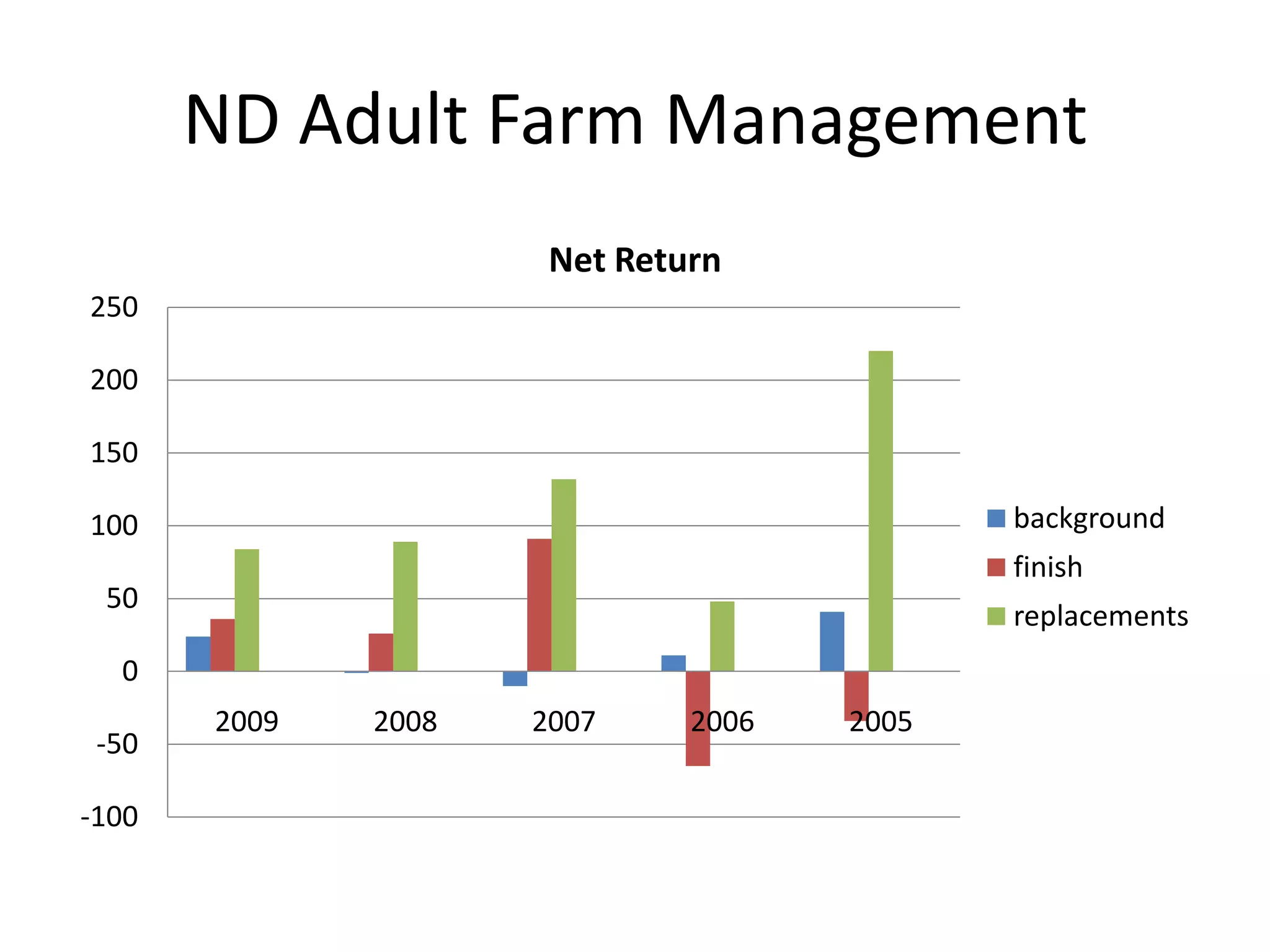
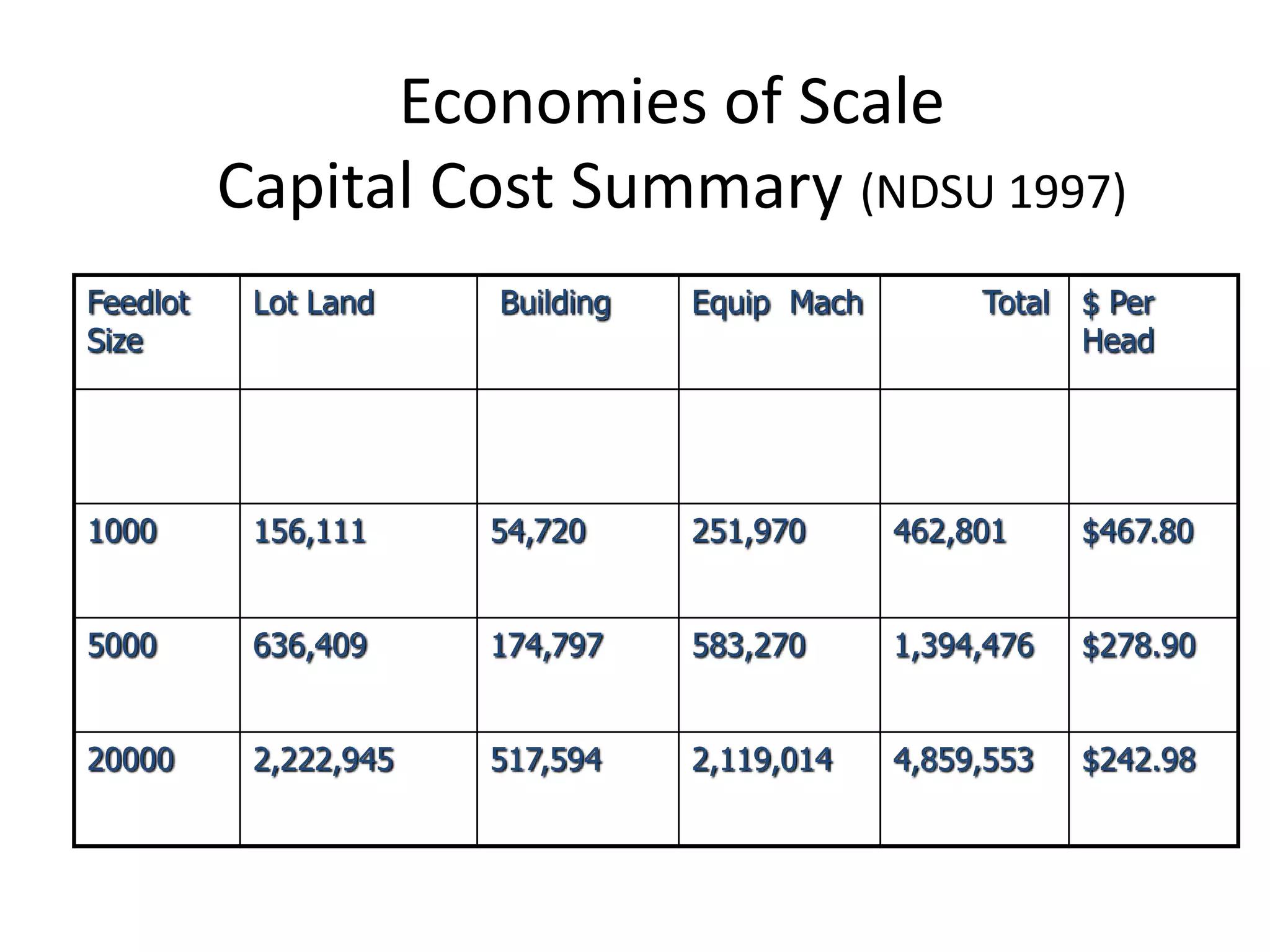
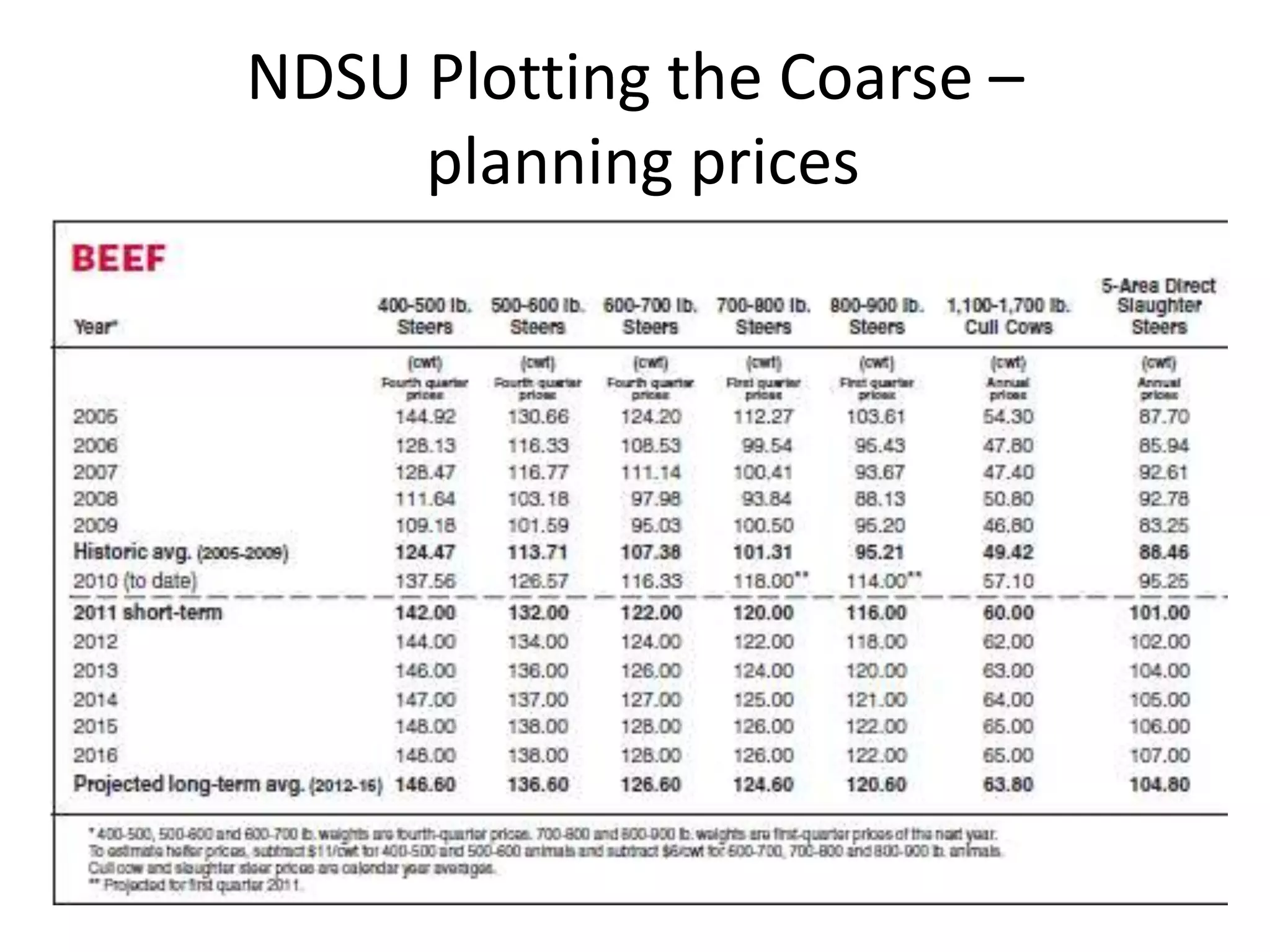
