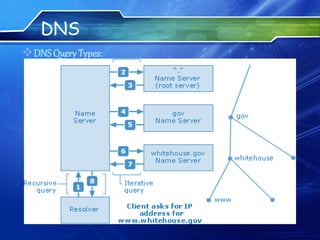
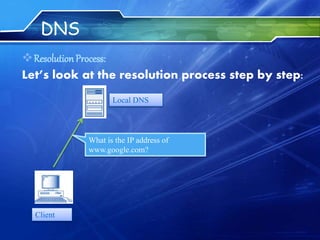
The document provides an overview of the Domain Name System (DNS) and Internet Relay Chat (IRC). It defines DNS as a protocol that translates between domain names and IP addresses, allowing users to use easy-to-remember names instead of numeric addresses. It describes how DNS works by querying name servers in a hierarchical system to resolve domain names to IP addresses. The document also defines IRC as a protocol for real-time text communication over the Internet, allowing users on different systems to communicate in group channels or privately. It notes some popular IRC clients and discusses advantages like low-cost communication and disadvantages like potential for addiction or abuse.