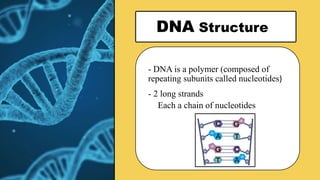
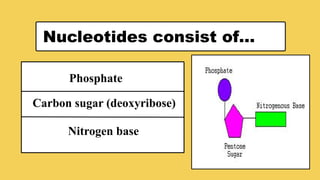
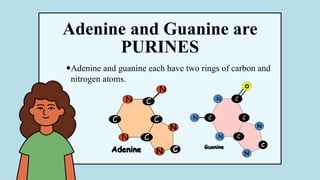
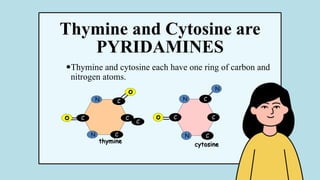
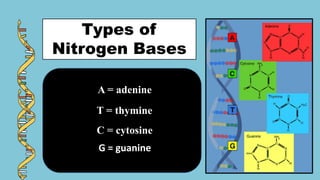
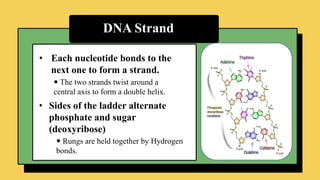
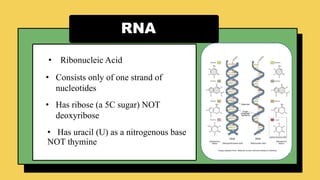
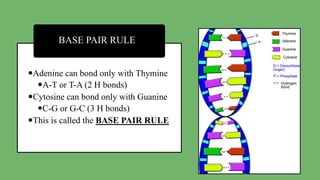
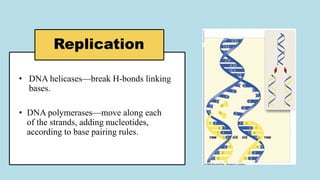
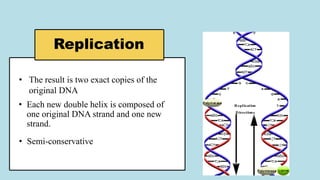
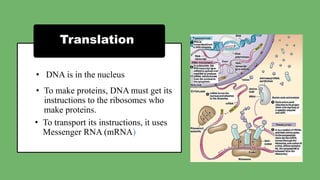
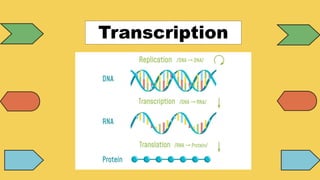
The document explains the fundamental differences between DNA and RNA, highlighting DNA as the blueprint of life containing instructions for protein synthesis, while RNA serves as a messenger in this process. It details the structure of DNA, replication mechanisms, and transcription processes essential for cellular function and growth. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of studying DNA for medical and agricultural advancements.