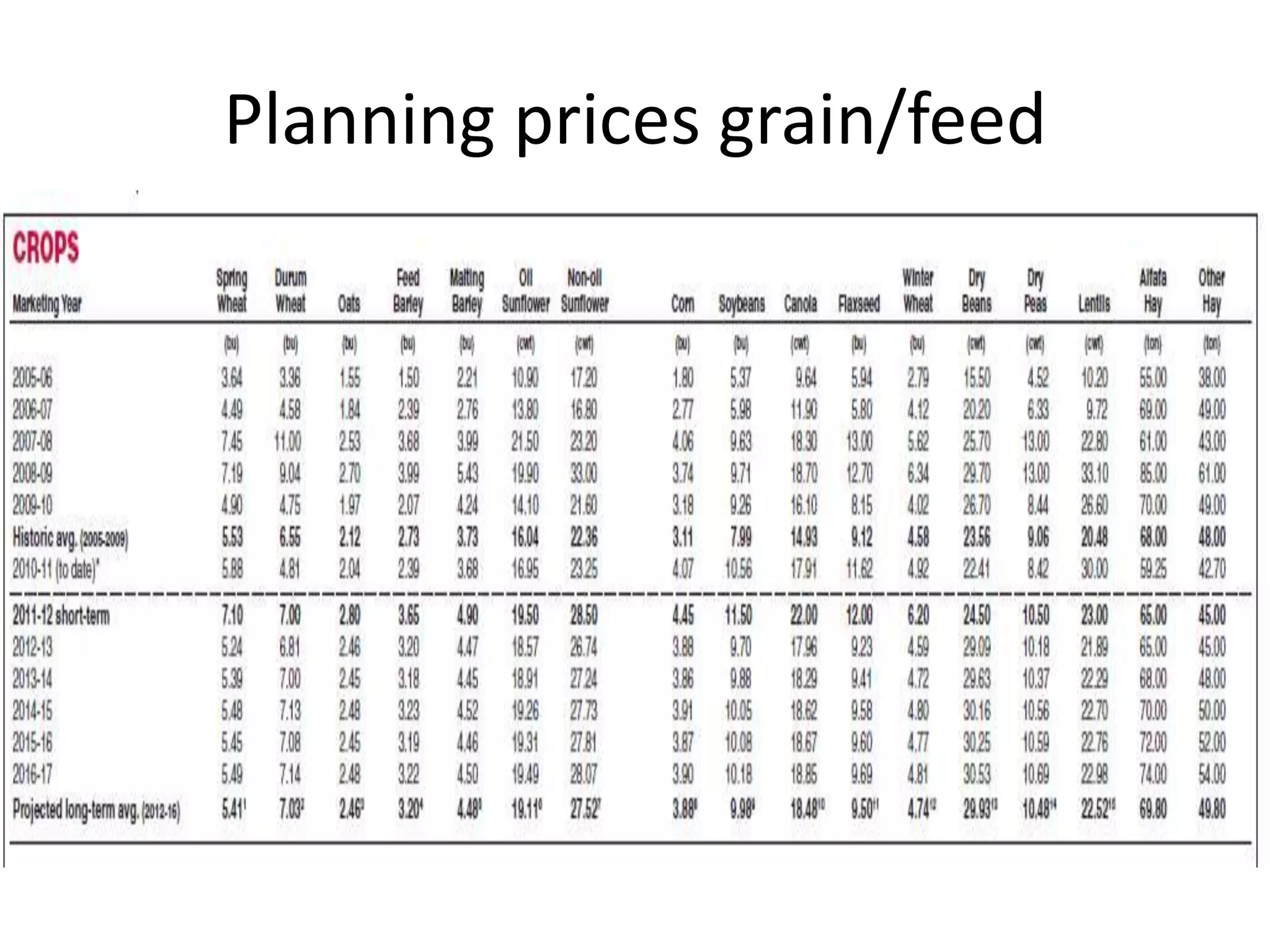
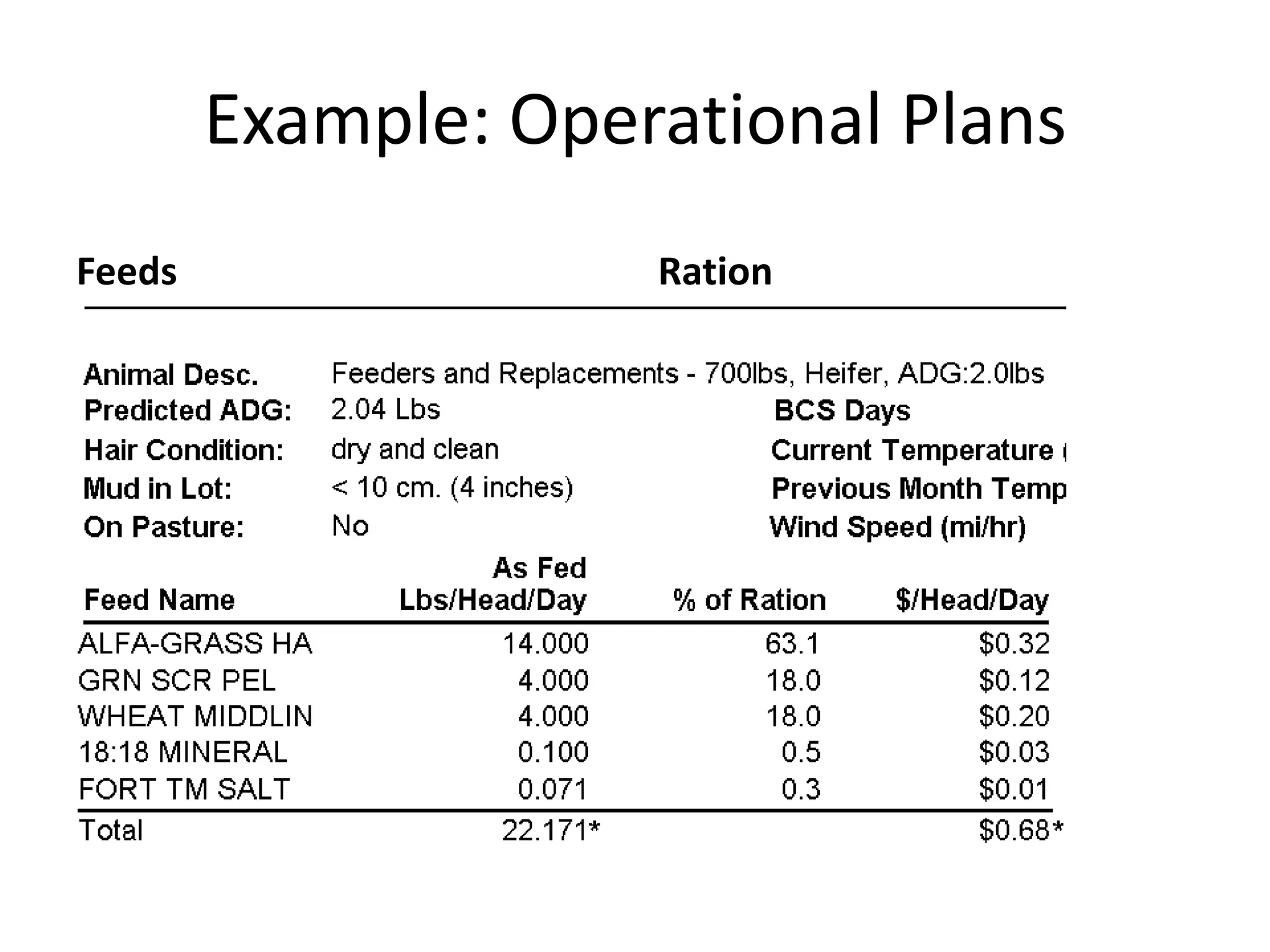
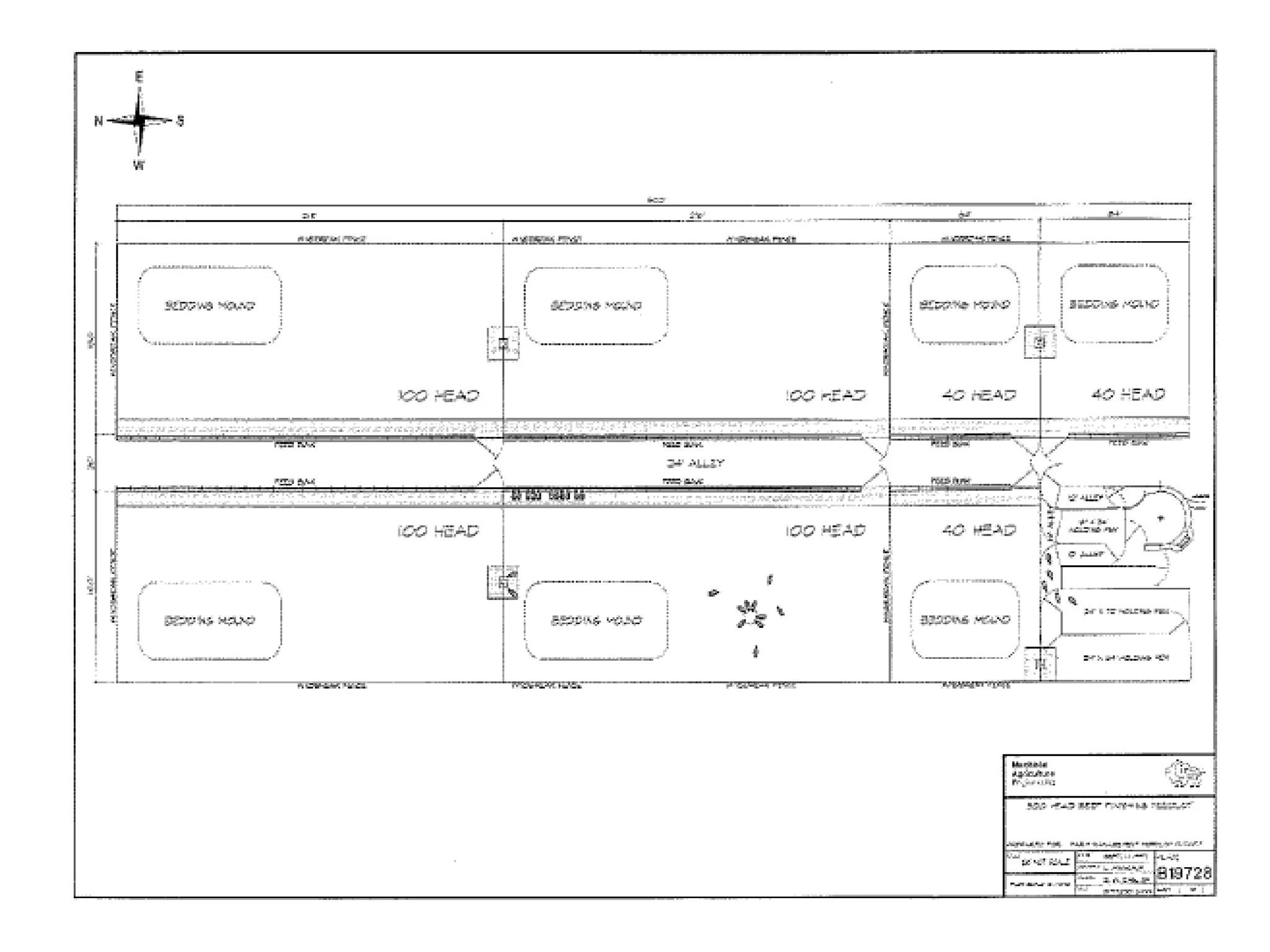
