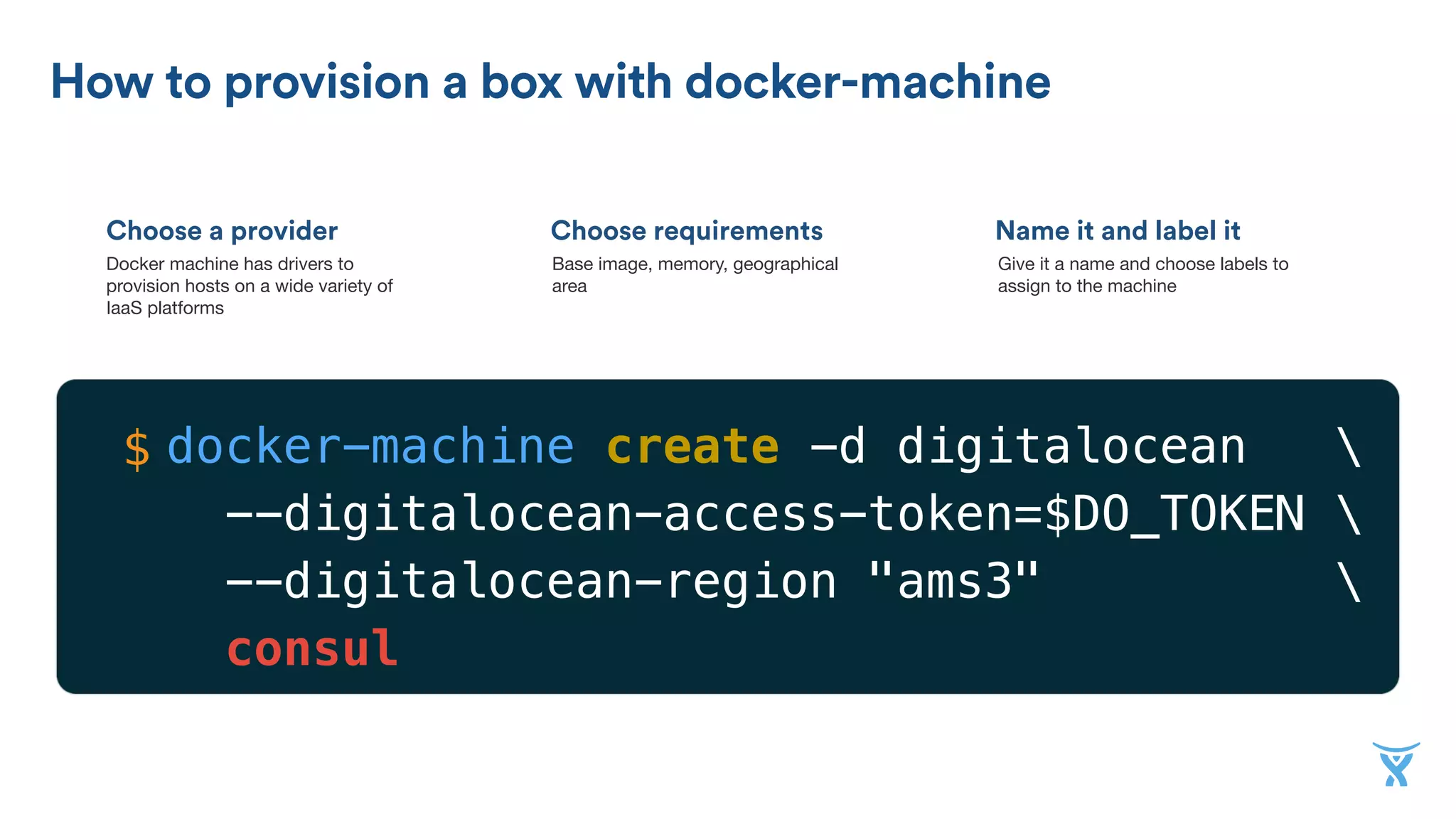
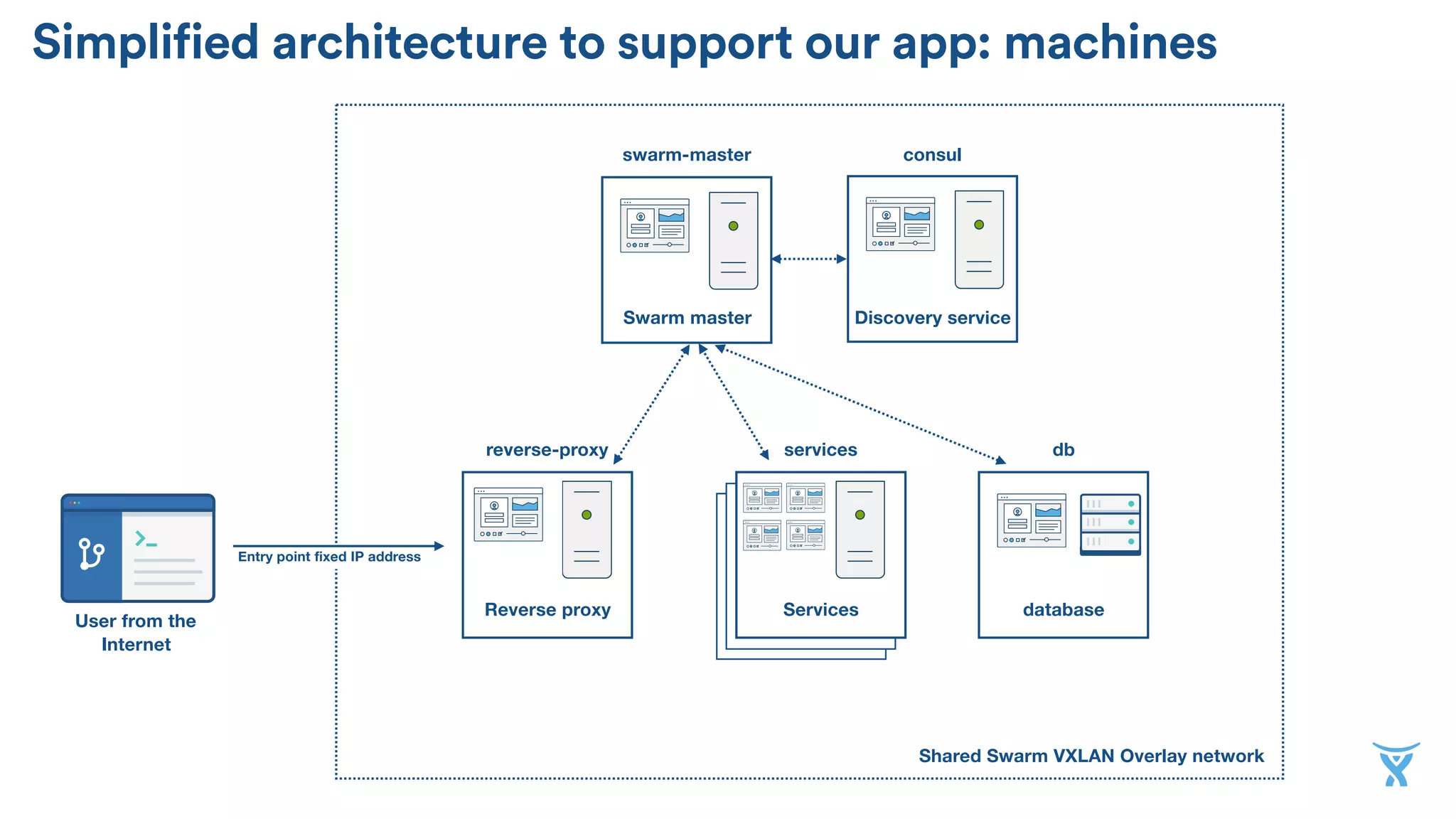
![Specify the discovery service
Creating a machine part of the Swarm
Specify it’s part of the swarm Name it
Docker machine has drivers to
provision hosts on a wide variety of
IaaS platforms
Base image, memory, geographical
area
Give it a name
docker-machine create -d digitalocean
[...]
--digitalocean-image "debian-8-x64"
--digitalocean-region "ams3"
--swarm --swarm-master
--swarm-discovery=consul://$(docker-machine ip consul):8500
--engine-opt="cluster-store=consul://$(docker-machine ip consul):8500"
--engine-opt="cluster-advertise=eth0:2376"
cluster
$](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8y2jh1ytsbijerpr19gh-signature-97ac0cba55d83fa6f2a2f253a387270677bf11da9177d0b7d555fb911fc34ba2-poli-160526084215/75/Higher-order-infrastructure-from-Docker-basics-to-cluster-management-Nicola-Paolucci-Codemotion-Amsterdam-2016-21-2048.jpg)