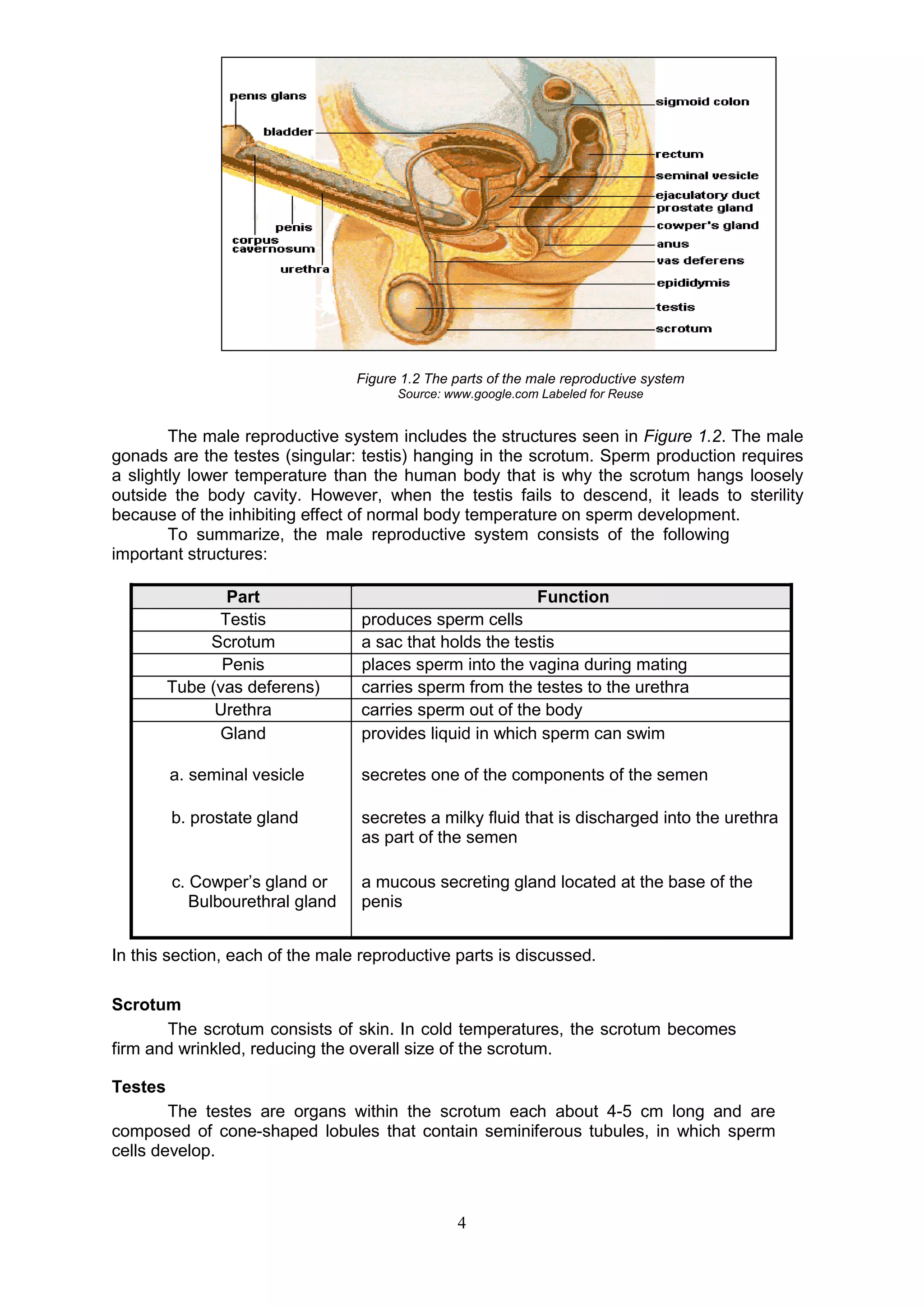
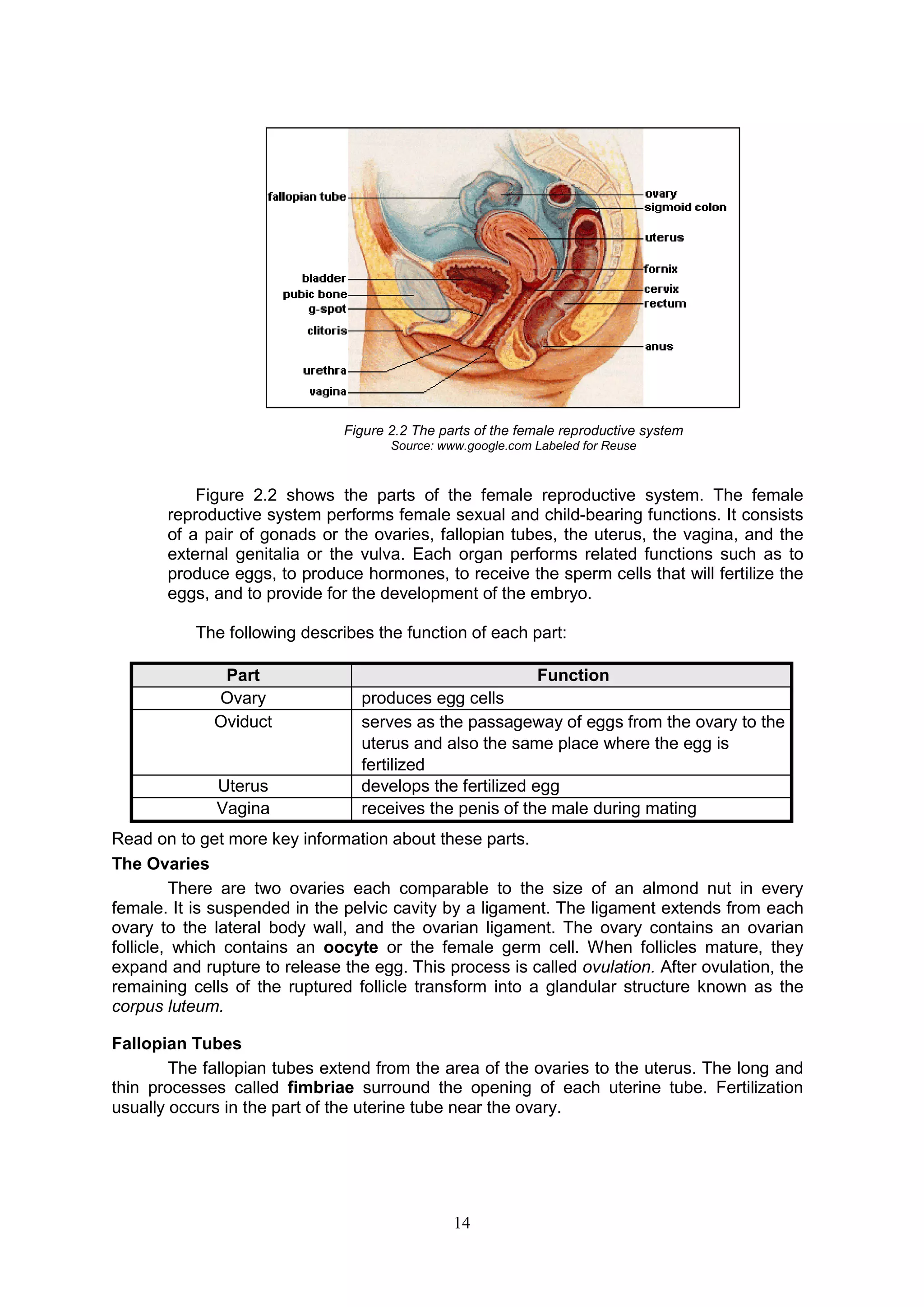
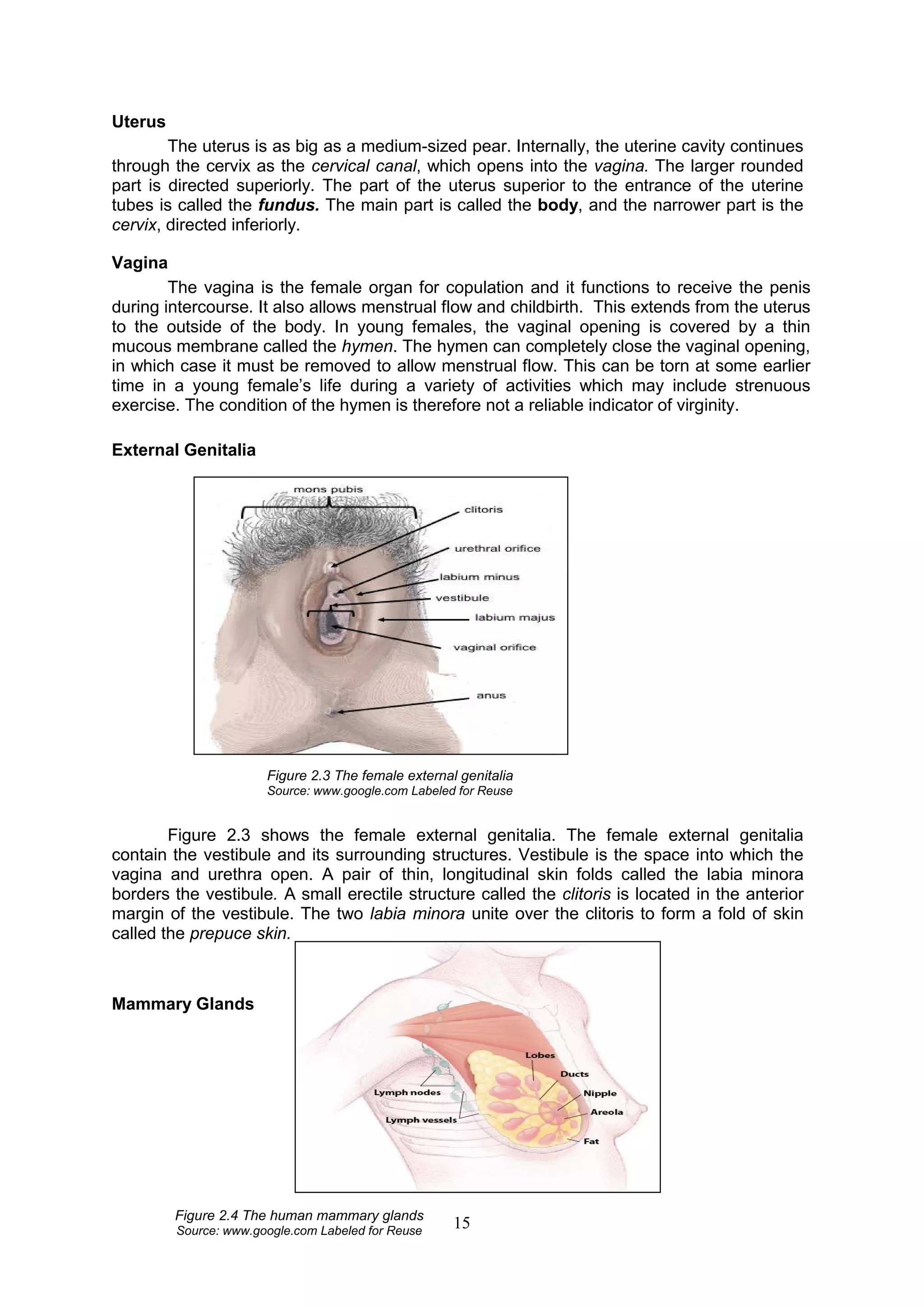
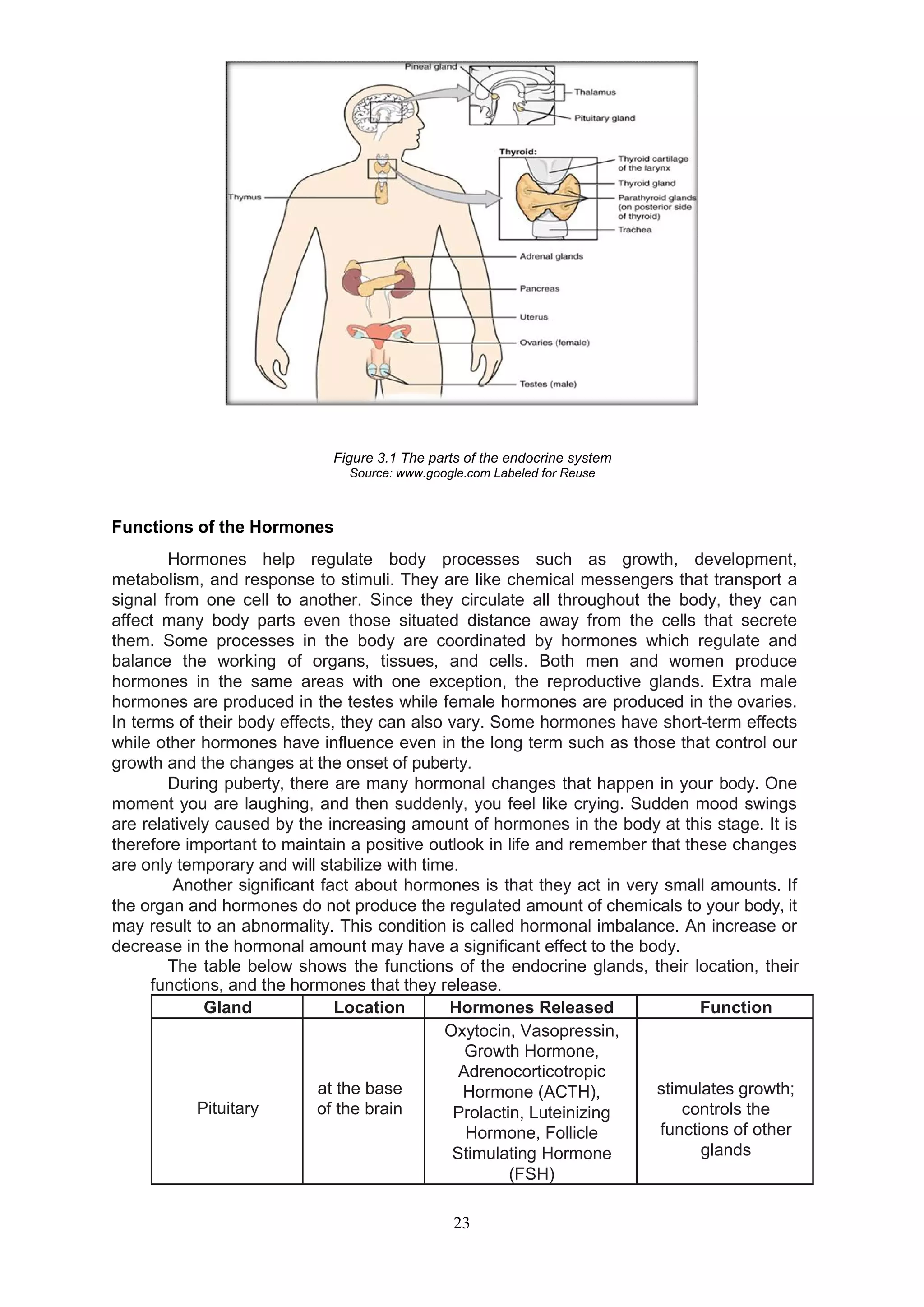
The male reproductive system consists of both internal and external organs that work together for reproduction. The internal organs include the testes, which produce sperm cells, and the epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, and prostate gland, which all play a role in transporting and nourishing sperm. The external organs are the scrotum and penis. The scrotum holds the testes in a loose sac outside of the body to regulate temperature for sperm production. The penis is used for urination and depositing sperm into the female during intercourse. Together, these organs allow males to produce, carry, and deliver sperm for fertilization.