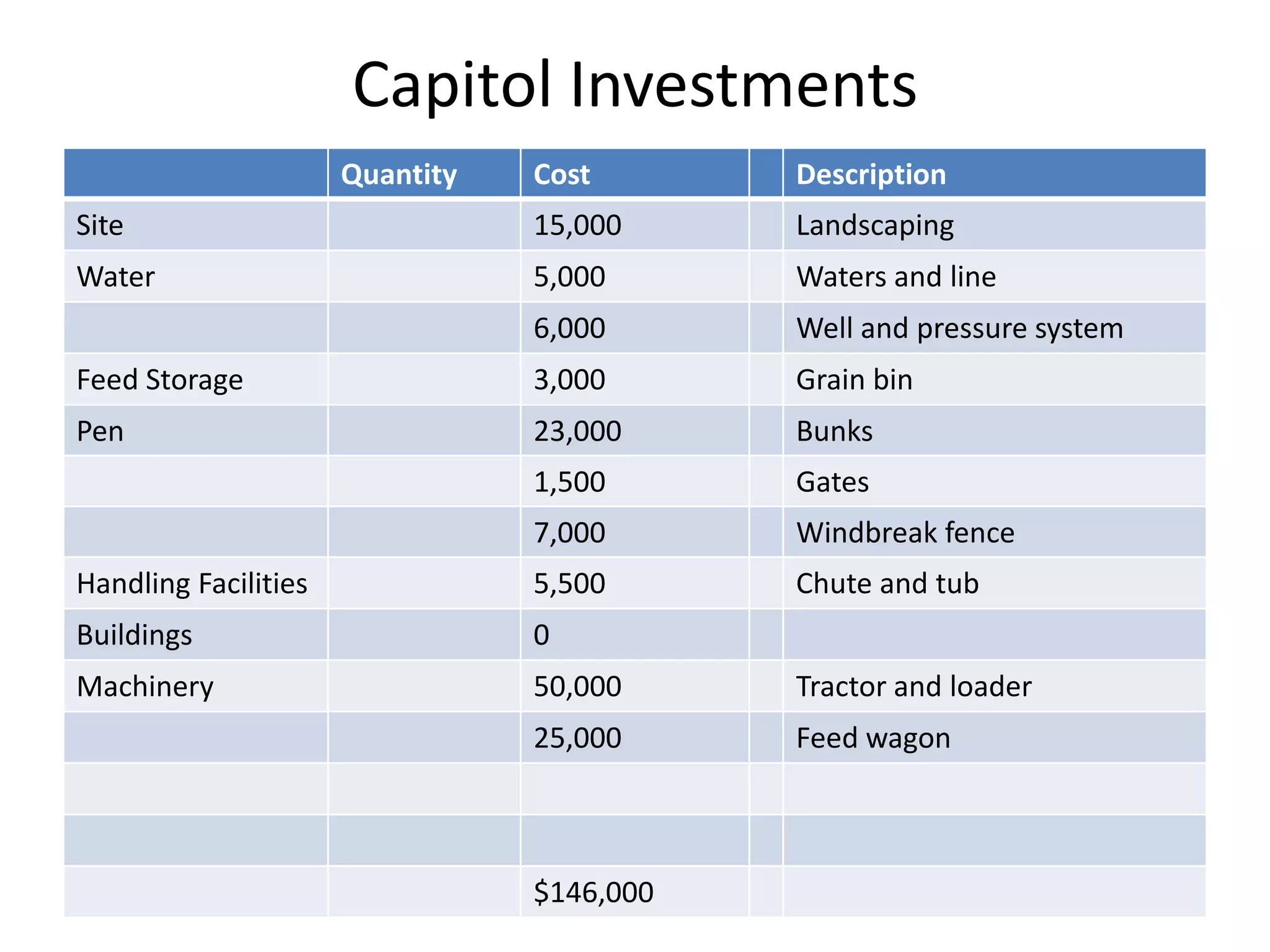
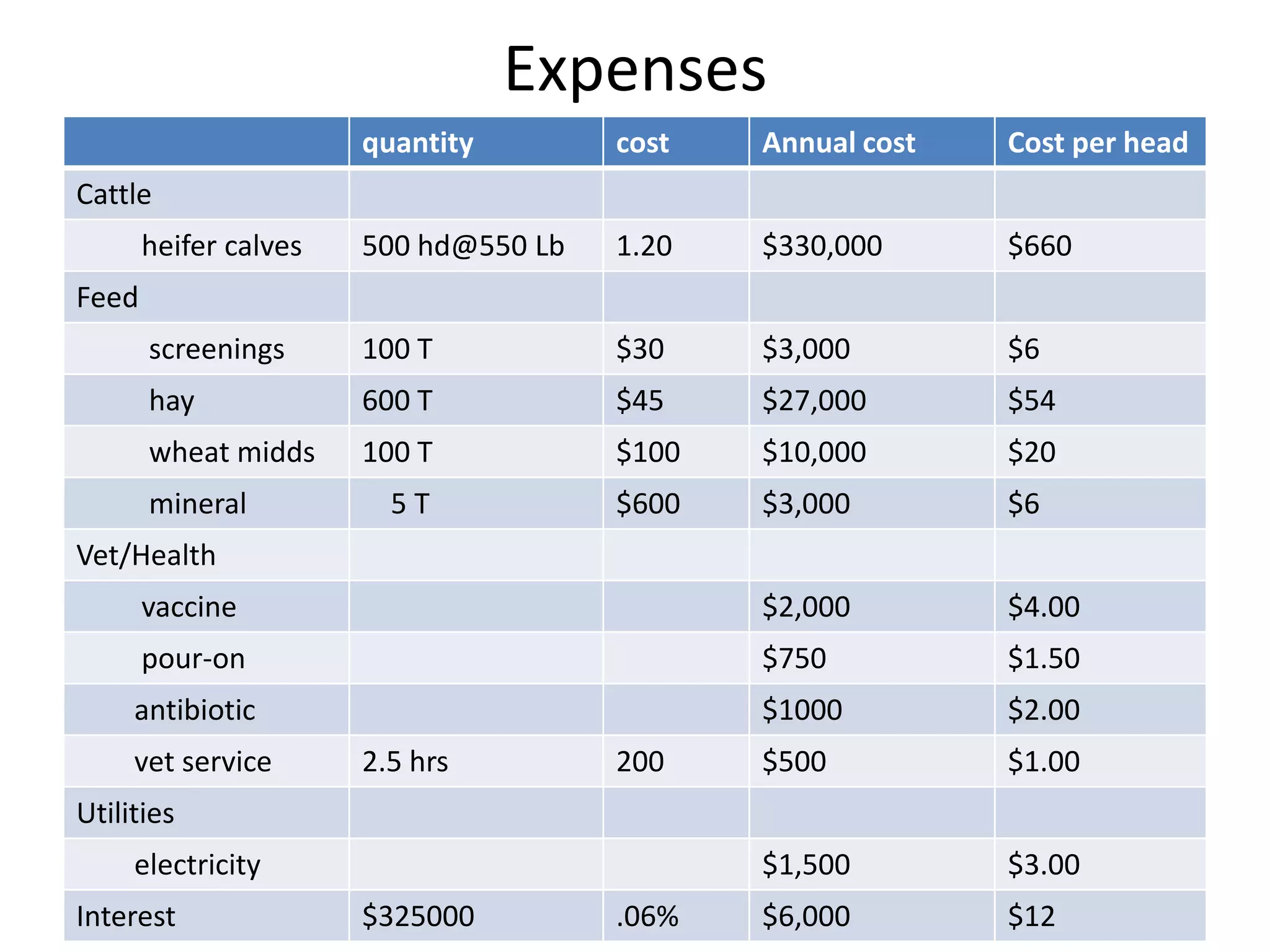
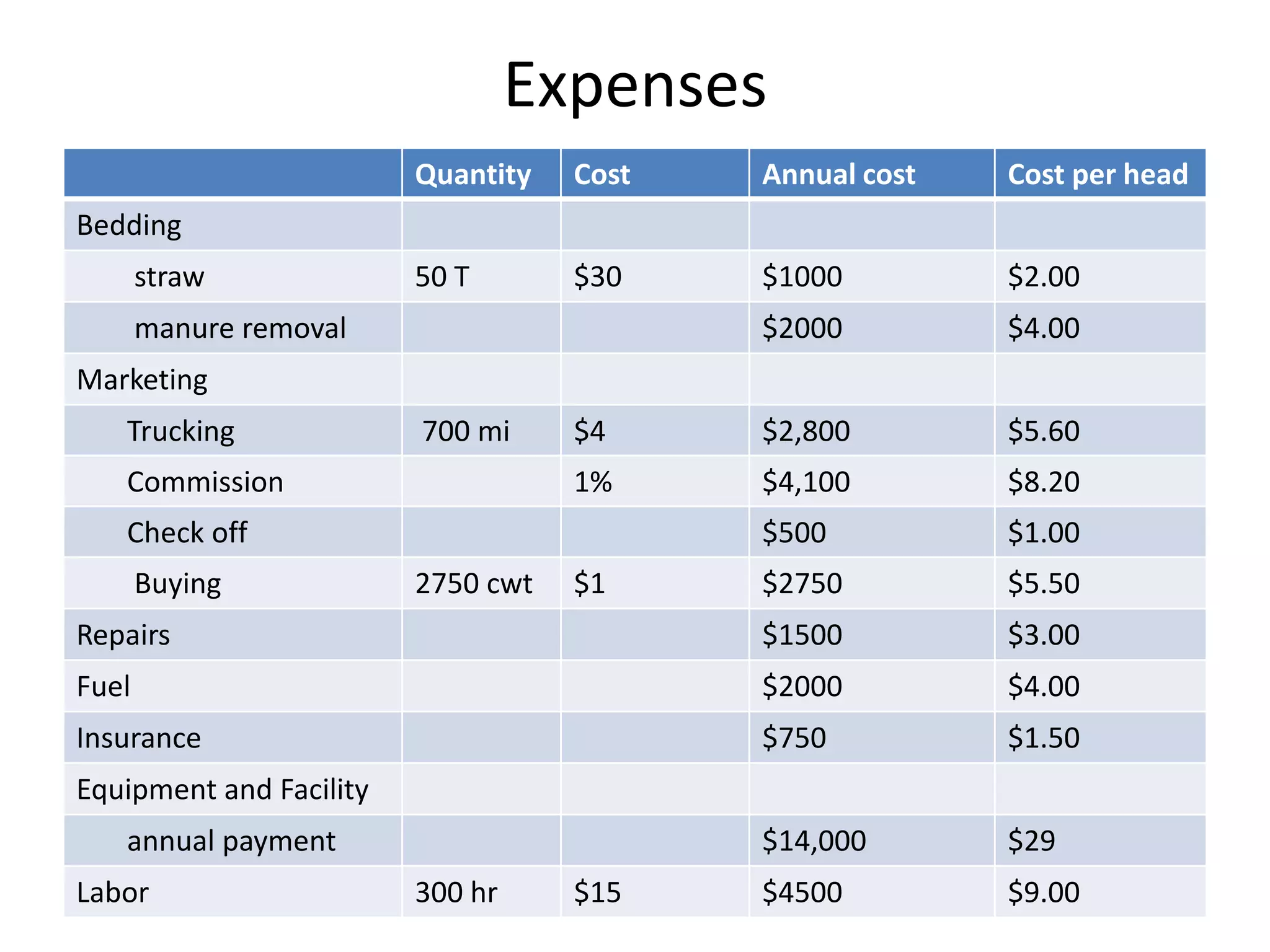
