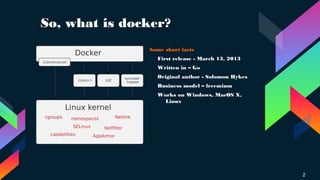
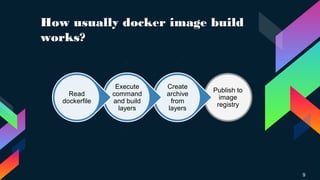
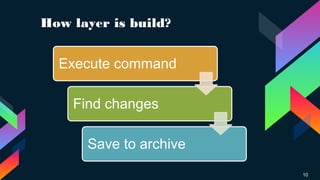
Docker is software that allows users to run applications securely isolated in containers to encapsulate services, libraries and configuration files. It was first released in 2013 and works across Windows, MacOS and Linux. Docker resources like images, containers, volumes and networks define how applications are built and run. Docker Compose and Swarm provide automation and orchestration for single node and multi-node setups respectively. Dockerfiles define application build instructions to create reusable images.