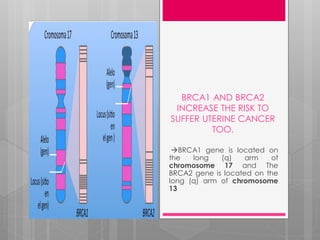
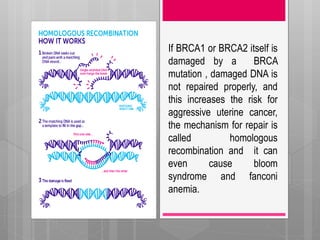
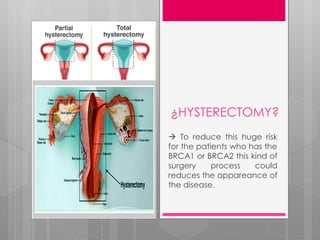
The document summarizes research on DNA repair mechanisms and their link to certain cancers. It discusses how mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes can increase risks of aggressive uterine cancer and metastatic prostate cancer by impairing homologous recombination DNA repair. Early detection of DNA repair mutations can help identify risk and allow preventative measures like hysterectomy or personalized therapies to reduce cancer development and improve patient outcomes.