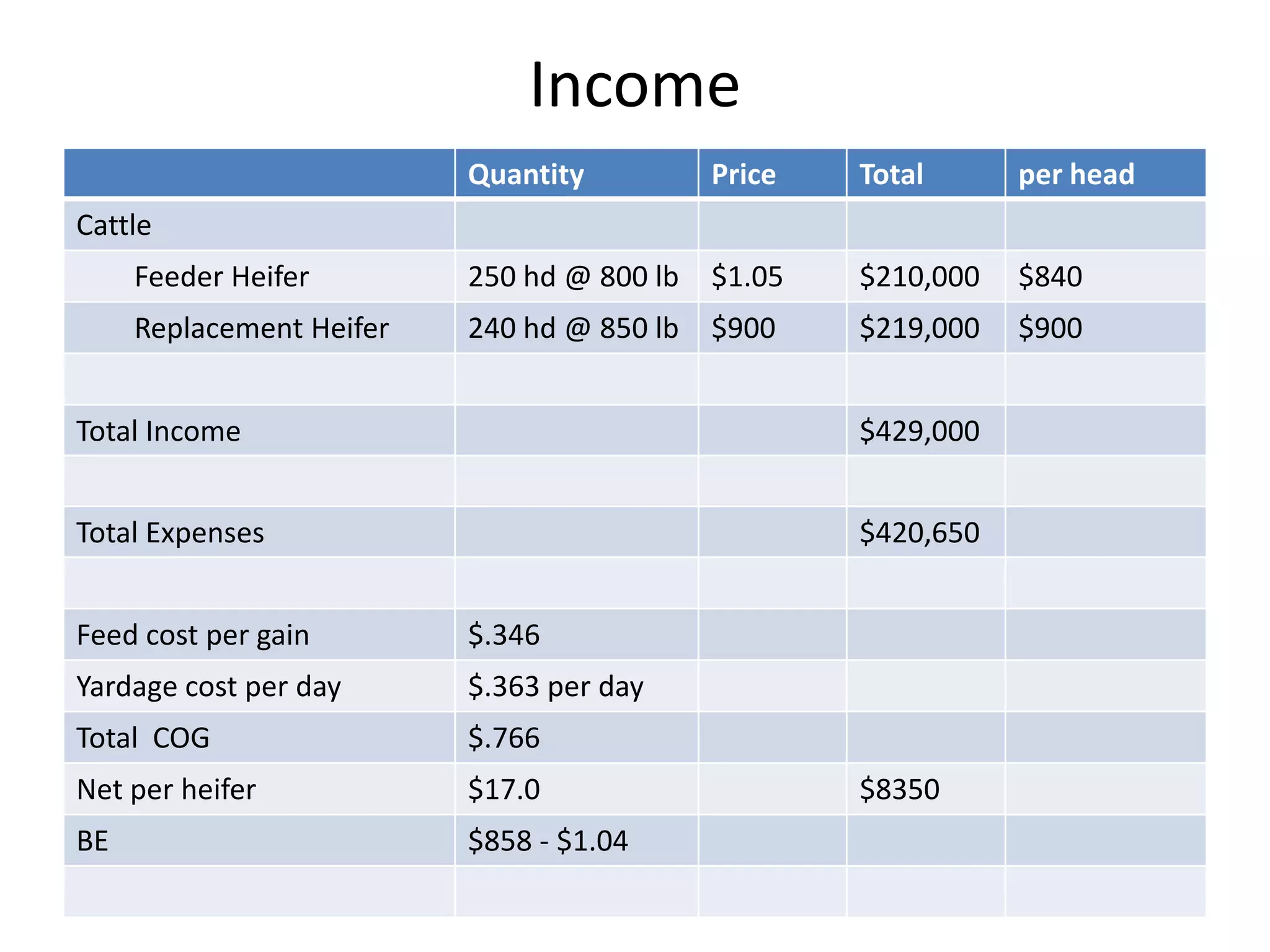
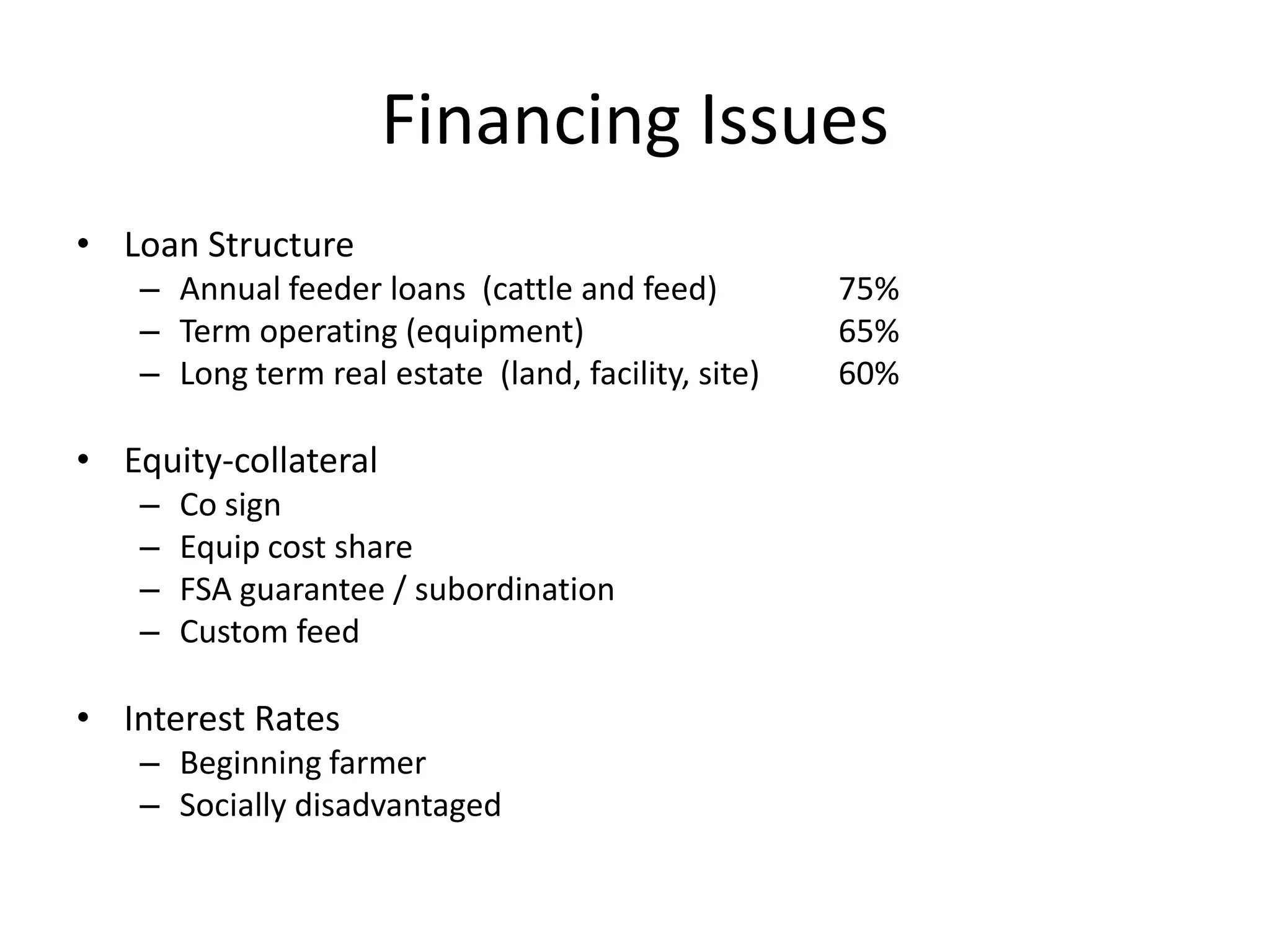
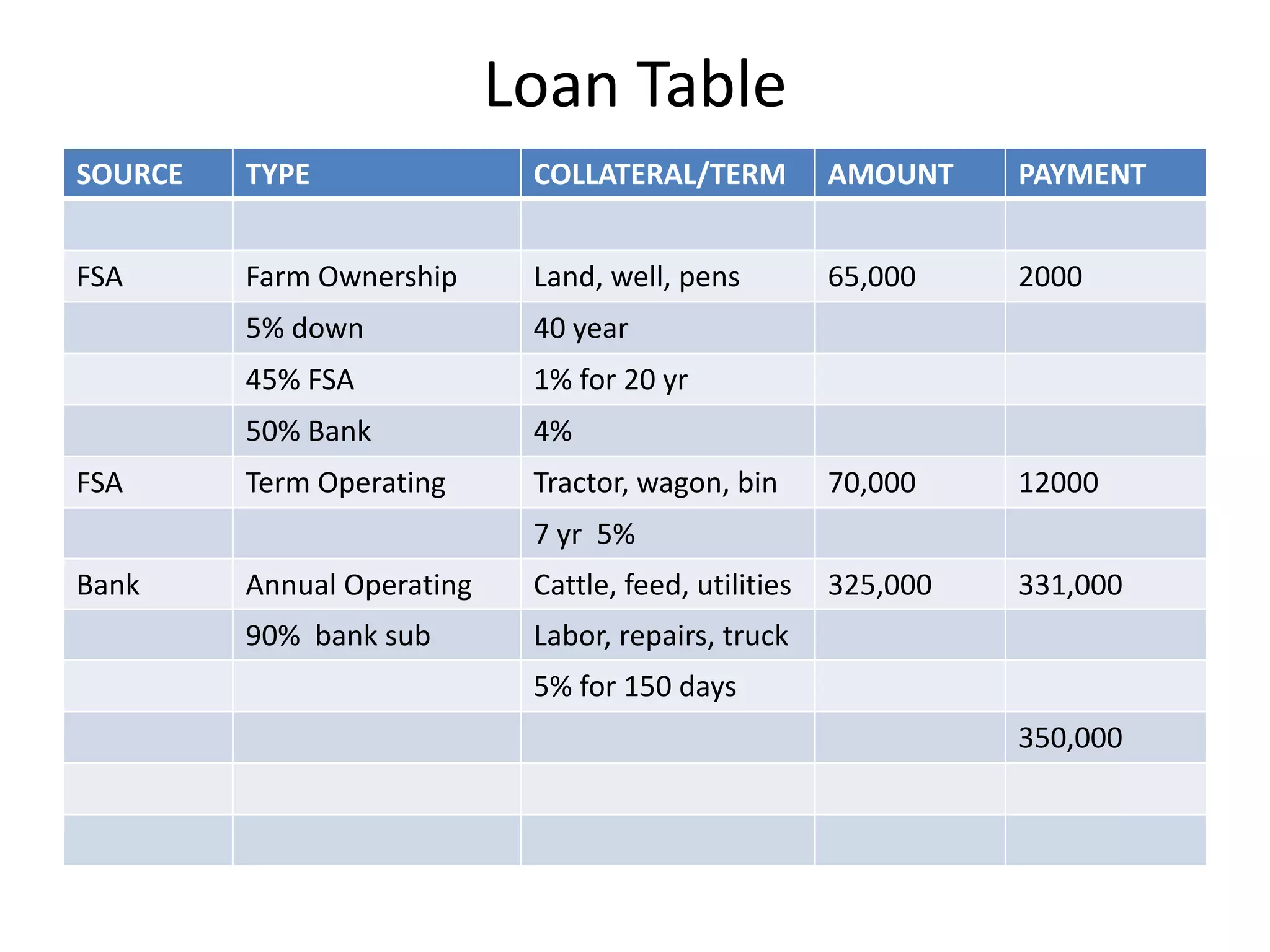
The document discusses key aspects of cattle feeding, emphasizing its economic benefits, competitive nature, and associated risks. It highlights the importance of business planning, resource utilization, and operational strategies, while considering factors like high grain prices, local feed resources, and necessary health protocols. Additionally, it outlines the requirements for a successful cattle feeding operation, including market planning and financing options.